Choosing the right helmet is crucial for safety, especially in high-impact sports. Two common liner materials, EPP and EPS, offer distinct protection levels. This blog delves into a comprehensive comparison, examining their impact absorption, durability, and suitability for various activities.
We’ll dissect the science behind each material, exploring how they manage force during collisions. By analyzing real-world scenarios and expert opinions, we aim to provide you with the ultimate guide to determine which helmet, EPP or EPS, offers superior safety for your needs.
What is an EPP Helmet?
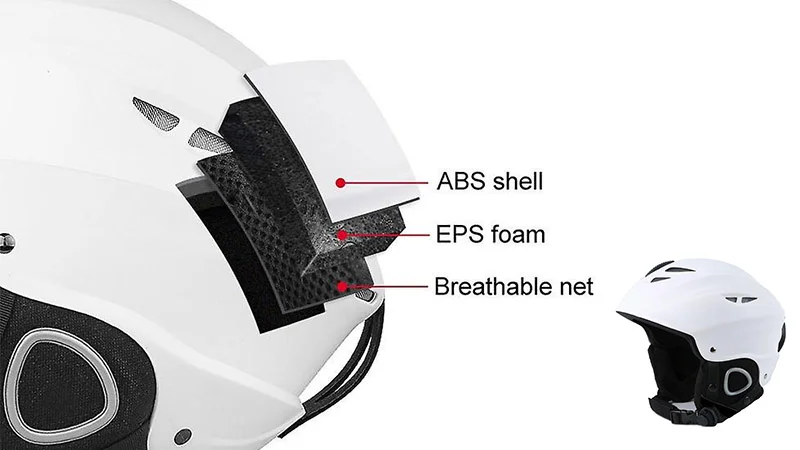

EPP, or Expanded Polypropylene, helmets utilize a foam liner known for its multi-impact capabilities. Unlike traditional EPS (Expanded Polystyrene) foam, which typically crushes and permanently deforms upon impact, EPP foam is designed to compress and rebound, absorbing multiple blows before needing replacement. This makes EPP helmets particularly suitable for activities where repeated impacts are likely, such as cycling, skateboarding, and certain contact sports.
The material’s unique properties stem from its closed-cell structure, which allows it to return to its original shape after impact. This resilience not only enhances durability but also provides consistent protection over a longer period.
While EPP helmets might be slightly heavier and sometimes more expensive than EPS counterparts, their ability to withstand multiple impacts makes them a valuable investment for those prioritizing long-term safety.
EPP helmets are commonly used in various sports and recreational activities, including cycling, skiing, snowboarding, skateboarding, and climbing. The EPP foam in these helmets is designed to absorb and distribute the energy from impacts, reducing the risk of head injuries in the event of falls or collisions.
Compared to helmets made from other materials such as EPS (Expanded Polystyrene) foam, EPP helmets offer advantages such as multiple impact protection, resilience to deformation, and the ability to withstand rough handling.
Additionally, EPP foam is often recyclable, contributing to the sustainability of helmet manufacturing.
Here are some key characteristics of EPP helmets:
- Energy Absorption and Distribution: The unique cellular structure of EPP allows it to effectively absorb and distribute the force of an impact, reducing the peak force transmitted to the wearer’s head. This helps minimize the risk of injury by spreading the impact energy over a larger area and slowing down the head’s deceleration.
- Multi-Impact Capabilities: EPP foam is designed to compress and rebound, absorbing multiple impacts without permanent deformation. This is crucial for activities where repeated, lower-energy impacts are likely, such as skateboarding or certain types of mountain biking, allowing the helmet to offer consistent protection.
- Lightweight and Durable: EPP is an exceptionally lightweight material, contributing to helmets that are comfortable for extended wear and reduce neck strain. EPP exhibits good resistance to water, chemicals, and UV radiation, enhancing the helmet’s overall durability and longevity in various environmental conditions.
What is an EPS Helmet?
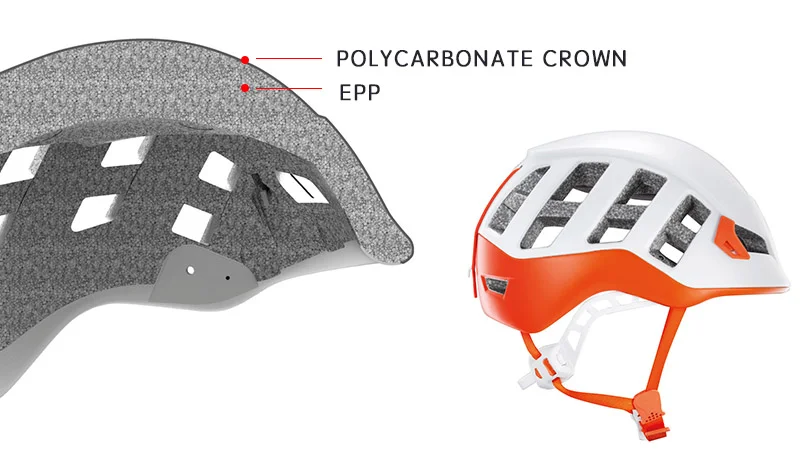

An EPS helmet is a type of helmet constructed using Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) foam as the primary material for impact absorption and protection. EPS foam is a lightweight, closed-cell foam material known for its ability to absorb and dissipate energy upon impact.
EPS helmets are commonly used in various sports and activities, including cycling, skateboarding, skiing, snowboarding, and motorcycling. The EPS foam in these helmets is designed to crush and deform upon impact, effectively absorbing the energy and reducing the force transmitted to the wearer’s head.
Compared to helmets made from other materials, EPS helmets offer advantages such as excellent impact absorption, lightweight design, and affordability. However, EPS foam typically provides single-impact protection and may need to be replaced after a significant impact or crash.
Here are some key characteristics of EPS helmets:
- Lightweight and Cost-Effective: EPS foam is inherently very lightweight, which allows manufacturers to create comfortable helmets that don’t add unnecessary bulk or strain. Additionally, the manufacturing process for EPS is generally more straightforward and less expensive, contributing to the widespread availability and affordability of EPS helmets across various price points.
- Single-Impact Protection: EPS foam is engineered to crush permanently on impact, which is highly effective at absorbing and dissipating the energy from a single significant blow. This irreversible deformation is crucial for maximizing protection during a critical accident, making it a standard in many cycling and motorcycling helmets.
- Excellent Energy Absorption: When subjected to an impact, the thousands of tiny beads within the EPS foam collapse and deform, effectively converting the impact energy into heat and deformation. This process significantly reduces the force transmitted to the head, thereby minimizing the risk of severe brain injuries in high-speed or high-force collisions.
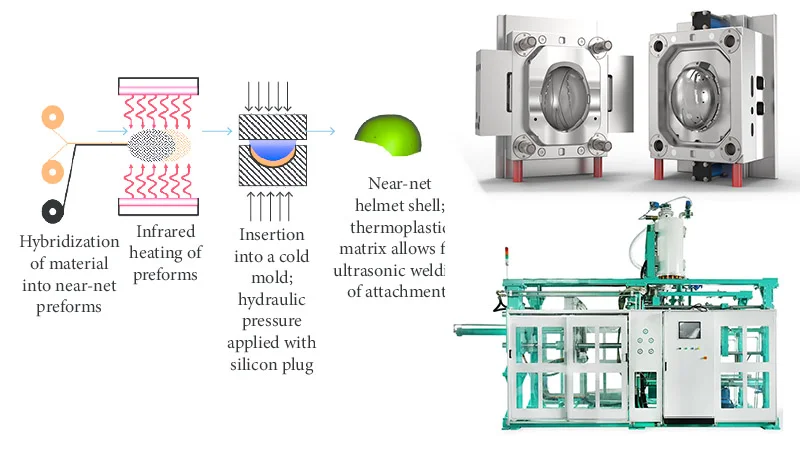
EPS Helmet Production Process

The production of an EPS helmet involves several precise steps, beginning with the raw polystyrene beads and transforming them into the rigid, protective foam liner. This process ensures the material’s ability to effectively absorb impact energy for wearer safety. Each stage is carefully controlled to achieve the desired density and shape.
Step 1: Pre-expansion
Raw polystyrene beads, containing a blowing agent like pentane, are introduced into a pre-expander machine. Here, steam is applied, causing the beads to soften and expand significantly, often up to 40 times their original size. This creates the individual closed-cell foam beads that are crucial for the EPS material’s lightweight and energy-absorbing properties.
Step 2: Storage and Aging
After pre-expansion, the enlarged EPS beads are transferred to large storage silos. They are then allowed to “age” for several hours. This resting period allows the beads to cool down and stabilize, releasing residual pentane gas and permitting air to diffuse into the cells, preparing them for the final molding process.
Step 3: Molding
The aged, pre-expanded beads are fed into a specialized helmet mold, often made of aluminum. Inside the mold, steam is again injected. This causes the beads to further expand and fuse under pressure, taking the exact shape of the helmet liner cavity. The precise control of steam and pressure is critical for achieving the correct foam density and structural integrity.
Step 4: Cooling and Finishing
Once molded, the helmet liner is cooled, typically with water or air, to solidify the EPS foam and maintain its shape. After cooling, the finished liner is carefully removed from the mold. Excess material is then trimmed, and the liner undergoes various finishing processes, including quality checks, before being assembled with the outer shell, straps, and padding to complete the helmet.
EPP Helmet Production Process

The production of EPP helmets involves several precise stages, transforming raw polypropylene into a resilient, impact-absorbing foam liner. This multi-step process ensures the material’s unique properties are optimized for head protection, resulting in a durable and effective helmet component.
Step 1: Preparation of EPP Beads
The process begins with raw polypropylene resin, which is expanded into small, uniform EPP beads using steam. This pre-expansion is crucial as it creates the closed-cell foam structure, making the material lightweight and ready for the subsequent molding phase, ensuring consistent material properties.
Step 2: Molding
Next, the pre-expanded EPP beads are carefully placed into a helmet-shaped mold. Inside the mold, steam is applied, causing the beads to further expand and fuse together under heat and pressure. This critical step forms the desired helmet liner shape, creating a cohesive and strong structure.
Step 3: Cooling and Demolding
After molding, the newly formed EPP helmet liner is cooled within the mold to stabilize its shape and structure. Once sufficiently cooled, the solid EPP part is carefully demolded. This step ensures the helmet retains its precise dimensions and structural integrity before further processing.
Step 4: Trimming and Finishing
The final stage involves trimming any excess material from the molded EPP liner to achieve the exact helmet dimensions. Quality control checks are performed to ensure the liner meets all safety and design specifications. This meticulous finishing prepares the EPP component for integration into the complete helmet assembly.
EPP vs EPS Helmet: Which is Safer
The core difference between EPP (Expanded Polypropylene) and EPS (Expanded Polystyrene) helmets lies in their impact management. EPS, the more common material, excels at absorbing single, high-energy impacts by crushing and dissipating the force.
However, this crushing is permanent, meaning the helmet must be replaced after even a minor collision. EPP, on the other hand, is designed for multiple impacts, compressing and rebounding, offering repeated protection.
For single, severe impacts like those in high-speed cycling crashes, EPS may offer superior initial protection.
However, for sports with frequent, lower-energy impacts, such as skateboarding or mountain biking on technical trails, EPP’s multi-impact capability provides a more consistent and potentially longer-lasting safety margin.
| Aspect | EPP Helmet | EPS Helmet |
|---|---|---|
| Impact Resistance | Superior due to multi-layered construction | Effective for single impacts, may degrade over time |
| Comfort and Fit | Often provides a snugger fit | Offers comfortable fit, personal preference varies |
| Durability and Longevity | Retains protective properties after multiple impacts | May require replacement sooner due to degradation |
| Cost Considerations | Higher price due to advanced construction | More budget-friendly option |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, contributes to sustainability | Recycling poses challenges, efforts ongoing |
EPP vs EPS Helmet
EPS helmets provide reliable safety performance in single-impact scenarios by absorbing and dissipating energy upon impact. While effective for initial impacts, EPS helmets may lose some protective capability after a significant collision, necessitating replacement to ensure continued safety.
| Aspect | EPP Helmet | EPS Helmet |
|---|---|---|
| Safety Performance | Offers longevity, maintains protection after multiple impacts | Reliable safety in single impacts may lose effectiveness over time |
| Longevity and Durability | Exceptional durability can withstand multiple impacts | A finite lifespan may require replacement after a significant impact |
| Cost Considerations | Higher upfront cost, cost-effective long-term investment | More affordable upfront, potential replacement costs over time |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable and reusable, it contributes to sustainability | Less recyclable, disposal may contribute to environmental waste |
| Hardness | Higher hardness maintains protection over repeated impacts | Slightly lower hardness may compress more readily |
| Size | Available in various sizes with adjustable fitting systems | Multiple sizes with adjustable straps for personalized fit |
| Maintenance | Requires minimal maintenance, easy cleaning process | May need more frequent maintenance, gentle washing is recommended |
Inspect EPS helmets regularly for signs of wear, damage, or deterioration, and replace them as needed to maintain optimal safety standards. Want to know about EPP or EPS Helmet: Which is Safer, The above guidelines are important.
Difference Between EPP and Polypropylene
Expanded polypropylene (EPP) is a type of foam that is made from polypropylene (PP) plastic resin. While PP is a tough, rigid plastic, EPP is a lightweight, flexible foam with a closed-cell structure. The manufacturing process of EPP involves expanding the PP beads with steam and pressure, fusing them into a low-density, highly resilient material.
The key differences between the two materials stem from this difference in structure and manufacturing.
- Applications: PP is used for a wide range of products like food containers, automotive parts, and textiles, where rigidity and chemical resistance are needed. EPP is ideal for applications requiring high shock absorption, such as automotive bumper cores, protective packaging, and model aircraft.
- Structure: PP is a solid thermoplastic polymer, while EPP is a closed-cell bead foam made mostly of air (up to 95%).
- Properties: EPP excels at energy absorption and impact resistance, as its closed-cell structure allows it to withstand multiple impacts without permanent deformation. PP is rigid and tough, but it doesn’t have the same cushioning or resilience.
- Weight: Due to its foamed structure, EPP is significantly lighter than solid PP, which is already known for being one of the lightest commodity plastics.
How to Choose EPP and EPS Helmet?
Choosing between an EPP and EPS helmet largely depends on the specific activity and the type of impacts you anticipate. Both materials are highly effective at absorbing energy, but they do so in different ways, making each suited for distinct scenarios where head protection is paramount. Understanding these differences is key to making an informed decision about your safety gear.
Here’s how to choose:
- Factor in Helmet Lifespan and Replacement: EPS helmets must be replaced after any significant impact, as their internal structure is permanently compromised. EPP helmets, due to their multi-impact nature, may withstand several smaller impacts, potentially offering a longer lifespan for certain uses, though regular inspection is still crucial.
- Consider the Impact Profile of Your Activity: If your activity involves high-speed, single, severe impacts, like road cycling or motorcycling, an EPS helmet is generally the preferred choice. It’s engineered to deform and crush upon a major hit, offering maximum one-time energy absorption for critical protection.
- Evaluate for Multi-Impact Scenarios: For sports with frequent, lower-energy impacts, such as skateboarding, whitewater kayaking, or certain types of climbing where minor bumps are common, an EPP helmet excels. Its ability to compress and rebound allows it to maintain protective qualities through multiple smaller incidents.
EPS vs MIPS helmet
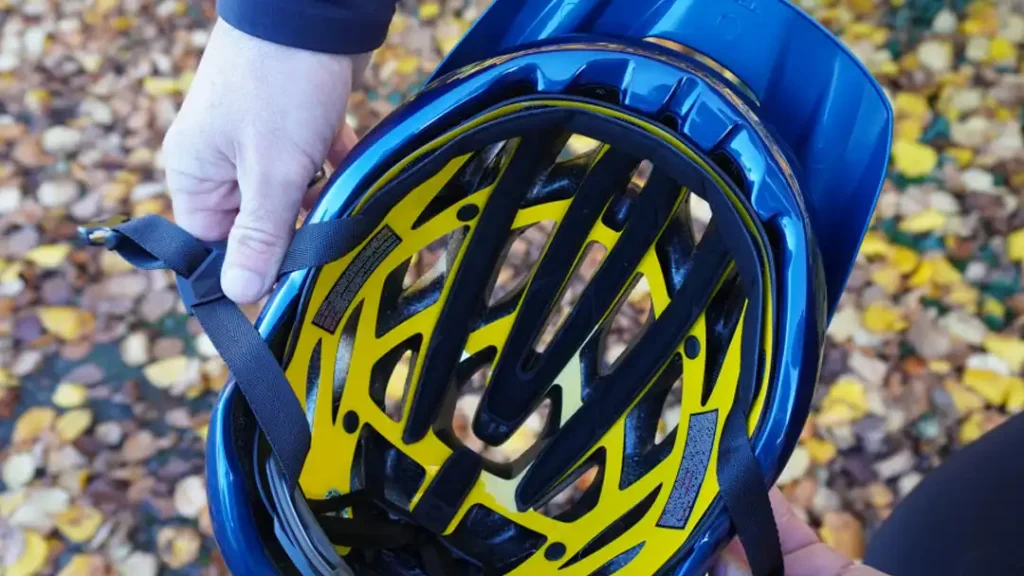

EPS and MIPS (Multi-directional Impact Protection System) are both technologies used in helmet construction, but they address different aspects of head protection:
EPS (Expanded Polystyrene) helmets are constructed with a layer of expanded polystyrene foam, which is designed to absorb impact by compressing upon impact, thereby reducing the force transmitted to the head. EPS helmets are effective at providing protection against direct impacts.
MIPS helmets, on the other hand, incorporate an additional layer inside the helmet that allows for a small amount of movement between the helmet and the head in the event of an angled impact. This movement mimics the brain’s own protective mechanism, reducing rotational forces on the brain and decreasing the risk of injury from certain types of impacts.
Here’s a comparison between EPS and MIPS helmets:
| Property | EPS Helmet | MIPS Helmet |
|---|---|---|
| Impact Absorption | Good | Good |
| Rotational Force Reduction | No | Yes |
| Multiple Impact Usage | No | Yes |
| Additional Layer | No | Yes, MIPS layer |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Suitability | Suitable for direct impacts | Suitable for both direct and angled impacts |
While EPS helmets provide effective protection against direct impacts, MIPS helmets offer an additional layer of protection by reducing rotational forces on the brain, especially in situations involving angled impacts. However, MIPS helmets tend to be more expensive due to the additional technology involved.
Are EPP helmets more durable than EPS helmets?
Yes, EPP helmets are generally more durable than EPS helmets. The expanded polypropylene material used in EPP helmets offers excellent impact resistance and can withstand multiple impacts without compromising its integrity. This durability ensures that EPP helmets maintain their protective qualities over an extended period, making them a reliable choice for various activities.
Do EPP helmets provide better impact protection?
EPP helmets are renowned for their superior impact protection capabilities. The unique cellular structure of expanded polypropylene efficiently absorbs and disperses energy upon impact, reducing the force transmitted to the wearer’s head. This translates to enhanced safety, as EPP helmets can effectively mitigate the risk of head injuries during accidents or collisions.
Are EPS helmets more affordable?
Answer: Yes, EPS helmets are generally more affordable than their EPP counterparts. Expanded polystyrene foam, the material used in EPS helmets, is cost-effective to manufacture, resulting in lower production costs. This affordability makes EPS helmets a popular choice for individuals seeking adequate head protection without breaking the bank.
Can EPP helmets be customized easily?
Answer: Yes, EPP helmets can be customized relatively easily to suit individual preferences and requirements. The flexible nature of expanded polypropylene allows for intricate molding and shaping, enabling manufacturers to create helmets with custom designs, colors, and features. This customization potential ensures that users can personalize their helmets for optimal comfort and style.
Where Are EPS and EPP Helmets Used?
EPS (Expanded Polystyrene) helmets are widely used across various sports and activities where single, high-impact protection is paramount. This includes common applications like cycling helmets (road and recreational), motorcycle helmets, skiing and snowboarding helmets, and even many construction hard hats. Their excellent energy absorption capabilities upon a singular significant impact make them the industry standard for minimizing head trauma in severe accidents.
EPP (Expanded Polypropylene) helmets, conversely, are favored in scenarios that often involve multiple, less severe impacts, due to their ability to rebound and retain protective qualities. You’ll find EPP helmets extensively used in whitewater sports (kayaking, rafting), skateboarding and roller sports, climbing helmets, and some multi-sport helmets where repeated bumps and knocks are anticipated. EPP’s durability against multiple smaller impacts offers consistent protection throughout the activity’s duration.
Conclusion
The optimal choice depends on the specific activity and anticipated impact scenarios. EPS excels in single, high-energy impacts, while EPP provides superior multi-impact protection. Understanding these differences allows informed decisions for personal safety.
Consider your sport’s nature and prioritize a proper fit, relevant certifications, and comfort. Both materials offer vital protection, but choosing wisely ensures maximum safety. Combining both materials in a single helmet is also becoming more common.
For wholesale EPP or EPS helmets, contact Epsole today. We offer a wide range of high-quality helmets designed for various activities, ensuring your customers receive top-tier protection. Reach out now to discuss your bulk order needs.



