Expanded Polypropylene (EPP) stands out as a recyclable closed-cell molded foam, boasting an impressive array of properties rarely matched by other materials.
Once the EPP beads undergo expansion, they are seamlessly fused into basic blocks suitable for CNC prototyping or intricately molded into complex shapes within a steam chest.
What is EPP Foam Made Of?

Expanded Polypropylene (EPP) foam is primarily made of polypropylene beads, a type of thermoplastic polymer. These beads are expanded using steam and pressure during the manufacturing process, forming closed-cell foam structures characteristic of EPP foam.
Additionally, additives may be included during production to enhance specific properties of the foam, such as increased rigidity or flame resistance, depending on the intended application.
What is the Process of EPP Foaming?
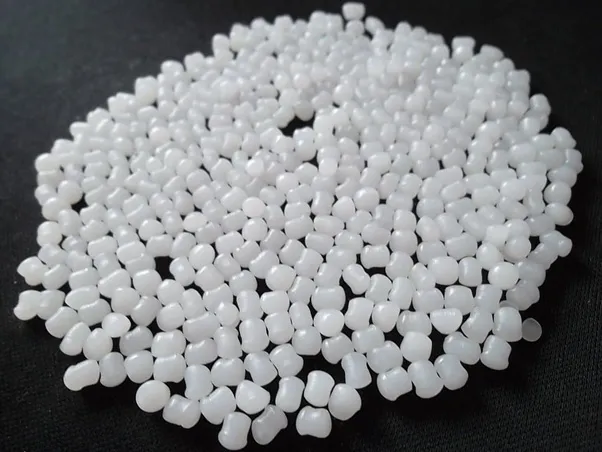

Step 1: Preparation of Raw Materials
Polypropylene beads, the primary material for EPP foam, are prepared. Additives may also be mixed in at this stage to impart specific properties to the foam.
Step 2: Pre-Expansion
The polypropylene beads are heated in a steam chest or autoclave, causing them to expand due to the internal pressure of the steam. This pre-expansion process creates small, closed-cell beads with a low density.
Step 3: Molding Closing
The pre-expanded beads are then placed in a mold, which could be either a block mold for creating simple shapes or a complex mold for intricate designs. The mold is closed, and the beads expand when subjected to steam and pressure.
Inject the material into the mold through the material gun. Introduce steam into the mold in three sequential stages:
- Steam Flushing: Allow steam to flow from the top to the bottom of the mold to remove air from the steam chamber. Concurrently, open the steam inlet valve at the top and the condensate water discharge valve at the bottom to facilitate the expulsion of condensate water.
- Lateral Steam: Direct steam laterally from one side of the steam chamber to penetrate the material and reach the opposite side. During this phase, close one condensate water valve while opening the steam inlet valve. Simultaneously, close the steam inlet valve on the opposite side and open the condensate water valve to enable steam to disperse from the opposite direction. For molds featuring thin flanges, it’s optimal for steam to circulate the flange to ensure thorough steaming and melting of the material clamped inside.
- Pressure Holding: Following lateral steam injection, maintain pressure within the mold or conduct a double-sided steaming and melting process. Throughout this stage, keep the steam inlet valve open while closing the condensate water discharge valve. Gradually increase the pressure to its maximum level.
Step 4: Drying and Setting
EPP foam products, once , undergo post-processing in a dedicated drying room where the current temperature is maintained around 75 degrees Fahrenheit. The duration of post-processing varies depending on factors such as product density, shape, and seasonal conditions.
Generally, post-processing is quicker in summer compared to winter. High-density products require less time than low-density ones, while thin products necessitate shorter post-processing periods than thicker counterparts. Complex-shaped items typically require less time than simpler ones.
Efficient post-processing begins by promptly transferring de-molded EPP products to the drying room. It’s essential to maintain a uniform temperature within the drying room while utilizing trolleys for transportation whenever possible. The environment within the drying room should facilitate moisture evaporation from the interior of the products while allowing for the penetration of hot air.
The success of post-processing hinges on meticulous attention to timing, temperature, and personnel allocation. Drying time must strike a delicate balance, avoiding both excessive prolongation and premature cessation, while temperature control is crucial, ensuring it remains within optimal parameters. Therefore, assigning a dedicated individual to oversee the process is imperative.
In instances of particularly low ambient temperatures, it’s advisable to allow finished products to gradually cool within the drying room instead of immediate removal. Typically, product dimensions stabilize after approximately 12 hours post-drying.
EPP Shape Moulding Machine
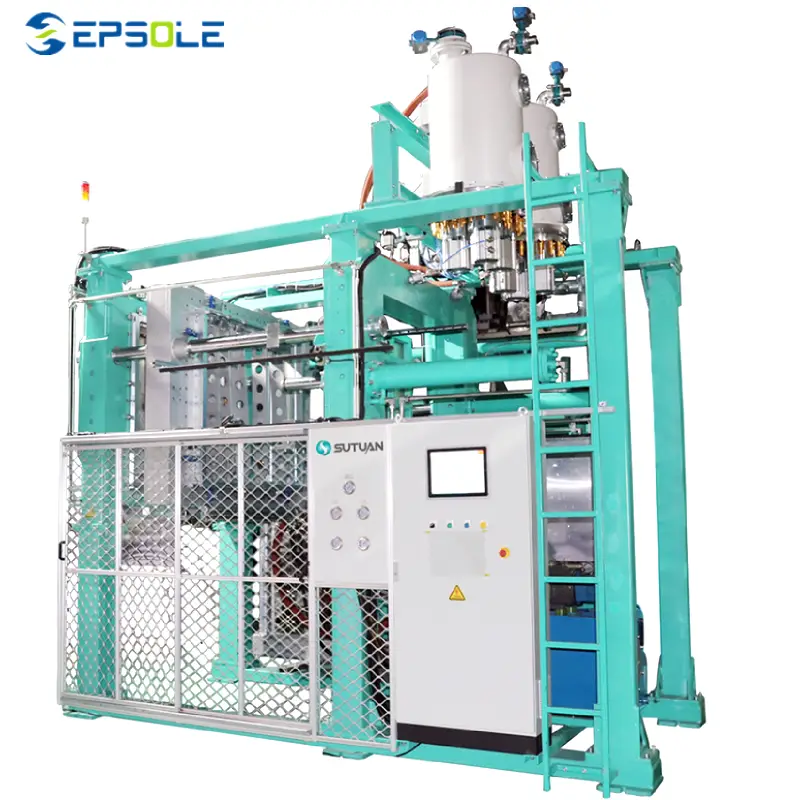
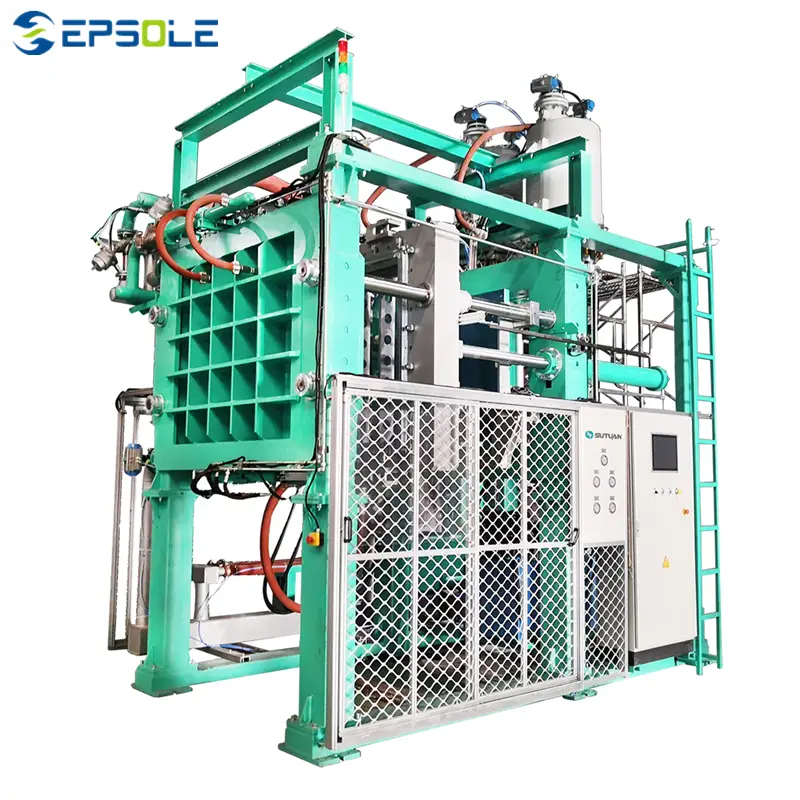
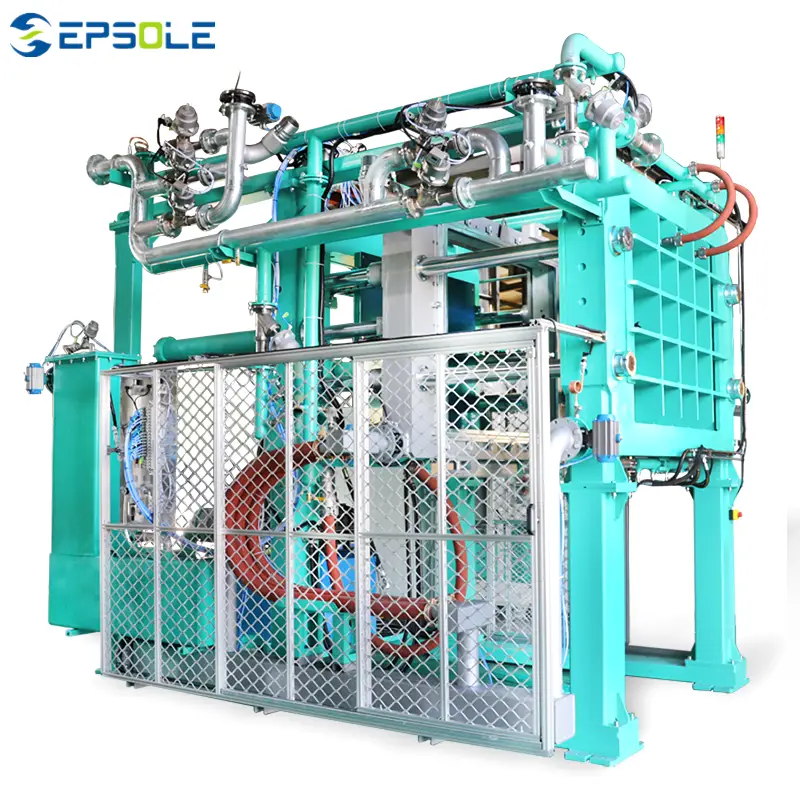



The EPS shape molding machine boasts excellent energy-saving features, leveraging advanced steam proportional pressure-reducing valve technology for precise control and stable steam pressure delivery. Its simple yet robust structure enhances stability and strength significantly.
Equipped with a specialized cooling system, this machine is vital due to its energy-efficient vacuum system technology, reducing energy consumption. The large-scale three-dimensional spray vacuum condensing machine further optimizes vacuum condensation, safeguards the vacuum water pump, and provides an intermediate vacuum interface for future needs.
Operating and controlling the EPS shape molding machine is straightforward, utilizing a user-friendly touchscreen interface for intuitive operation. Additionally, an integrated alarm system ensures systematic operator safety.
