In industrial steam systems, the steam accumulator plays a vital but often overlooked role. These unassuming devices are crucial for ensuring efficiency, stability, and reliability in various applications. But what exactly is a steam accumulator, and why is it so important? Let’s dive into the details.
What is a Steam Accumulator
A steam accumulator is essentially a large, insulated pressure vessel designed to store steam energy. Think of it as a battery for steam: it absorbs excess steam during periods of low demand and releases it when demand peaks. This ability to balance supply and demand makes steam accumulators indispensable in many industrial settings.
How Does a Steam Accumulator Work
The operation of a steam accumulator can be broken down into three main phases:
- Charging Phase: During this phase, the boiler produces more steam than the process requires. This excess steam is directed into the accumulator. Inside the accumulator, the steam condenses upon contact with the water, transferring its heat energy to the water. As a result, the water’s temperature and pressure increase.
- Storage Phase: In this phase, the accumulator holds the heated, pressurized water. The vessel is insulated to minimize heat loss and keep the stored energy ready for use.
- Discharging Phase: When steam demand exceeds the boiler’s capacity, the high-pressure water in the accumulator flashes into steam. This steam is then supplied to the process, meeting the increased demand without any drop in pressure.
Steam Accumulator Working Principle
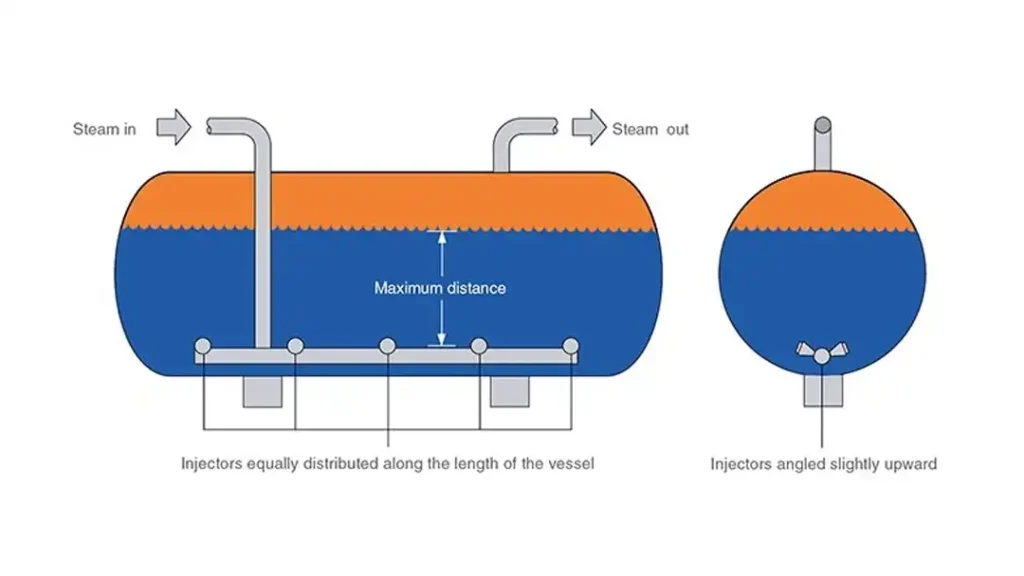
The working principle of a steam accumulator revolves around its role as a storage and balancing mechanism in steam systems. Here’s a breakdown of how it operates:
Components of a Steam Accumulator:
- Pressure Vessel: A robust container, often cylindrical and insulated, designed to withstand high pressure.
- Water: Partially fills the vessel, serving as the medium for storing energy.
- Steam Inlet and Outlet: Pipes that allow steam to enter and exit the accumulator.
- Pressure and Temperature Controls: Devices to monitor and regulate internal conditions.
- Safety Valves: Installed to prevent overpressure and ensure safe operation.
Working Phases:
Charging Phase:
- Excess Steam Introduction: When the steam generation exceeds immediate demand, surplus steam is directed into the accumulator.
- Condensation and Heat Transfer: As the steam enters the accumulator, it condenses upon contact with the cooler water, transferring its latent heat energy to the water. This raises the temperature and pressure within the accumulator.
- Energy Storage: The heat energy from the excess steam is stored in the form of high-pressure, high-temperature water in the accumulator.
Storage Phase:
- Maintaining Conditions: The insulated pressure vessel retains the high pressure and temperature conditions, preserving the stored energy for future use. The water now holds both sensible heat (due to its elevated temperature) and latent heat (from the condensed steam).
Discharging Phase:
- High Demand Period: When demand for steam surpasses the boiler’s capacity, the accumulator releases steam.
- Flashing Process: As steam is withdrawn, the pressure within the accumulator drops slightly. This decrease in pressure causes some of the high-pressure water to “flash” into steam.
- Steam Supply: The newly generated steam supplements the boiler output, ensuring a continuous and stable steam supply to meet increased demand.
Key Points:
- Pressure Regulation: Precise control of pressure is crucial for efficient steam storage and release. Pressure and temperature controls help maintain optimal operating conditions.
- Energy Efficiency: By storing excess steam and releasing it as needed, the accumulator enhances overall system efficiency.
- Safety Measures: Safety valves and regular maintenance are essential to prevent overpressure situations and ensure safe operation.
Benefits of Steam Accumulator
- Load Balancing: Helps manage fluctuations in steam demand, alleviating strain on the boiler and maintaining a steady supply.
- Energy Conservation: Prevents wastage of excess steam, contributing to improved energy utilization and cost savings.
- System Stability: Maintains stable pressure and temperature conditions critical for processes requiring precise steam parameters.
- Cost Reduction: Reduces fuel consumption and operational expenses by optimizing boiler operation and minimizing cycling.
- Equipment Longevity: Decreases wear and tear on the boiler, extending its operational lifespan and reducing maintenance requirements.
Why Use a Steam Accumulator?
Steam accumulators offer several significant benefits:
- Load Balancing: They help smooth out fluctuations in steam demand, providing a consistent steam supply and reducing strain on the boiler.
- Energy Efficiency: By storing excess steam, they prevent energy waste, making the system more efficient.
- System Stability: Accumulators maintain stable steam pressure and temperature, which is crucial for processes that require precise conditions.
- Cost Savings: Improved efficiency and reduced boiler cycling translate to lower fuel and operational costs.
- Extended Boiler Life: Minimizing frequent start-ups and shut-downs helps extend the boiler’s lifespan and reduce maintenance costs.
Steam Accumulator Applications
Steam accumulators find diverse applications across industries where a reliable and efficient steam supply is essential. Here are some common applications:
- Power Generation Plants: Steam accumulators are used in power plants to manage load fluctuations and ensure a stable steam supply to turbines for electricity generation. They help maintain grid stability by providing backup steam during peak demand periods.
- Manufacturing Industries: Various manufacturing processes rely on consistent steam supply for operations. Industries such as food processing, paper manufacturing, chemical production, and pharmaceuticals use steam accumulators to balance steam demand, ensuring uninterrupted production and product quality.
- Textile Industry: Textile mills utilize steam for various processes, including dyeing, bleaching, and fabric finishing. Steam accumulators help regulate steam supply to meet the specific requirements of different textile manufacturing stages, optimizing energy use and production efficiency.
- District Heating Systems: Steam accumulators play a crucial role in district heating systems, where steam is distributed to multiple buildings or facilities for space heating and hot water production. By storing excess steam during low-demand periods, accumulators ensure a continuous and stable supply of heat to consumers, even during peak usage times.
- Pulp and Paper Industry: In pulp and paper mills, steam is used for various purposes such as pulping, drying, and paper machine operation. Steam accumulators help manage steam demand fluctuations, improving process efficiency and reducing energy costs in this energy-intensive industry.
- Food Processing Plants: Steam is widely used in food processing for sterilization, cooking, and heating. Steam accumulators enable food processing plants to maintain consistent steam supply, ensuring food safety and quality while optimizing energy consumption.
- Breweries and Distilleries: Breweries and distilleries rely on steam for heating, boiling, and sterilization processes in beer and spirit production. Steam accumulators help these facilities maintain precise control over steam supply, supporting efficient and reliable production operations.
- Hospitals and Healthcare Facilities: Steam is essential in healthcare facilities for sterilizing medical equipment, laundry, and providing space heating. Steam accumulators ensure a reliable and continuous steam supply, critical for maintaining sanitary conditions and patient care standards.
- Chemical and Petrochemical Industries: Chemical processing plants use steam in various reaction processes, distillation, and heat exchange operations. Steam accumulators help optimize steam utilization and maintain process stability in chemical and petrochemical manufacturing facilities.
- District Cooling Systems: In some cases, steam accumulators are also employed in district cooling systems where steam is used for air conditioning and cooling purposes. They help regulate steam supply to meet cooling demand fluctuations, improving system efficiency and reliability.
Sizing a Steam Accumulator
Proper sizing is critical to the effectiveness of a steam accumulator. The process involves:
- Assessing peak and average steam demand.
- Evaluating boiler capacity and available excess steam.
- Calculating the total steam deficit during peak periods.
- Determining the required volume to store this steam, factoring in efficiency and safety margins.
Maintenance and Safety
Regular maintenance is essential to keep steam accumulators functioning optimally. This includes inspecting the pressure vessel, checking pressure and temperature controls, testing safety valves, and ensuring insulation integrity. Adhering to relevant codes and standards for pressure vessels is also crucial for safe operation.
Conclusion
Steam accumulators are crucial for steam systems. They manage the steam supply and demand effectively, improving industrial processes. To optimize energy use and cut costs, industries rely on steam accumulators. They benefit power plants, manufacturing facilities, and district heating systems, offering operational advantages.

