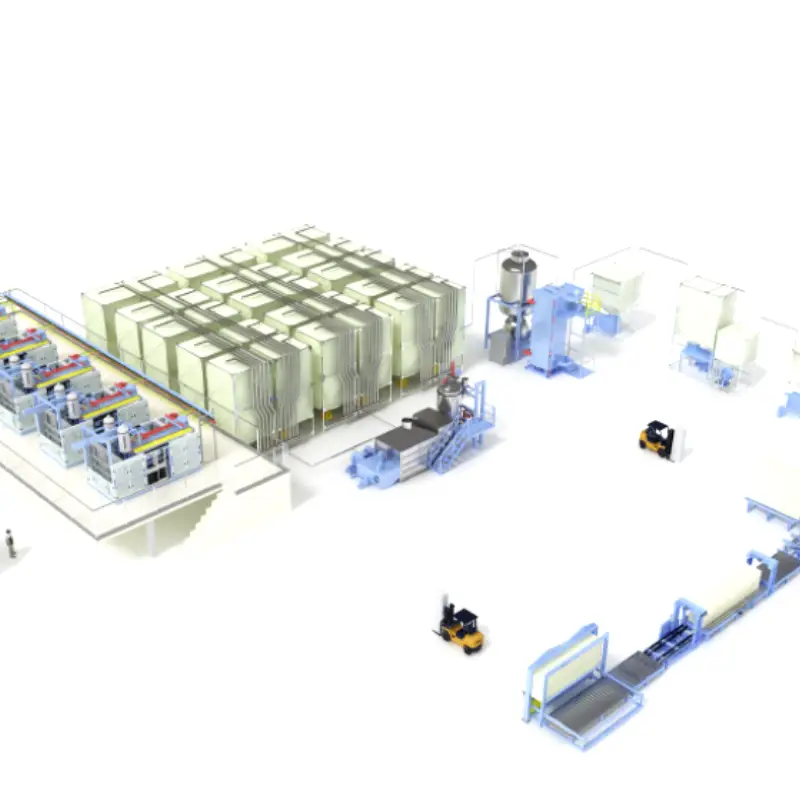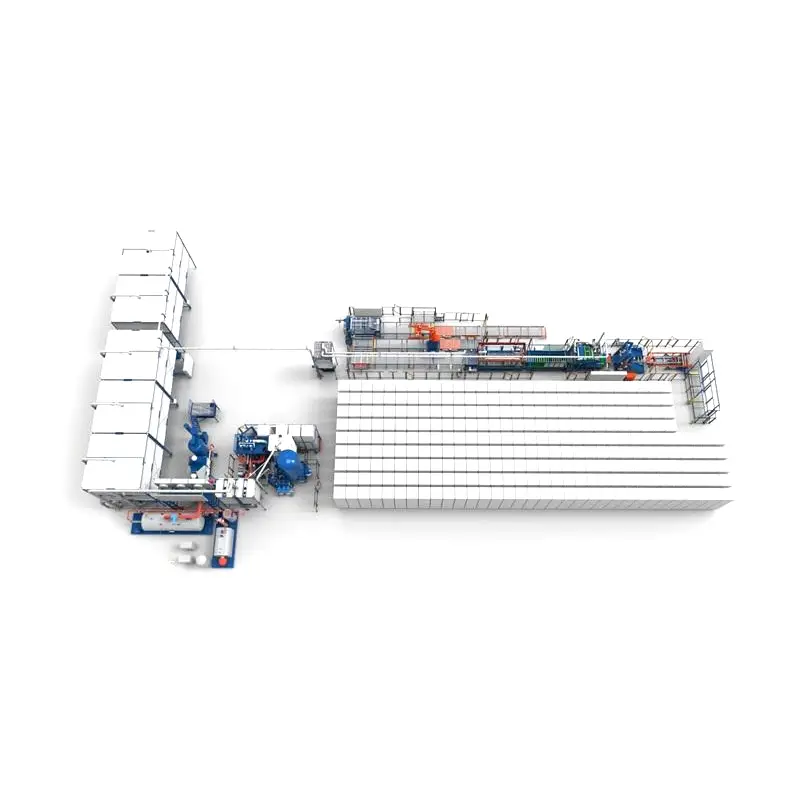
EPS Plant: Get Substantial Profits with EPS
An EPS plant is a manufacturing facility that produces Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) foam products. This versatile material, commonly known as Styrofoam, is created by expanding polystyrene beads using steam and pressure. The result is a lightweight, rigid, and insulating material with numerous applications.
EPS Production Process
EPS recycling machine is playing a crucial role in reducing waste and promoting sustainability. We can offer the premium EPS recycling machine to meet all of your requirements, here we can provide you all to support EPS recycling machine.
1. Pre-Expansion
- Bead Preparation: Small polystyrene beads are mixed with a blowing agent, typically pentane or carbon dioxide.
- Expansion: The bead mixture is heated using steam in a pre-expander. This causes the beads to expand significantly as the blowing agent vaporizes, creating a cellular structure.
2. Aging
- The pre-expanded beads are allowed to cool and stabilize over a while. This process is crucial for consistent product quality.
3. Molding
- Block Molding: The most common method, where pre-expanded beads are placed in a mold and subjected to steam and pressure. The beads expand further, fusing together to form a solid block.
- Sheet Molding: Pre-expanded beads are spread evenly on a mold, then expanded and fused together using steam and pressure.
- Injection Molding: Molten polystyrene is injected into a mold, where it cools and solidifies into the desired shape.
4. Cooling and Trimming
- The molded EPS is cooled to solidify the structure.
- Excess material is trimmed to achieve the desired shape and size.
FAQs about EPS Plant
What is EPS plant?
An EPS plant is a manufacturing facility that produces Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) foam products.
This type of plant specializes in transforming tiny polystyrene beads into the lightweight, rigid, and insulating material we commonly know as Styrofoam.
how does EPS plant work?
An EPS (Expanded Polystyrene) plant transforms tiny polystyrene beads into the familiar Styrofoam product. Let’s break down the process:
The EPS Production Process
EPS Bead Preparation:
Small polystyrene beads are mixed with a blowing agent, typically pentane or carbon dioxide.
Pre-expansion:
The bead mixture is heated with steam, causing the beads to expand significantly as the blowing agent vaporizes.
Aging:
The pre-expanded beads are allowed to cool and stabilize before the next step.
Molding:
The pre-expanded beads are placed in a mold and subjected to steam and pressure.
The beads expand further and fuse together to form the desired shape.
Cooling and Trimming:
The molded EPS is cooled to solidify the structure.
Excess material is trimmed to achieve the final product.
Visual Representation:
Key Components of an EPS Plant
- Bead storage and handling systems: For storing and transporting polystyrene beads.
- Pre-expander: Heats and expands the beads.
- Aging silos: For storing pre-expanded beads.
- Molding machines: Shapes the EPS product.
- Cooling systems: Cools the molded product.
- Trimming equipment: Cuts the EPS to the desired size.
An EPS plant is a complex system that involves precise control of temperature, pressure, and time to produce high-quality EPS products.
What is EPS machine?
An EPS machine is essentially a piece of industrial equipment used to manufacture Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) products. It encompasses a series of interconnected machines that work together to transform tiny polystyrene beads into the familiar Styrofoam material.
Key Components of an EPS Machine
While “EPS machine” often refers to the entire production line, there are specific machines that play crucial roles:
- Pre-expander: This machine heats and expands polystyrene beads using steam.
- Molding machine: This equipment shapes the expanded beads into the desired product form.
- Cooling system: Cools the molded EPS product to solidify its structure.
- Trimming machine: Cuts excess material to achieve the final product dimensions.
Other supporting equipment may include bead storage silos, conveying systems, and control systems.
Types of EPS Machines
Depending on the specific product and production scale, there are different types of EPS machines:
- Block molding machines: Produce large blocks of EPS for insulation purposes.
- Shape molding machines: Create custom-shaped EPS products for packaging, automotive, and other industries.
- Sheet molding machines: Produce flat EPS sheets for various applications.
what are EPS plant uses?
An EPS (Expanded Polystyrene) plant produces a versatile material with numerous applications across various industries. Here are some of the primary uses:
Construction
- Insulation: EPS is widely used for insulating walls, roofs, and floors due to its excellent thermal properties.
- Foundation fill: EPS can be used as a lightweight fill material for foundations.
- Concrete forms: EPS blocks can be used as forms for concrete structures.
Packaging
- Protective packaging: EPS is commonly used to protect fragile items during shipping and transportation.
- Consumer packaging: EPS is found in packaging for electronics, appliances, and other products.
Automotive
- Interior components: EPS is used for creating various interior components, such as headliners and door panels.
- Crash protection: EPS provides impact absorption in car components.
Marine
- Buoyancy: EPS is used in life jackets, buoys, and other marine equipment.
- Insulation: EPS can be used to insulate marine vessels.
Other Applications
- Agriculture: EPS is used for packaging agricultural products and creating growing containers.
- Horticulture: EPS trays are used for starting seedlings.
- Consumer products: EPS is found in products like coolers, packaging peanuts, and disposable cutlery.
In essence, EPS plants produce a material that offers excellent insulation, shock absorption, and buoyancy properties, making it a valuable resource for many industries.