Expanded polystyrene (EPS) is a widely used material known for its versatility and lightweight properties. Found in various applications ranging from construction and packaging to insulation, EPS has become a staple in many industries. However, a common question arises among users and professionals alike: Is expanded polystyrene waterproof?
This article delves into the properties of expanded polystyrene, examining its interaction with water, and the benefits and limitations of its use in wet conditions.
What Is Expanded Polystyrene?

Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) is a lightweight, rigid, closed-cell foam material made from polymerized styrene beads containing dissolved pentane gas. When heated, these beads expand up to 40 times their size, forming a solid foam structure.
EPS is highly versatile, used in construction for insulation, in packaging for protection, and in products like coolers and surfboards due to its excellent thermal insulation, shock absorption, and lightweight nature. Despite being mostly air, EPS is strong and durable, with significant resistance to moisture, compression, and impact.
Environmentally, EPS is 100% recyclable and can be reprocessed into new products, making it sustainable and resource-efficient. Overall, EPS is a functional, adaptable material with broad applications, valued for its insulating properties, durability, and eco-friendliness.
What Is Expanded Polystyrene Waterproof Properties?

The waterproof properties of expanded polystyrene (EPS) refer to its ability to resist the penetration of water. While EPS is not entirely waterproof, it does exhibit water-resistant characteristics due to its closed-cell structure. This structure makes it highly resistant to moisture absorption, making it suitable for use in environments with high humidity or occasional exposure to water.
However, prolonged exposure to water or submersion can eventually lead to water ingress. Therefore, while EPS offers some degree of waterproofing, it is essential to consider additional protective measures or alternative materials for applications requiring complete waterproofing.
Why Does “Is Expanded Polystyrene Waterproof” Matter?
Material Suitability:
Knowing the waterproof properties of EPS helps in determining its suitability for specific applications. For instance, if a project requires materials that can withstand exposure to moisture without degradation, knowing whether EPS meets this requirement is essential.
Durability:
In environments where water exposure is common, such as in construction or outdoor applications, the durability of materials like EPS becomes paramount. Knowing whether EPS is waterproof informs decisions about its longevity and performance in such environments.
Insulation Performance:
Waterproofing can impact the insulation performance of EPS. Moisture infiltration can reduce the effectiveness of insulation, leading to energy loss and potentially compromising the comfort and efficiency of buildings or products.
Structural Integrity:
For construction and structural applications, the ability of materials to resist water ingress is crucial for maintaining structural integrity over time. Understanding whether EPS is waterproof helps ensure the long-term stability and safety of structures.
Cost-effectiveness:
Using waterproof materials can contribute to cost-effectiveness by reducing the need for frequent replacements or repairs due to water damage. Knowing whether EPS is waterproof allows for better cost-benefit analysis in material selection.
Environmental Impact:
Waterproofing can also impact the environmental sustainability of EPS. Materials that resist water ingress may have a lower likelihood of degradation, reducing the need for disposal and minimizing environmental impact over the lifecycle of the product.
Understanding whether expanded polystyrene is waterproof is essential for selecting the right material for various applications, ensuring durability, insulation performance, structural integrity, cost-effectiveness, and environmental sustainability.
What Factors Affect Expanded Polystyrene Waterproof Properties?
When considering the question, “Is expanded polystyrene waterproof?”, it’s important to understand the factors that influence its water-resistant properties:
Cell Structure:
EPS has a closed-cell structure, meaning its cells are sealed off from one another. This structure is crucial for water resistance because tightly packed, closed cells limit water penetration. The more compact and uniformly closed these cells are, the better the material can resist moisture infiltration.
Density:
The density of EPS plays a significant role in its water resistance. Higher-density EPS has fewer gaps and tighter cell structures, which reduces the pathways for water to seep through. Consequently, denser EPS materials offer better water-resistant properties.
Surface Treatment:
Applying coatings or laminates to EPS can significantly enhance its waterproof properties. These treatments add an extra layer of protection, preventing water from penetrating the material. This is particularly useful in applications where the EPS is exposed to moisture frequently.

Exposure Duration:
The duration of water exposure affects the waterproof properties of EPS. Short-term exposure generally does not compromise EPS integrity, but prolonged immersion can lead to gradual water ingress. Continuous or extended contact with water may eventually allow moisture to penetrate the material.
Environmental Conditions:
The effectiveness of EPS’s water resistance can be influenced by environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and the presence of chemicals. Extreme temperatures and high humidity can degrade the material over time, while certain chemicals in the water can affect its structural integrity and water resistance.
Manufacturing Quality:
The quality of the manufacturing process impacts the water resistance of EPS. Uniform cell structure and thorough expansion during production ensure that the material has consistent and reliable water-resistant properties. Poor manufacturing practices can result in irregular cell structures and weak points that allow water penetration.
How Does EPS Interact With Water?
Initial Resistance:
EPS is primarily composed of closed cells, which means each cell is a small, sealed pocket of air surrounded by polystyrene. This structure gives EPS a degree of water resistance, as the closed cells prevent water from easily penetrating the material.
Limited Absorption:
Although EPS is not completely waterproof, it does not absorb water easily. The material can resist moisture to a certain extent, making it suitable for applications where occasional or brief contact with water is expected.
Prolonged Exposure:
Over extended periods, EPS can begin to absorb small amounts of water. Prolonged or continuous exposure to water can lead to the material becoming saturated, which may compromise its structural integrity and thermal insulation properties.
Impact on Insulation:
When EPS absorbs water, its effectiveness as an insulator decreases. The trapped moisture can conduct heat, reducing the material’s insulating efficiency. This is particularly important in construction applications where maintaining thermal performance is crucial.
Environmental Factors:
The interaction of EPS with water can be influenced by environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and the presence of chemicals. High temperatures and humidity can accelerate the degradation process, while certain chemicals in water can react with the polystyrene, potentially weakening the material.
Surface Treatment and Protection:
To enhance its water resistance, EPS can be treated with coatings or laminates that create an additional barrier against moisture. These treatments help prevent water from penetrating the surface of the EPS, extending its durability and effectiveness in wet conditions.
Applications Of Expanded Polystyrene Waterproof Properties
Building And Construction

Foundations and Basements: Waterproof EPS insulation boards are installed below ground level to offer thermal insulation and resist moisture in foundations and basements. This helps in maintaining stable indoor temperatures and prevents water infiltration, safeguarding the structural integrity of the building.
Roofing Systems: EPS panels, coated with waterproof materials, are utilized as insulation layers in roofing systems. These panels not only provide insulation but also act as a barrier against moisture intrusion, thus protecting the building’s interior from water damage. Additionally, by enhancing energy efficiency, they contribute to reduced heating and cooling costs.
Exterior Insulation and Finish Systems (EIFS): Waterproof EPS boards form an integral part of EIFS applications, providing insulation and weatherproofing for building exteriors. These boards offer thermal insulation while effectively shielding the building from external moisture, ensuring durability and enhancing aesthetic appeal.
Packaging
Shipping Containers: Waterproof EPS packaging solutions are employed to safeguard goods during transportation, particularly for items vulnerable to moisture damage like electronics and perishable goods. These containers provide a protective barrier against external moisture, ensuring that the enclosed products arrive at their destination in optimal condition.
Cold Chain Logistics: Waterproof EPS coolers and containers are instrumental in cold chain logistics for transporting temperature-sensitive products. These containers effectively maintain the desired temperature and protect the contents from moisture ingress. By ensuring that the products remain dry throughout the transit, EPS helps preserve their quality and integrity, crucial for industries such as food and pharmaceuticals.
Marine and Aquatic Applications
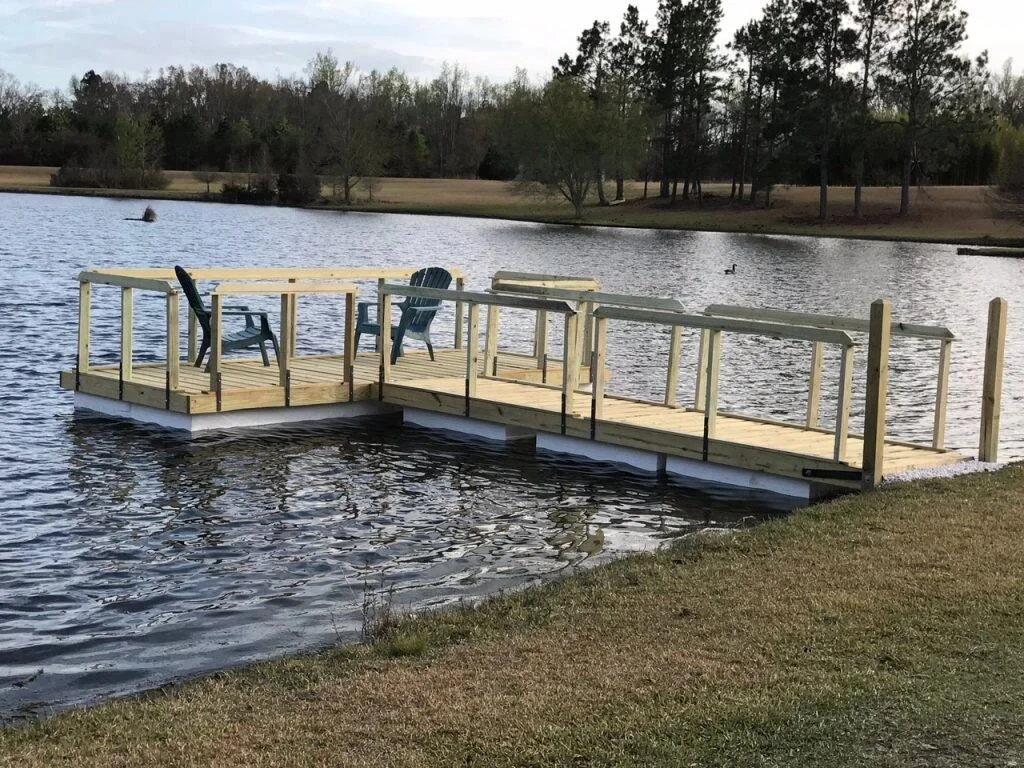

Boat and Dock Construction: Waterproof EPS foam finds extensive use in constructing boats, docks, and marine structures. Its buoyancy and resistance to water absorption make it an ideal material for these applications. By maintaining buoyancy and structural integrity even when submerged, EPS ensures the durability and stability of marine constructions.
Underwater Insulation: Waterproof EPS panels are utilized as insulating materials in underwater environments, such as subsea pipelines and underwater habitats. In these settings, where protection against water intrusion is critical, waterproof EPS panels provide thermal insulation while preventing moisture ingress. This helps maintain stable temperatures and protects sensitive equipment or habitats from water-related damage.
Conclusion
In summary, while EPS displays water-resistant characteristics owing to its closed-cell structure, it falls short of being entirely waterproof. While suitable for scenarios with occasional moisture exposure, prolonged or consistent water contact can compromise its integrity. Recognizing these limitations is crucial for informed decision-making in diverse applications.
Implementing protective measures like surface treatments can bolster its water resistance when necessary. Overall, understanding these nuances enables prudent use of EPS, balancing its benefits with potential water-related risks.
