When it comes to insulation materials, expanded and extruded polystyrene are two commonly used options. While they might seem similar, they have distinct differences that can impact their performance and suitability for various applications.
Understanding these disparities is crucial for making informed decisions regarding construction and insulation projects.
Let’s delve into the dissimilarities between expanded and extruded polystyrene to grasp their unique characteristics and applications.
Characteristics of Expanded Polystyrene
1. Manufacturing Process
Expanded polystyrene (EPS) is produced through a process involving the expansion of polystyrene beads. These beads are expanded using steam, resulting in a lightweight and versatile material.
2. Cell Structure
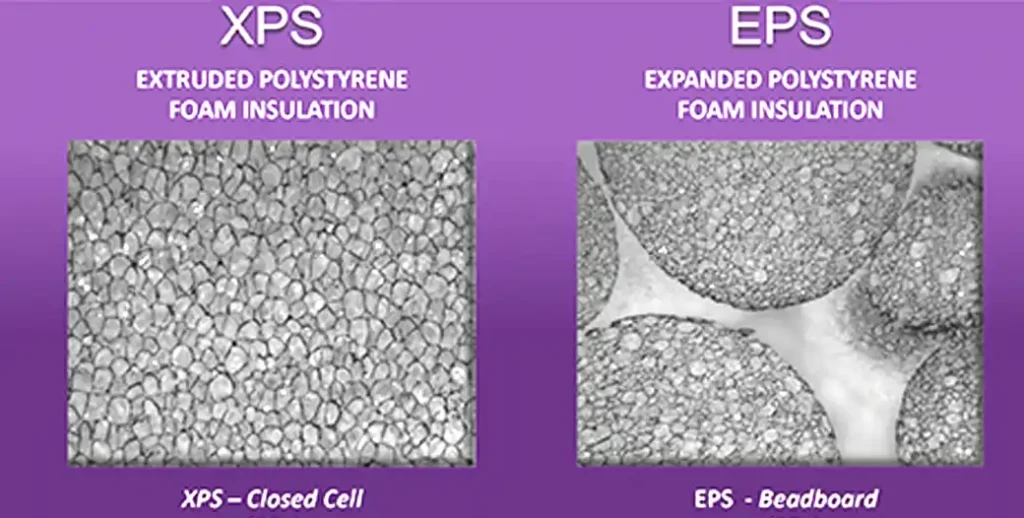
EPS is characterized by its closed-cell structure, which consists of small, interconnected bubbles. This structure provides excellent thermal insulation properties and buoyancy, making EPS suitable for a wide range of applications, from packaging to construction.
3. Density
The density of expanded polystyrene varies depending on the application. Lower density EPS is often used for packaging, while higher density EPS is preferred for insulation purposes.
4. Thermal Conductivity
One of the key advantages of EPS is its low thermal conductivity, which makes it an efficient insulating material. Its ability to trap air within its cellular structure helps reduce heat transfer, making it ideal for maintaining indoor temperatures and energy efficiency.
5. Strength and Rigidity
While EPS is lightweight, it offers sufficient strength and rigidity for many applications. Its compressive strength allows it to withstand heavy loads, making it suitable for construction projects requiring structural support.
Characteristics of Extruded Polystyrene
1. Manufacturing Process
Extruded polystyrene (XPS) is manufactured through an extrusion process, where polystyrene pellets are melted and then formed into rigid boards. This process results in a dense and uniform material with a closed-cell structure.
2. Cell Structure
Unlike EPS, XPS has a more uniform and compact cell structure, which enhances its strength and durability. This structure also contributes to its moisture resistance, making it suitable for below-grade applications where moisture intrusion is a concern.
3. Density
XPS typically has a higher density compared to EPS, which gives it increased strength and resistance to compression. This makes it a preferred choice for applications requiring high load-bearing capacity, such as under concrete slabs and foundation walls.
4. Thermal Conductivity
While both EPS and XPS offer excellent thermal insulation properties, XPS tends to have a slightly lower thermal conductivity than EPS. This makes it a popular choice for applications where superior insulation performance is required.
5. Strength and Rigidity
XPS is known for its high compressive strength and rigidity, making it suitable for demanding applications where structural integrity is crucial. Its resistance to moisture and ability to maintain its physical properties over time make it a reliable choice for long-term insulation solutions.
Here’s a comparison table highlighting the main differences between Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) and Extruded Polystyrene (XPS):
| Aspect | Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) | Extruded Polystyrene (XPS) |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Beads expanded with steam | Polystyrene pellets extruded |
| Cell Structure | Closed-cell | Closed-cell |
| Density | Varies (lower density) | Higher density |
| Thermal Conductivity | Slightly higher | Slightly lower |
| Strength and Rigidity | Good compressive strength | High compressive strength |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Applications | Insulation, packaging, fill | Below-grade insulation, cold storage, architectural modeling |
This table provides a concise overview of the key differences between EPS and XPS, covering aspects such as manufacturing process, cell structure, density, thermal conductivity, strength, and applications.
Let’s delve deeper into the applications of Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) and Extruded Polystyrene (XPS), highlighting their respective uses in various industries and projects.
Applications of Expanded vs Extruded Polystyrene
Insulation:
EPS is widely used as insulation material for walls, roofs, and floors in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. Its lightweight nature and excellent thermal insulation properties make it an ideal choice for maintaining indoor comfort and energy efficiency.
Packaging:
EPS is commonly utilized as packaging material for fragile items such as electronics, appliances, and glassware. Its cushioning properties and shock-absorption capabilities help protect delicate goods during shipping and handling.
Lightweight Fill:
In construction projects, EPS serves as a lightweight fill material for applications such as road embankments, void fill, and landscaping. Its ease of handling and ability to conform to irregular shapes make it a versatile option for filling voids and providing structural support.
Floral and Craft Applications:
EPS foam is also used in floral arrangements and craft projects due to its lightweight and moldable properties. It can be easily shaped and carved to create intricate designs and decorative elements.
Extruded Polystyrene (XPS) Applications:
Below-Grade Insulation:
XPS is commonly employed as insulation for below-grade structures such as basements, foundation walls, and slabs. Its moisture resistance and high compressive strength make it well-suited for applications where exposure to moisture and soil pressure is a concern.
Cold Storage Facilities:
XPS insulation boards are used in cold storage facilities, refrigerated trucks, and freezer rooms to maintain temperature control and prevent heat transfer. Its superior thermal performance ensures energy efficiency and preserves the quality of perishable goods.
Architectural Modeling and Prototyping:
Due to its uniform density and smooth surface finish, XPS foam is favored by architects and designers for creating architectural models and prototypes. Its ease of shaping and carving allows for detailed representations of building designs and concepts.
Geotechnical Engineering Applications:
XPS is utilized in geotechnical engineering projects for applications such as soil stabilization, slope protection, and lightweight fill. Its high compressive strength and resistance to moisture make it suitable for challenging environmental conditions.
Expanded vs. Extruded Polystyrene Applications Comparison Table:
| Application | Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) | Extruded Polystyrene (XPS) |
|---|---|---|
| Insulation | Widely used for thermal insulation in walls, roofs, and floors. EPS boards are lightweight and easy to install. | Preferred for applications requiring high compressive strength and moisture resistance, such as below-grade insulation and roofing. XPS boards offer superior thermal performance. |
| Packaging | Commonly used for protective packaging due to its lightweight and shock-absorbing properties. EPS packaging provides excellent cushioning for fragile items during transit. | Suitable for packaging applications where moisture resistance and durability are essential. XPS foam offers better protection against moisture and compression. |
| Lightweight Fill Material | Used as fill material in construction projects to reduce weight and improve structural stability. EPS fill material is cost-effective and provides thermal insulation. | Ideal for lightweight fill applications where moisture resistance and long-term durability are required. XPS fill material offers superior compressive strength and stability. |
| Concrete Formwork | EPS panels are used as concrete formwork for casting walls, slabs, and columns. They offer thermal insulation and easy demolding properties. | XPS panels are preferred for concrete formwork in cold climates due to their superior thermal insulation and moisture resistance. They provide a smooth surface finish and excellent dimensional stability. |
| Road and Bridge Construction | EPS geofoam blocks are used as lightweight fill material in road embankments and bridge approaches. They reduce settlement and improve soil stability. | XPS insulation boards are used to insulate bridge decks and roads, preventing frost heave and reducing thermal expansion and contraction. They offer long-term durability and resistance to moisture and chemicals. |
| Floral and Decorative Arrangements | EPS foam blocks and shapes are used in floral arrangements and decorative displays. They are lightweight, easy to shape, and provide support for floral designs. | XPS foam sheets are suitable for creating floral arrangements and decorative props. They offer a smooth surface finish and can be painted or coated for custom designs. |
| Surfboards and Water Sports Equipment | EPS foam cores are used in surfboards, stand-up paddleboards, and kayaks due to their lightweight and buoyant properties. EPS boards provide excellent performance in water sports. | XPS foam sheets are used to create water sports equipment such as surfboards and bodyboards. They offer superior strength and durability, making them suitable for high-performance applications. |
| Stage and Set Design | EPS foam blocks and shapes are used in stage and set design for theater productions, film sets, and events. They are lightweight, easy to carve, and provide a versatile medium for creative designs. | XPS foam sheets are used in stage and set design to create props, backdrops, and scenery. They offer a smooth surface finish and can be painted or coated for custom finishes. |
| Floating Docks and Marine Structures | EPS foam blocks and pontoons are used to create floating docks, marinas, and marine structures. They provide buoyancy and stability in water environments. | XPS foam boards are used in floating docks and marine structures for their superior strength and resistance to moisture. XPS pontoons offer long-term durability and stability in marine applications. |
| Ice Chests and Coolers | EPS foam coolers are widely used for picnics, camping trips, and outdoor activities to keep food and beverages cold. They provide excellent insulation and lightweight portability. | XPS foam ice chests are preferred for outdoor activities and commercial use due to their superior insulation properties and durability. XPS coolers offer long-lasting ice retention and resistance to moisture. |
| Art and Craft Projects | EPS foam sheets and shapes are used in art and craft projects for sculpting, modeling, and crafting. They are easy to cut, shape, and decorate with paints or coatings. | XPS foam boards and blocks are suitable for art and craft projects requiring precision cutting and detailed sculpting. XPS foam offers a smooth surface finish for painting and decorating. |
| Soundproofing and Acoustic Insulation | EPS foam panels and tiles are used for soundproofing and acoustic insulation in recording studios, theaters, and home theaters. They absorb sound waves and reduce echo and reverberation. | XPS foam boards are used for soundproofing and acoustic insulation in residential and commercial buildings. XPS panels offer superior thermal insulation and noise reduction properties. |
| DIY Projects and Home Improvement | EPS foam boards and shapes are used in DIY projects and home improvement tasks such as insulation, molding, and crafting. They are easy to cut, shape, and install with basic tools. | XPS foam sheets and panels are suitable for DIY projects requiring insulation, flooring underlayment, or decorative finishes. XPS foam offers superior durability and moisture resistance for long-term performance. |
This table provides a concise comparison of the primary applications of expanded and extruded polystyrene, showcasing their versatility and suitability for various industries and projects.
Applications of Expanded vs Extruded Polystyrene
Let’s delve deeper into the applications of Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) and Extruded Polystyrene (XPS), highlighting their respective uses in various industries and projects:
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) Applications:
1. Insulation:
- EPS is widely utilized as an insulation material in construction for its exceptional thermal properties. It is commonly used in walls, roofs, and floors of both residential and commercial buildings to enhance energy efficiency and maintain comfortable indoor temperatures.
2. Packaging:
- EPS is a popular choice for packaging fragile items due to its lightweight and shock-absorbing qualities. It is often used to protect electronics, appliances, and delicate goods during shipping and transportation.
3. Lightweight Fill:
- In construction projects, EPS serves as a lightweight fill material for various applications. It is used to fill voids, create embankments, and provide structural support in areas where weight must be minimized, such as beneath roadways and behind retaining walls.
4. Floral and Craft Applications:
- Due to its versatility and ease of shaping, EPS foam is commonly used in floral arrangements and craft projects. Its lightweight nature makes it ideal for creating decorative elements, sculptures, and props for events and displays.
Extruded Polystyrene (XPS) Applications:
1. Below-Grade Insulation:
- XPS is often chosen for insulation in below-grade applications, such as basements, foundation walls, and slab-on-grade construction. Its closed-cell structure and moisture resistance make it well-suited for environments where exposure to groundwater or moisture is a concern.
2. Cold Storage Facilities:
- XPS insulation boards are commonly used in cold storage facilities, refrigerated trucks, and freezer rooms to maintain temperature control and prevent heat transfer. Its superior thermal performance helps preserve the freshness and quality of perishable goods.
3. Architectural Modeling and Prototyping:
- Architects and designers favor XPS foam for creating detailed architectural models and prototypes. Its uniform density and smooth surface finish allow for precise carving and shaping, making it an ideal material for visualizing building designs and concepts.
4. Geotechnical Engineering Applications:
- XPS is utilized in various geotechnical engineering projects for applications such as soil stabilization, slope protection, and lightweight fill. Its high compressive strength and resistance to moisture make it suitable for use in challenging environmental conditions.
Cost Comparison of Expanded vs Extruded Polystyrene
Cost of Expanded Polystyrene
The cost of EPS varies depending on factors such as density, thickness, and quantity. Generally, EPS is a cost-effective insulation solution compared to other materials, making it a popular choice for both residential and commercial projects.
Cost of Extruded Polystyrene
XPS tends to be slightly more expensive than EPS due to its higher manufacturing costs and superior properties. However, its long-term durability and performance justify the initial investment for many applications.
The main differences between Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) and Extruded Polystyrene (XPS) lie in their manufacturing processes, cell structures, densities, thermal conductivities, and applications.
- Manufacturing Process:
- EPS is produced by expanding polystyrene beads using steam, resulting in a lightweight material with a closed-cell structure.
- XPS, on the other hand, is manufactured through an extrusion process where polystyrene pellets are melted and formed into rigid boards with a more uniform and dense cell structure.
- Cell Structure:
- EPS has a closed-cell structure consisting of small, interconnected bubbles, providing excellent insulation properties and buoyancy.
- XPS has a more uniform and compact cell structure, enhancing its strength, durability, and moisture resistance.
- Density:
- EPS comes in varying densities depending on the application, with lower density EPS being used for packaging and higher density EPS for insulation purposes.
- XPS typically has a higher density compared to EPS, giving it increased strength and resistance to compression.
- Thermal Conductivity:
- Both EPS and XPS offer excellent thermal insulation properties, but XPS tends to have slightly lower thermal conductivity, making it ideal for applications where superior insulation performance is required.
- Strength and Rigidity:
- EPS is lightweight but offers sufficient strength and rigidity for many applications, with good compressive strength.
- XPS is known for its high compressive strength and rigidity, making it suitable for demanding applications where structural integrity is crucial, such as below-grade insulation.
- Applications:
- EPS is commonly used in insulation for walls, roofs, and floors, as packaging material, and in lightweight fill applications.
- XPS finds applications in below-grade insulation, cold storage facilities, architectural modeling, and geotechnical engineering due to its superior moisture resistance and strength.
FAQs
What is Expanded Polystyrene?
Expanded polystyrene (EPS) is a lightweight, rigid plastic foam insulation material produced from solid beads of polystyrene.
What is Extruded Polystyrene?
Extruded polystyrene (XPS) is a dense, closed-cell foam insulation material manufactured through an extrusion process, resulting in a uniform and rigid board.
Which is better, expanded or extruded polystyrene?
The choice between EPS and XPS depends on specific project requirements and budget constraints. Both materials offer excellent insulation properties, with EPS being more cost-effective and XPS offering superior strength and moisture resistance.
Is expanded polystyrene recyclable?
Yes, expanded polystyrene is recyclable and can be reused in various applications, including insulation, packaging, and construction.
Is extruded polystyrene better for insulation?
Extruded polystyrene offers superior strength, moisture resistance, and thermal performance compared to expanded polystyrene, making it a preferred choice for below-grade insulation applications.
How does the cost of expanded and extruded polystyrene compare?
While expanded polystyrene is generally more cost-effective than extruded polystyrene, the latter offers enhanced durability and performance, justifying its higher initial cost for certain applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the differences between expanded and extruded polystyrene is essential for selecting the right insulation material for your project. While both offer excellent thermal insulation properties, they vary in terms of density, strength, and cost.
Whether you opt for expanded or extruded polystyrene depends on factors such as project requirements, budget, and environmental considerations.
