In the world of foam materials, Expanded Polypropylene (EPP) and Expanded Polyolefin (EPO) foams are important. They have different features and are used in various industries.
This article will compare EPP vs EPO foams, focusing on what they are made of, how they are made, what they’re like, where they’re used, and their impact on the environment.
What is EPP Foam?

EPP foam, short for Expanded Polypropylene, is a highly adaptable closed-cell bead foam renowned for its exceptional properties. These include outstanding energy absorption, resilience to multiple impacts, effective thermal insulation, buoyancy, and resistance to water and chemicals. Additionally, EPP boasts an exceptionally high strength-to-weight ratio and is 100% recyclable, making it a sustainable choice.
It can be manufactured in a wide range of densities, from 15 to 200 grams per liter, which are then transformed through molding into densities ranging from 18 to 260 grams per liter. The steam chest molding process fuses individual beads into the final product form, resulting in a sturdy yet lightweight structure.
What is the process of EPP foam production?
The manufacturing process of EPP (Expanded Polypropylene) involves several steps to achieve the desired foam product:
Mold Preheating: The mold is preheated to the melting point, ensuring its surface temperature is optimal for the molding process.
Material Feeding: EPP material is fed into the mold through a material gun, filling the mold cavity.
Steam Introduction: Steam is introduced into the mold in three stages:
- Steam Flushing: Steam is flushed from top to bottom to expel air and condensate water, with steam inlet valves open and condensate water discharge valves open.
- Lateral Steam: Steam sweeps laterally across the material, penetrating it from one side to the other. Steam inlet valves are opened on one side while closed on the opposite side, allowing steam to pass through thin flanges for thorough heating.
- Pressure Holding: Pressure is applied to ensure complete melting and molding of the material. Steam inlet valves are open, and condensate water discharge valves are closed to increase pressure gradually.
Cooling: After steam introduction, the mold’s internal temperature typically reaches 140°C. Cooling is initiated to lower the mold temperature to around 70°C, facilitating smooth demolding of the product.
Demolding: Once the internal pressure is released and the mold temperature reaches the permitted demolding temperature, the EPP foam product can be safely removed from the mold.
What is EPO Foam?
EPO foam, short for Expanded Polystyrene Polyethylene blend, is a unique copolymer resulting from a special polymerization process. It comprises 30% polyethylene and 70% polystyrene, making its composition and structure distinct.
Expanded Polyolefin (EPO) foam is a lightweight, closed-cell foam material used in various applications, particularly in the manufacturing of model aircraft, UAVs (unmanned aerial vehicles), and other hobbyist projects. It’s a type of thermoplastic foam that offers excellent strength-to-weight ratio, buoyancy, thermal insulation, and resistance to water and chemicals.
What is the process of EPO foam production?
EPO foam is produced by expanding beads of polyolefin resin using heat and pressure. The result is a foam with a uniform cellular structure, providing it with stability and durability. It can be easily molded into different shapes and sizes, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
What is the difference between EPP foam and EPO Foam?

EPP foam is suitable for manufacturing protective packaging, sports equipment (such as helmets and padding), automotive components, aerospace parts, and other products that require high-strength and lightweight structures. It is also commonly used in the production of water toys, buoys, model aircraft, and other items that require buoyancy and durability.
On the other hand, EPO foam is suitable for disposable packaging, flexible cushioning materials (such as packaging fillers, and pads), low-cost model making, and other applications that require lightweight materials with some energy-absorbing capabilities.
EPP vs EPO foam
| Feature | EPP Foam | EPO Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Mainly composed of polypropylene | Blend of polyethylene and polystyrene |
| Manufacturing | Produced using thermal molding and expansion | Manufactured through a special polymerization |
| Density | Typically higher, resulting in greater strength and hardness | Generally lower, hence lighter and less dense but with lower strength |
| Elasticity | Exhibits excellent elasticity and resilience | Less elastic, but capable of energy absorption |
| Durability | Very durable, suitable for repeated use | More brittle, prone to damage, often used for disposable packaging |
| Molding Ability | Challenging to precisely mold, suitable for simple shapes | Can be accurately molded, suitable for complex shapes |
| Eco-friendliness | Recyclable, environmentally friendly | Less environmentally friendly, slower to degrade |
| Application | Mainly used for protective packaging and manufacturing lightweight structural components | Primarily used for disposable packaging and flexible cushioning materials |
| Cost | Generally higher cost but offers better durability | Typically lower cost, suitable for disposable applications |
| Compression Properties | Exhibits higher compression properties, able to absorb impact and compression forces | Poor compression properties, prone to damage upon compression |
The Applications of EPP
EPP Application of Car Parts:
EPP molded parts play a crucial role across various industries, notably in automotive manufacturing. Their exceptional energy-absorbing characteristics enhance passive safety measures and offer enhanced protection for vehicle occupants. This makes them ideal for producing components like fenders, headrests, and other impact-absorbing elements.
Another advantage lies in the lightweight nature of EPP, contributing to reduced fuel consumption and promoting eco-friendliness in cars. Furthermore, the ability to achieve precise shapes makes EPP versatile in applications such as sun visors, paneling, or custom toolboxes designed to accommodate breakdown sets efficiently.
EPP Parts for Electronic Equipment:
With the trend towards larger TVs, traditional EPS packaging is no longer sufficient to ensure their safe transportation. As a result, EPP cushions have emerged as the preferred packaging material for large TVs.
The EPP Electrostatic Discharge Protection (ESDP) grade offers enhanced protection against electrostatic discharge, featuring a permanent surface resistance of less than 10^7 ohms. This property promotes rapid static decay, effectively shielding against sparking and other electrical hazards during transit.
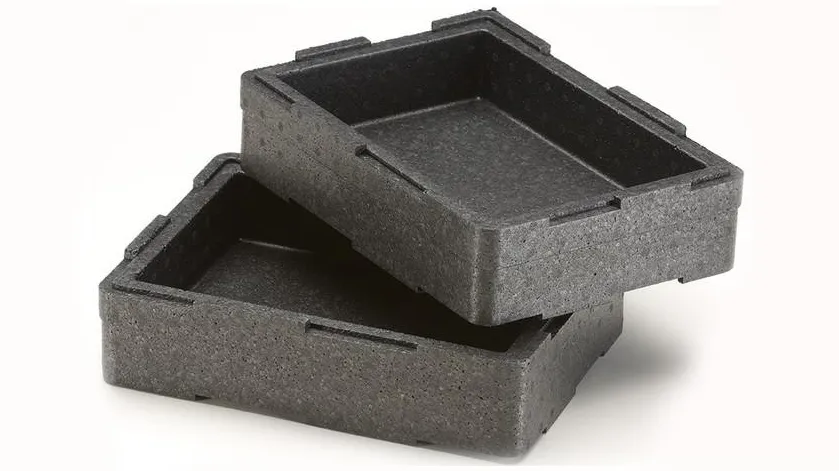
EPP Thermo Box:
Whether you’re in the restaurant industry, catering business, or food retail sector, the EPP box offers tailored solutions for every sector’s needs. Additionally, our practical recreational boxes are perfect for private use, whether for shopping trips or camping adventures.
The EPP box excels in insulation, featuring a high-stacking rim with special knobs and reinforced corners that guarantee a secure fit for the lid. This ensures safe transportation and optimal insulation for hot, cold, and fresh food items. Moreover, its sturdy yet lightweight construction makes it a durable and convenient choice for various applications.
EPP Sport & Leisure:
EPP has been used to make; climbing, skiing, horse riding, skateboarding, surfing, baseball, and cycling helmets, ski boot insoles, body boards, swimming floats, body protection, shin pads, bicycle rims, exercise/yoga rolls, and more.
EPP Pallets and Plank:
Direct production of EPP beads offers a substantial reduction in material costs and provides a viable alternative to EPS pallets. These beads enable goods to be loaded with weights of up to 3000kg. Additionally, EPP planks are lighter yet stronger, offering superior product protection using less material. Prototyping is also feasible to ensure the product aligns perfectly with your requirements.
Why are most RC airplanes made out of EPO foam?
EPO foam has found widespread use in RC airplanes due to its lightweight nature, exceptional durability, and impressive impact resistance. Its ability to withstand crashes and rough landings surpasses that of many other materials commonly used in RC aircraft construction. Another advantage of EPO foam is its ease of repair using CA glue, making maintenance straightforward for hobbyists.
Although EPO foam may show signs of wear such as scuffing, it remains resilient and can be easily restored with paint or other touch-up materials, maintaining its aesthetic appeal. These qualities, coupled with its balanced combination of durability and weight, make EPO foam a preferred choice among RC enthusiasts for constructing reliable and long-lasting aircraft models.
Related: EPS vs EPP Foam: What Are Differences Between Them?
Conclusion
In conclusion, while both EPP and EPO foam offer unique advantages and applications, they differ in several key aspects. EPP foam stands out for its exceptional strength, lightweight nature, and superior impact resistance, making it an ideal choice for various industries, including automotive, packaging, and recreational equipment.
On the other hand, EPO foam is prized for its balance of durability and weight, making it popular for applications such as RC airplanes.
EPP foam’s remarkable strength and resilience make it a preferred material for demanding environments where impact protection is crucial, while EPO foam’s lightweight and durable properties make it a versatile option for applications requiring a balance between durability and weight.