Exploring the realm of manufacturing processes reveals the ingenious method of the EPP Molding Process, an intricate technique leveraging Expanded Polypropylene.
What is EPP?
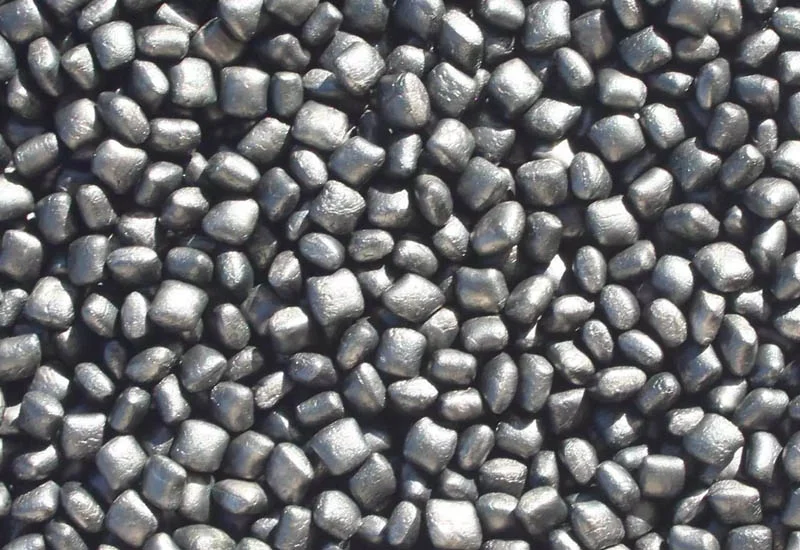

EPP, a cellular plastic material, boasts a unique structure characterized by interconnected beads, offering unparalleled strength and resilience. Understanding the composition of EPP lays the foundation for comprehending its molding process.
Machines used in the EPP Molding Process
Mold Cavity:
Defines the shape and dimensions of the end product, crucial for achieving desired specifications.
Steam Chambers:
Utilized to expand the polypropylene beads within the mold cavity, ensuring uniform distribution.
Injection Molding Machines:
Central to the EPP molding process, these machines inject the expanded polypropylene beads into the mold cavity under controlled conditions. Their efficiency and precision contribute significantly to the overall quality of the final product.
Steps of the EPP Foam Molding Process
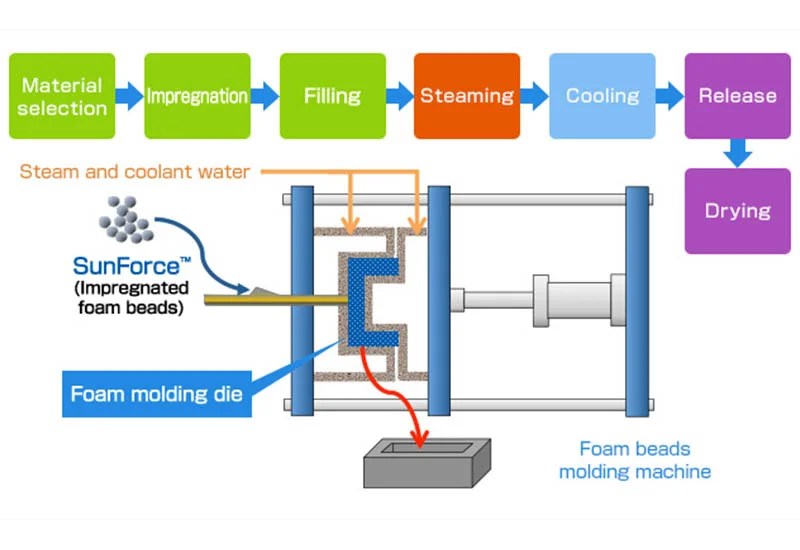
Expanded polypropylene (EPP) foam molding is a process used to create lightweight, durable foam products for various applications, such as packaging, automotive parts, and insulation. Here are the general steps involved in the EPP foam molding process:
Preparation of Raw Material:
The process starts with the preparation of raw EPP beads or pellets. These beads are typically small, round particles of expanded polypropylene.
Pre-expansion:
The raw EPP beads are pre-expanded using steam or a chemical blowing agent. Pre-expansion involves heating the beads in a steam environment, causing them to expand and increase in volume.
Preheat the mold so that the surface temperature of the mold reaches the melting point. Feed the material through the material gun into the mold.
Aging:
After pre-expansion, the expanded beads are left to age for a specific period. Aging allows the beads to stabilize and ensures consistent molding properties.
Molding Tool Preparation:
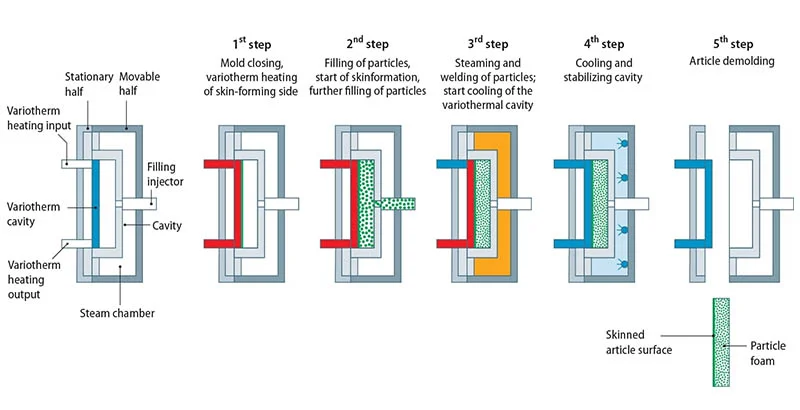
The mold tool, which determines the final shape of the EPP product, is prepared. This may involve cleaning, applying release agents, and heating, depending on the molding method used (e.g., compression molding, injection molding).
To remove air from the steam chamber and drain condensate water, steam is directed from the top downward, while simultaneously opening the steam inlet valve at the top and the condensate water discharge valve at the bottom.
Bead Charging:
The pre-expanded EPP beads are charged into the mold cavity. The amount of beads added depends on the desired density and thickness of the final product.
Molding Process:
The mold is closed, and the EPP beads are subjected to heat and pressure to form the final shape. The specific molding process can vary depending on the equipment used:
Compression Molding:
In compression molding, the mold is closed, and pressure is applied to compress the EPP beads within the mold cavity. Heat is also applied to soften the beads, allowing them to fuse and take the shape of the mold.
Injection Molding:
In injection molding, the pre-expanded EPP beads are fed into a hopper and then heated to a molten state. The molten EPP is injected into the closed mold cavity under pressure, where it solidifies into the desired shape.
Steam Molding:
Steam molding involves placing the pre-expanded beads into a mold cavity and then exposing them to steam. The steam softens the beads, allowing them to expand and conform to the shape of the mold.
Cooling:
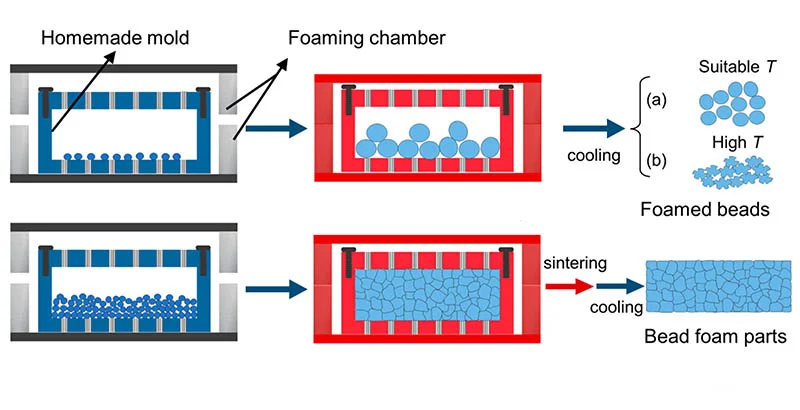
After molding, the EPP product is cooled either by natural cooling or through forced air or water cooling, depending on the specific requirements of the product and the molding process.
Once steam is introduced, the internal temperature of the mold typically rises to 140℃. To facilitate smooth demolding of the product, the mold temperature needs to be reduced to 70℃. Demolding is feasible once the internal pressure is released and the temperature decreases to the approved demolding temperature.
Demolding:
Once the product has sufficiently cooled and solidified, the mold is opened, and the molded EPP product is removed from the mold cavity.
Trimming and Finishing:
Any excess material or flash around the edges of the molded product is trimmed off, and any finishing touches, such as surface texturing or painting, may be applied as needed.
Quality Control:
The finished EPP products undergo quality control inspections to ensure they meet the required specifications for dimensions, density, strength, and appearance.
Drying and setting
Typically, EPP molded products require placement in a drying room for drying purposes. The drying temperature is typically set between 60℃ to 80℃, and it’s essential for the drying room to maintain dry air and adequate ventilation. Otherwise, EPP product surfaces may be susceptible to shrinking.
Advantages of EPP Molding
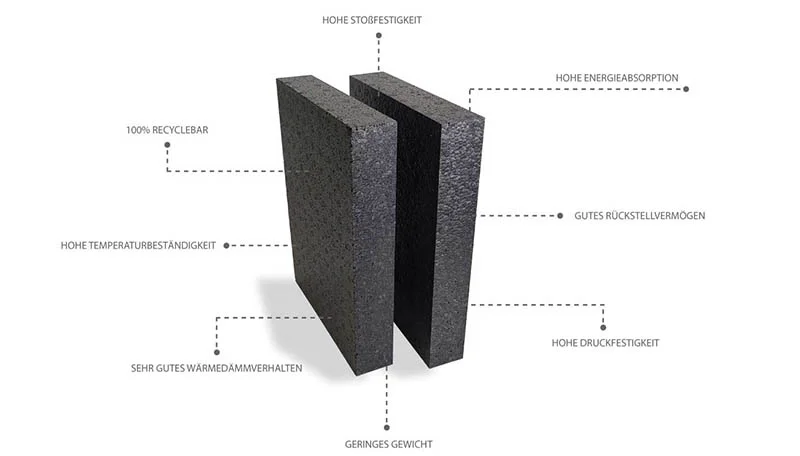
Lightweight and Durable:
EPP products are renowned for their lightweight nature coupled with exceptional durability. This unique combination makes them ideal for applications where strength, impact resistance, and weight are crucial factors.
Energy Absorption and Cushioning Properties of EPP:
One of the standout features of EPP is its ability to absorb and dissipate energy, making it an excellent choice for protective packaging, automotive components, and sports equipment. Its cushioning properties ensure superior protection against impacts and shocks.
Environmental Sustainability:
EPP is a fully recyclable material, aligning with the growing demand for eco-friendly solutions. Its recyclability not only reduces environmental impact but also offers cost-effective options for manufacturers aiming for sustainable practices.
FAQs
What are the key properties of EPP that make it suitable for various applications?
EPP exhibits lightweight, durability, energy absorption, and recyclability, making it an ideal choice for applications ranging from automotive parts to protective packaging.
How does the EPP molding process contribute to environmental sustainability?
The EPP molding process utilizes recyclable materials and energy-efficient manufacturing techniques, aligning with the principles of environmental sustainability and circular economy practices.
Can EPP products be customized to meet specific requirements?
Yes, manufacturers can customize EPP properties by incorporating additives during the molding process, allowing for tailored solutions to suit diverse application needs.
What are some common post-molding operations performed on EPP products?
Post-molding operations may include trimming, assembly, surface treatment, and printing, enhancing the functionality and aesthetics of EPP products.
What are the emerging trends in EPP molding technology?
Emerging trends in EPP molding include the adoption of sustainable materials, digital manufacturing processes, and advancements in smart packaging solutions, shaping the future of the industry.
Conclusion
In summary, the EPP molding process utilizes Expanded Polypropylene to create lightweight and durable foam products for various applications. With its unique properties, including energy absorption and recyclability, EPP offers advantages in industries like packaging and automotive. This process exemplifies innovation and efficiency in manufacturing, providing reliable solutions for modern needs.


