Expanded Polystyrene, commonly known as EPS, is a versatile and efficient insulating material. With its lightweight yet durable properties, EPS has revolutionized the construction and packaging industries.
Let’s delve into the intricacies of this remarkable material.
Expanded Polystyrene Insulation is a type of rigid foam insulation derived from polystyrene beads. Through a process of expansion using steam, these beads transform into a closed-cell structure, resulting in a lightweight and rigid foam board.
Expanded Polystyrene Foam Insulation

Expanded Polystyrene Foam Insulation, often abbreviated as EPS insulation, is a lightweight, rigid, and versatile material widely used for thermal insulation in buildings, packaging, and various other applications. It is composed of expanded polystyrene beads that are fused to form a closed-cell structure.
Here are some key points about EPS foam insulation:
- Composition: EPS insulation is made from expanded polystyrene, a type of plastic derived from styrene monomers. The manufacturing process involves expanding polystyrene beads using steam, which causes them to expand and fuse together to form a rigid cellular structure.
- Lightweight and Rigid: EPS foam insulation is lightweight, making it easy to handle and install. Despite its lightweight nature, it offers high rigidity and structural strength, making it suitable for various construction applications.
- Thermal Insulation: One of the primary functions of EPS foam insulation is to provide thermal insulation in buildings. The closed-cell structure of EPS foam traps air, which inhibits the transfer of heat. This property helps to maintain consistent indoor temperatures and reduce energy consumption for heating and cooling.
- Moisture Resistance: EPS foam insulation has low moisture absorption properties, making it resistant to water damage and mold growth. This characteristic is particularly advantageous in humid environments or areas prone to water intrusion.
- Versatility: EPS foam insulation comes in various forms, including boards, panels, and molded shapes, allowing it to be used in a wide range of applications. It can be easily cut and shaped to fit specific requirements, making it adaptable to different construction needs.
- Fire Performance: While EPS foam insulation is flammable, it can be manufactured with fire-retardant additives to improve its fire performance. Additionally, building codes often require the use of additional fire protection measures, such as thermal barriers or intumescent coatings, when EPS foam insulation is used in certain applications.
- Environmental Considerations: EPS foam insulation is recyclable, and many manufacturers offer recycling programs for used EPS materials. However, it’s important to note that the production of polystyrene involves the use of fossil fuels and contributes to environmental pollution if not properly managed.
- Cost-Effective: EPS foam insulation is typically cost-effective compared to other insulation materials, making it a popular choice for both residential and commercial construction projects.
Expanded Polystyrene Foam Insulation offers a combination of thermal performance, versatility, and cost-effectiveness, making it a widely used material for insulation in various applications. However, proper installation and consideration of fire safety measures are essential to maximize its benefits while ensuring safety and compliance with building codes.
Expanded Polystyrene Insulation R-Value
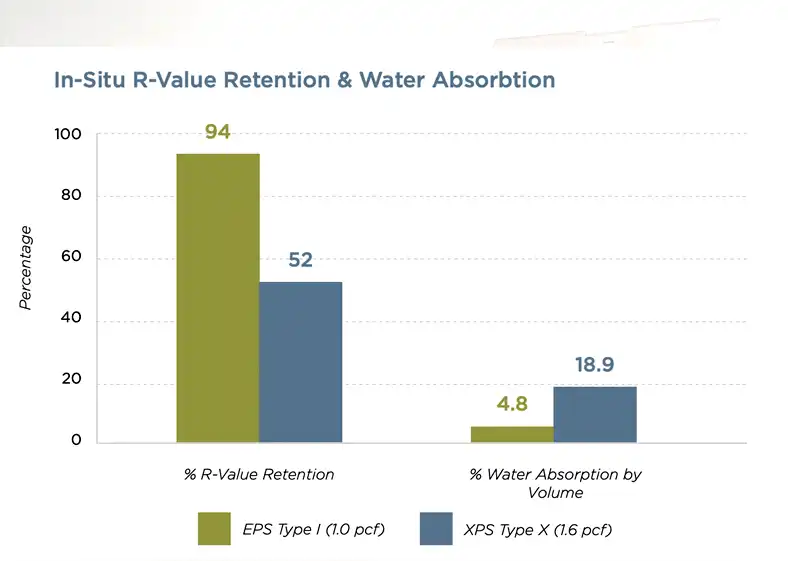
The R-value of expanded polystyrene (EPS) insulation typically ranges from around 3.6 to 4.2 per inch of thickness.
This means that for every inch of EPS insulation, it provides thermal resistance equivalent to 3.6 to 4.2 units. The exact R-value can vary depending on the density and specific formulation of the EPS material. Higher-density EPS foam generally has a higher R-value because it contains more trapped air pockets, which enhance its insulating properties.
However, it’s important to note that the R-value may decrease over time due to factors such as compression or moisture absorption.
Benefits of Expanded Polystyrene Insulation

Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) insulation offers several benefits, making it a popular choice for thermal insulation in various applications:
Excellent Thermal Insulation: EPS insulation provides high thermal resistance, effectively reducing heat transfer through walls, roofs, and floors. This helps maintain consistent indoor temperatures, leading to energy savings and enhanced comfort.
Lightweight and Easy to Install: EPS insulation is lightweight compared to other insulation materials, making it easy to handle, transport, and install. Its versatility allows for customization to fit specific building requirements, reducing installation time and labor costs.
Moisture Resistance: EPS insulation has low moisture absorption properties, making it resistant to water damage, mold, and mildew. This makes it suitable for use in humid environments or areas prone to moisture intrusion, such as basements and crawl spaces.
Durability and Longevity: EPS insulation is durable and resistant to degradation over time. It maintains its thermal performance and structural integrity for many years, providing long-term insulation benefits without the need for frequent replacement.
Versatility in Applications: EPS insulation comes in various forms, including boards, panels, and molded shapes, offering versatility in different construction applications. It can be used in walls, roofs, floors, and foundations, as well as in packaging and other industrial applications.
Fire Performance: While EPS insulation is flammable, it can be manufactured with fire-retardant additives to improve its fire performance. Additionally, when properly installed with appropriate fire safety measures, EPS insulation can meet building code requirements for fire protection.
Cost-Effective: EPS insulation is generally cost-effective compared to other insulation materials, offering a favorable balance between performance and affordability. Its low initial cost, combined with energy savings from improved thermal efficiency, results in overall cost-effectiveness over the life of the building.
Recyclability: EPS insulation is recyclable, and many manufacturers offer recycling programs for used EPS materials. Recycling helps reduce waste and environmental impact, making EPS insulation a more sustainable choice compared to non-recyclable insulation materials.
FAQs
Is Expanded Polystyrene Insulation Flammable?
Expanded Polystyrene Insulation is combustible, but it is treated with flame retardants to improve its fire resistance.
Can EPS be recycled?
Yes, Expanded Polystyrene is fully recyclable and can be reused in various applications, reducing environmental impact.
What is the lifespan of EPS insulation?
With proper installation and maintenance, Expanded Polystyrene Insulation can last for decades, offering long-term thermal performance.
Is EPS environmentally friendly?
Yes, EPS is environmentally friendly as it is recyclable, energy-efficient, and contributes to sustainable building practices.
How does EPS compare to other insulation materials?
Compared to traditional insulation materials like fiberglass or mineral wool, EPS offers superior thermal performance, moisture resistance, and ease of installation.
Can EPS be used in retrofitting existing buildings?
Yes, Expanded Polystyrene Insulation is commonly used in retrofitting projects to improve energy efficiency and thermal comfort.
Conclusion
Expanded Polystyrene Insulation continues to play a pivotal role in enhancing energy efficiency, sustainability, and comfort in buildings worldwide. Its lightweight, durable, and eco-friendly properties make it a preferred choice for architects, builders, and environmentalists alike.
By harnessing the power of EPS, we pave the way for a greener and more sustainable future in the construction industry.
