Steam chest molding is a widely used process for producing molded foam parts from EPP and EPS materials. By applying controlled steam and pressure, this method fuses pre-expanded beads into strong, lightweight components. It is commonly used in packaging, automotive, insulation, and industrial applications requiring consistency and durability.
Understanding how EPP and EPS parts are made through steam chest molding helps manufacturers improve product performance and production efficiency. From bead preparation to final cooling, each stage influences density, strength, and surface quality, making process control essential for reliable foam molding results.
What is Steam Chest Molding?
Steam chest molding is a foam manufacturing process used to form EPP and EPS parts by heating pre-expanded beads inside a closed mold with steam. The steam causes the beads to expand further and fuse together, creating lightweight, strong components with consistent shape, density, and insulating or impact-resistant properties.
EPS Steam Chest Molding Process
EPS steam chest molding is a structured manufacturing process used to produce lightweight foam parts with stable insulation and cushioning properties. By carefully controlling steam, pressure, and cooling, EPS beads are fused into precise shapes. Each step is performed independently to ensure consistent density, strength, and surface quality in the final molded products.
Step 1: Pre-expansion of EPS Beads
Tools Needed
- Pre-expander
- Steam generator
- Drying system
- Density control unit
Raw EPS beads are heated with steam in a pre-expander to increase their volume to a specified density. This step defines the basic physical properties of the final product, including weight, insulation performance, and mechanical strength.
After expansion, the beads are dried and cooled to remove surface moisture. Proper drying ensures smooth material flow, prevents bead agglomeration, and prepares the beads for stable aging and consistent molding behavior.
Step 2: Aging and Stabilization
Pre-expanded EPS beads are stored in ventilated silos to allow internal pressure equalization. Aging releases trapped gases and balances moisture, which is essential for achieving strong fusion during steam chest molding.
Sufficient stabilization time reduces shrinkage and improves dimensional accuracy. Well-aged beads respond evenly to steam, resulting in uniform density and improved structural consistency in the finished EPS parts.
Step 3: Mold Filling
Aged EPS beads are conveyed into the mold cavity of the steam chest molding machine. Uniform filling ensures even material distribution and helps avoid weak spots or density variation in the molded product.
Accurate filling control supports consistent wall thickness and shape formation. Proper mold loading is critical for achieving predictable fusion results and maintaining repeatable production quality.
Step 4: Steam Heating and Fusion
Steam is injected into the closed mold, reheating the EPS beads and causing them to expand further. Under controlled pressure and temperature, the beads fuse together and take the exact shape of the mold.
Careful control of steam parameters ensures strong bonding without over-expansion. This step defines the final strength, surface finish, and dimensional precision of the molded EPS component.
Step 5: Cooling and Demolding
After fusion, cooling air or water is introduced to reduce temperature and stabilize the molded EPS structure. Controlled cooling prevents deformation and locks in the final dimensions of the product.
Once fully cooled, the EPS part is removed from the mold and inspected. Proper demolding and quality checks ensure the product meets performance standards for packaging, insulation, or industrial applications.
EPP Steam Chest Molding Process
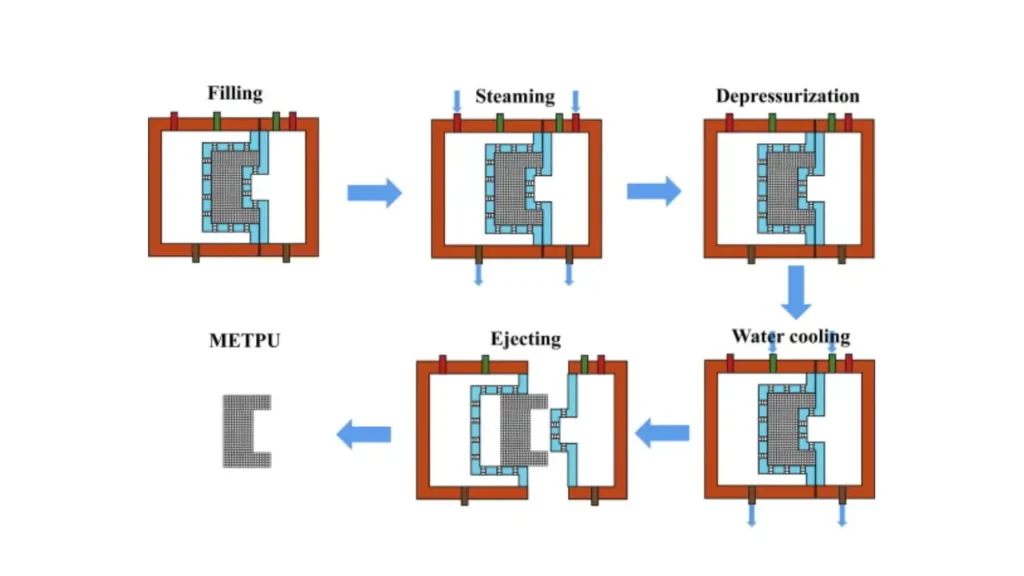
EPP steam chest molding is a controlled manufacturing process used to produce lightweight, resilient foam parts with excellent impact recovery. By applying steam and pressure to expanded polypropylene beads, this method forms durable components with consistent density and accurate dimensions. Each step is performed separately to ensure stable molding quality and reliable performance in industrial applications.
Step 1: Pre-expansion of EPP Beads
Tools Needed
- EPP pre-expander
- Steam generator
- Drying system
- Density control unit
Raw EPP beads are heated with steam inside a pre-expander to reach the required density. This step controls the balance between weight, strength, and resilience, which directly affects impact absorption and durability of the final molded parts.
After expansion, the beads are dried and cooled to remove surface moisture. Proper drying ensures smooth material flow, prevents bead sticking, and prepares the beads for effective aging and uniform fusion during molding.
Step 2: Aging and Stabilization
Pre-expanded EPP beads are stored in ventilated silos to stabilize internal pressure. Aging allows gases to escape gradually, helping the beads achieve consistent behavior during steam chest molding.
Adequate aging improves bead fusion, reduces shrinkage, and enhances dimensional stability. Properly stabilized beads result in uniform density and long-term performance of molded EPP components.
Step 3: Mold Filling
Aged EPP beads are transferred into the mold cavity of the steam chest molding machine. Even filling ensures consistent bead distribution and prevents weak zones within the molded part.
Controlled filling supports accurate shape formation and uniform wall thickness. This step is critical for maintaining repeatable quality and ensuring the final product meets design and functional requirements.
Step 4: Steam Heating and Fusion
Steam is injected into the closed mold, reheating the EPP beads and causing them to expand and fuse. Controlled temperature and pressure allow the beads to bond while maintaining elasticity and impact resistance.
Precise steam control prevents over-fusion or deformation. This step defines the mechanical strength, resilience, and surface finish of the molded EPP part.
Step 5: Cooling and Demolding
Cooling air or water is applied to solidify the molded EPP structure and lock in its shape. Proper cooling stabilizes dimensions and preserves the material’s elastic properties.
Once cooled, the EPP part is demolded and inspected. Careful removal and quality checks ensure the component meets performance standards for automotive, packaging, and industrial applications.
Where to Use Steam Chest Molding?
Steam chest molding is used wherever lightweight, molded foam parts with consistent structure and reliable performance are required. This process is especially suitable for shaping EPP and EPS materials into durable, insulated, or impact-resistant components. Because of its precision and efficiency, steam chest molding supports a wide range of industrial and commercial applications.
Consumer and Technical Products – Steam chest molding supports the production of foam parts for consumer goods and technical equipment. Applications include sports protection, medical packaging, and equipment housings requiring lightweight strength and consistent shape.
Packaging and Protective Inserts – Steam chest molding produces foam inserts that protect products during storage and transport. The molded shapes provide cushioning, prevent movement, and reduce damage risk, making them ideal for electronics, appliances, and fragile goods.
Automotive Components – In the automotive industry, steam chest molding is used to create EPP parts such as energy absorbers, tool holders, and load carriers. These components offer impact resistance, lightweight structure, and long service life.
Thermal Insulation Products – EPS parts made through steam chest molding are widely used for insulation panels and construction elements. The process ensures uniform density and stable thermal performance for building, cold storage, and industrial insulation applications.
Industrial Load Carriers and Trays – Steam chest molding is used to manufacture reusable EPP load carriers and trays. These products support automated handling, repeated use, and reliable protection in manufacturing, warehousing, and logistics systems.
Conclusion
Steam chest molding provides a stable and efficient way to manufacture EPP and EPS foam parts with uniform structure and dependable performance. The process allows precise control over density and shape, helping manufacturers meet application-specific requirements across multiple industries while maintaining consistent output and reduced material waste.
Both EPP and EPS benefit from steam chest molding, though they serve different functional needs. EPP offers resilience and reusability, while EPS delivers lightweight insulation and cost efficiency. Choosing the right material and molding parameters ensures optimal performance for packaging, automotive, and industrial foam products.
For reliable foam production and supply, material quality is just as important as the molding process. You can get wholesale EPS foam and EPP foam from our Epsole, supporting stable molding performance, consistent product results, and efficient large-scale manufacturing across diverse foam applications.


-1-300x300.webp)




