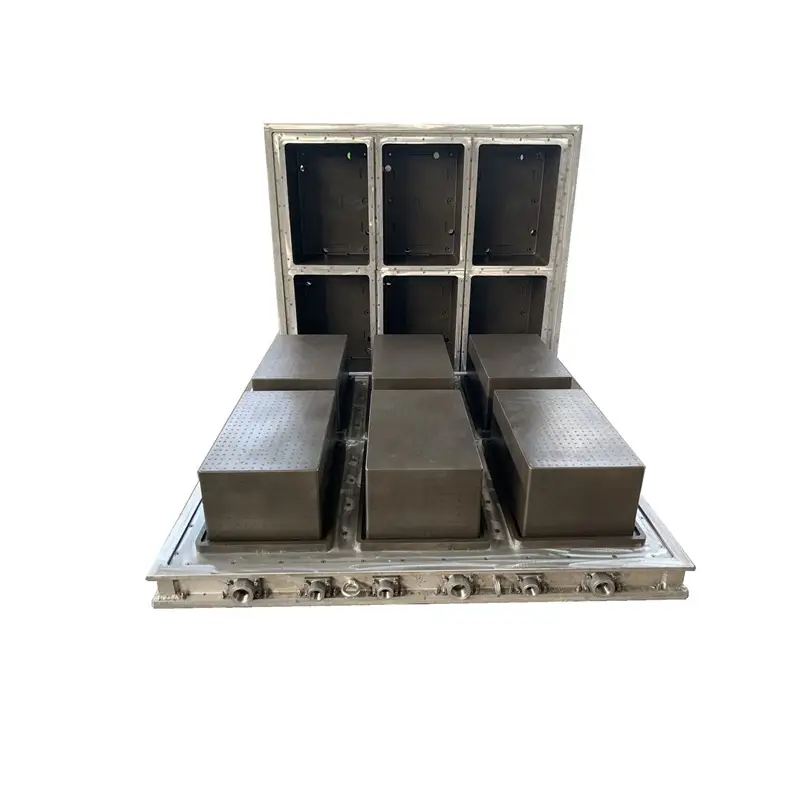
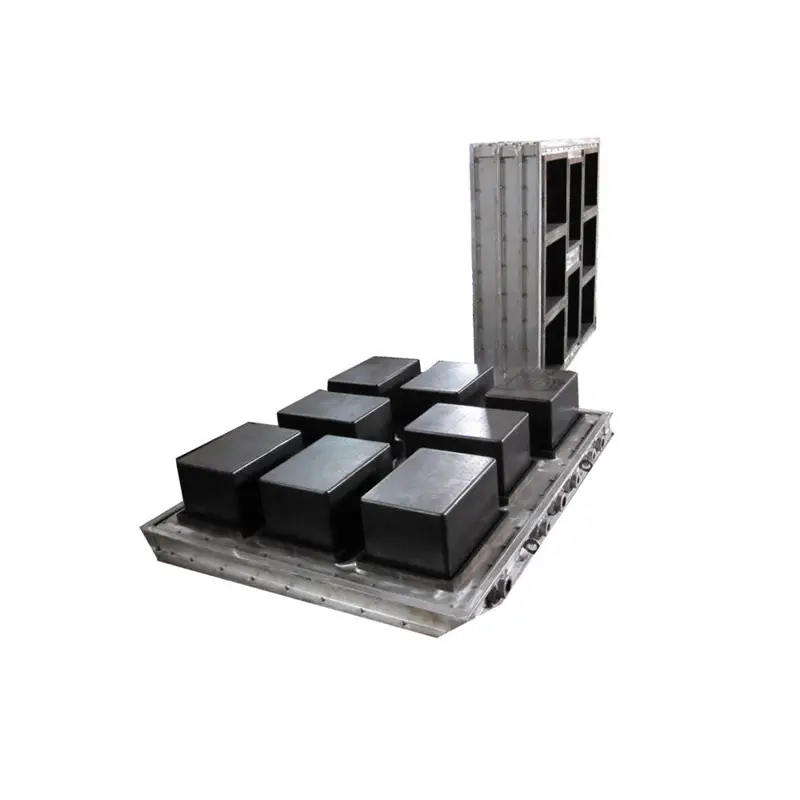
EPS Mold: Your One-Stop Custom EPS Mold Solutions
We specialize in high-precision Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) molds for all your packaging, construction, and design needs. Our expert engineering ensures durability, lightweight efficiency, and exact specifications for every project. From custom complex shapes to high-volume production, trust us for superior EPS molding solutions. Partner with us for reliable quality and fast turnaround times to bring your innovative products to life.
Our EPS Mold
Engineered Impact Resistance: The foam’s closed-cell structure excels at absorbing and dissipating energy from shocks and drops, offering superior cushioning protection for even the most fragile electronic or sensitive components during rough handling and transport.
Exceptional Lightweight Advantage: Composed of about 98% air, EPS dramatically reduces overall shipping weight, directly translating into significant savings on transportation fuel costs and lower overall logistics expenses for your business.
Unlimited Design Versatility: Our molds can capture extremely intricate and precise custom geometries, allowing us to create complex, nest-like protective packaging or unique architectural shapes perfectly contoured to your specific product needs.
Superior Thermal Insulation: The material inherently resists heat transfer, making it an ideal choice for cold chain logistics or any application requiring consistent temperature control to keep contents fresh or protected from heat fluctuations.
Cost-Effective, High-Volume Production: The molding process is efficient and rapid, enabling high-speed manufacturing of identical parts while using a relatively low-cost raw material, ensuring excellent value for your large production runs.
Various EPS Molds
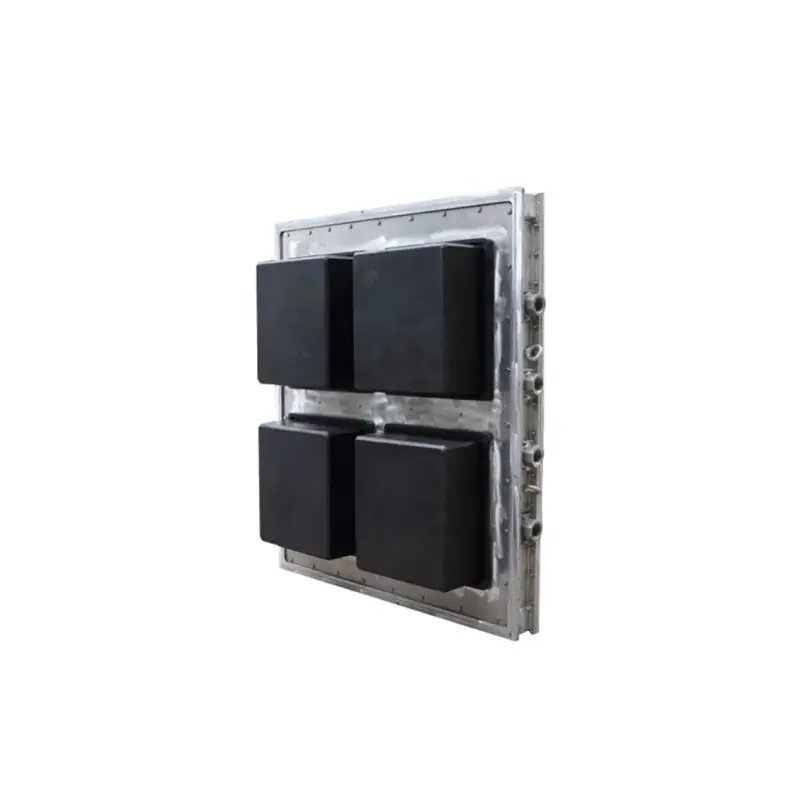

Designed to create fish boxes with specific dimensions and features like drainage holes and lid compartments. These molds ensure consistent product quality and optimize storage space.
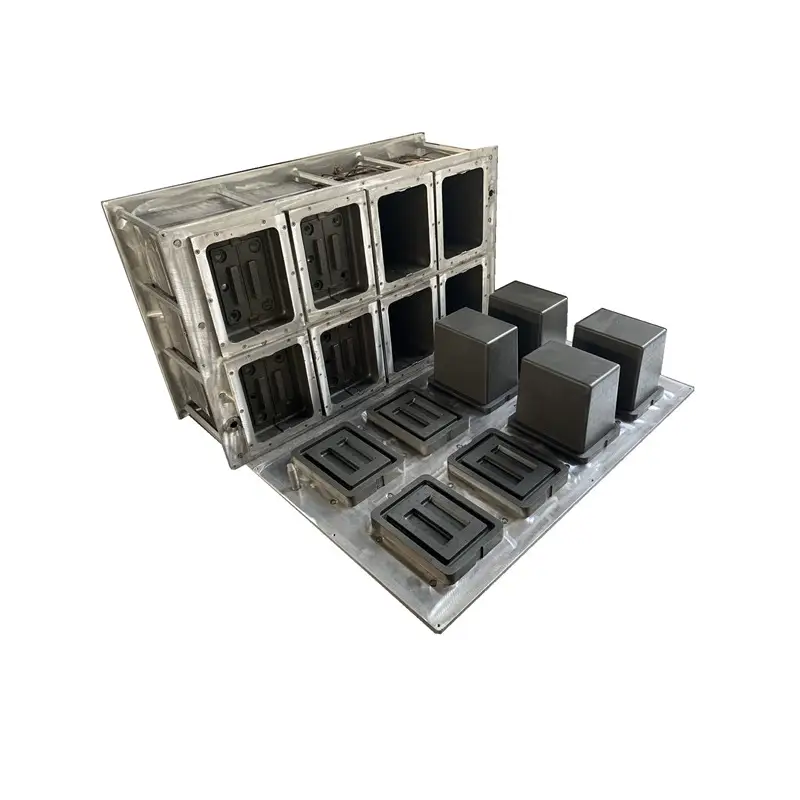

EPS Ice Mold
Used to produce ice in various shapes and sizes, EPS ice molds are commonly employed in commercial ice production. The mold design can incorporate different cavity shapes, such as cubes, spheres, or blocks. The material’s insulation properties help maintain ice quality for extended periods.
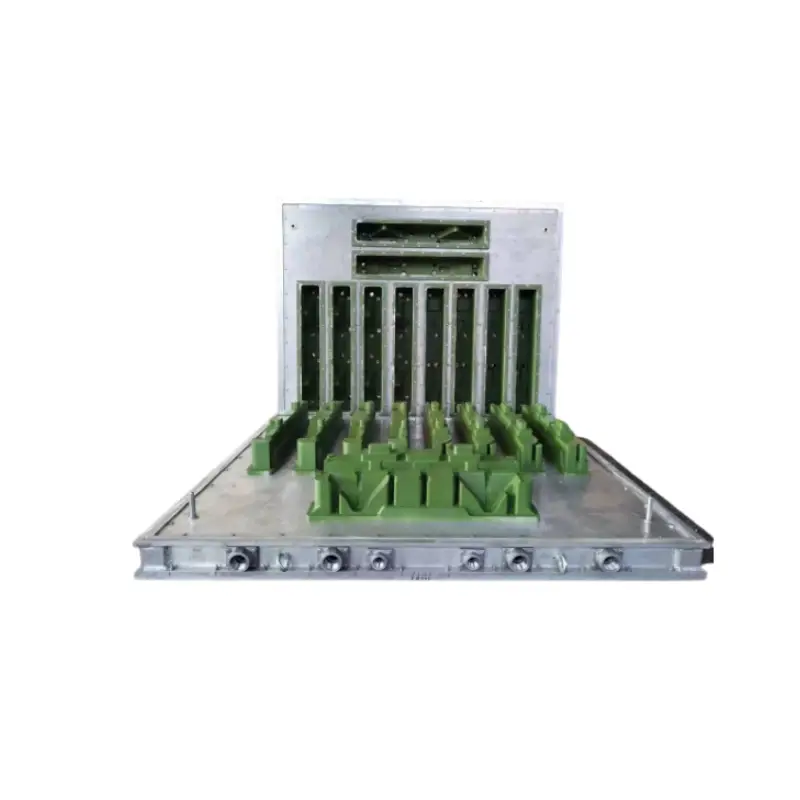

EPS Packaging Mold
EPS packaging molds are highly versatile and used to create custom packaging solutions for a wide range of products. These molds can be designed to protect fragile items, provide shock absorption, and optimize product presentation. They often feature interlocking designs for secure stacking.
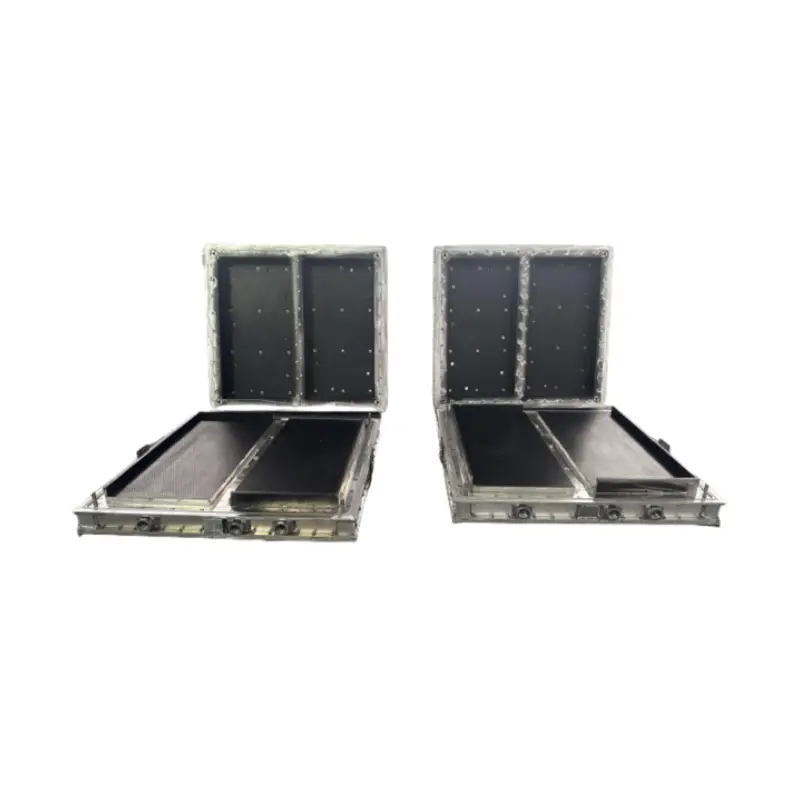

EPS Insulation Panel Mold
EPS insulation panel molds are used to produce panels for building insulation. These molds create panels with precise dimensions and interlocking edges for efficient installation. The mold design often incorporates features like tongue-and-groove profiles for improved insulation performance.
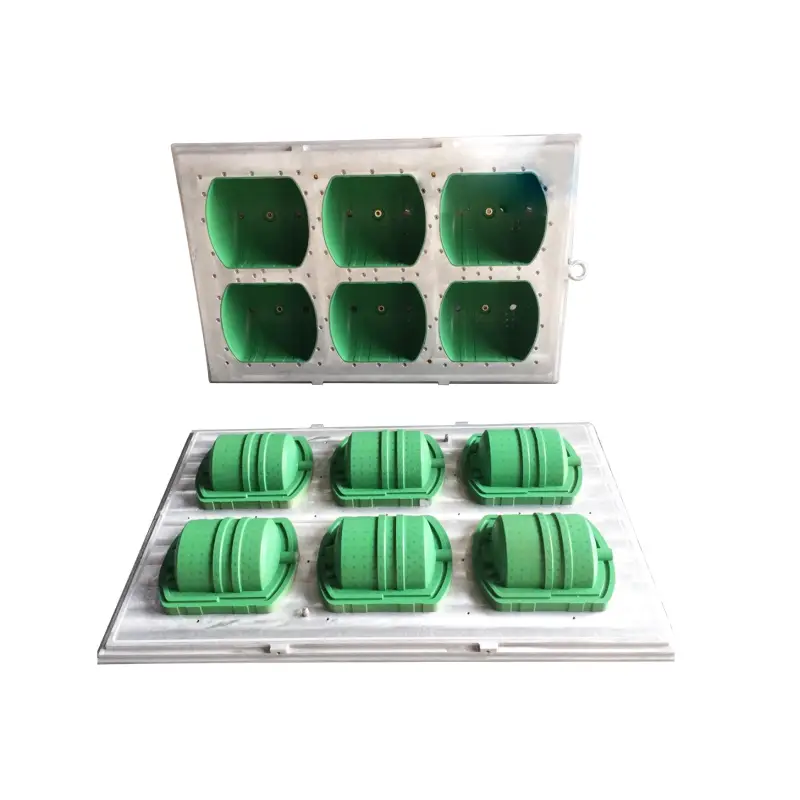

EPS Fruit Foam Mold
Designed for transporting and storing fresh seafood, EPS fish box molds incorporate drainage holes, lid compartments, and insulation. Customization options include size, shape, and additional features like ice compartments.
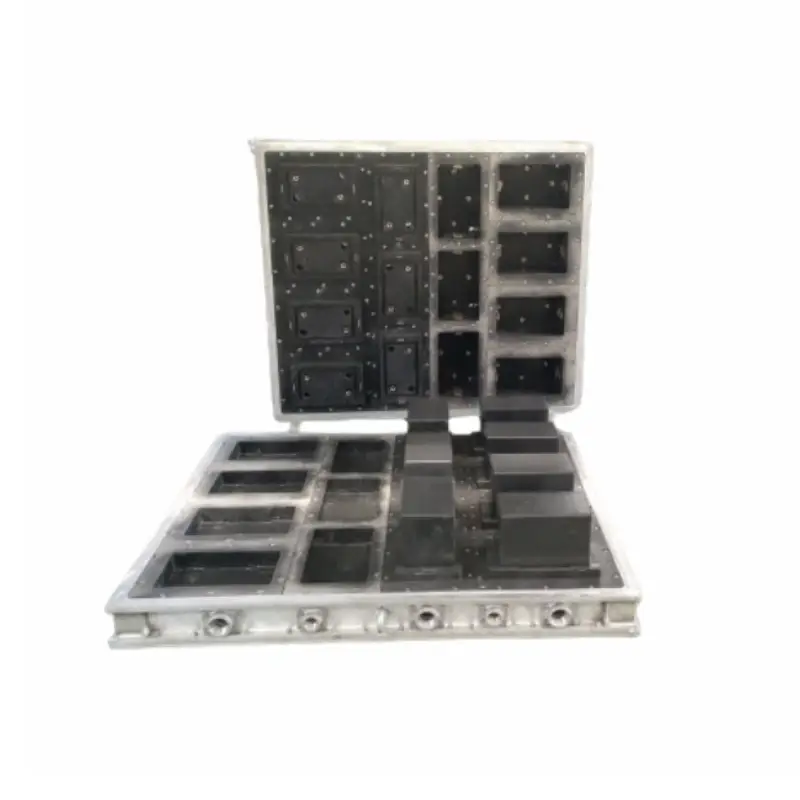

EPS Cooler Mold
Producing coolers in various sizes and shapes, these molds incorporate handles, latches, and insulation compartments. Customization options include cooler capacity and additional features.
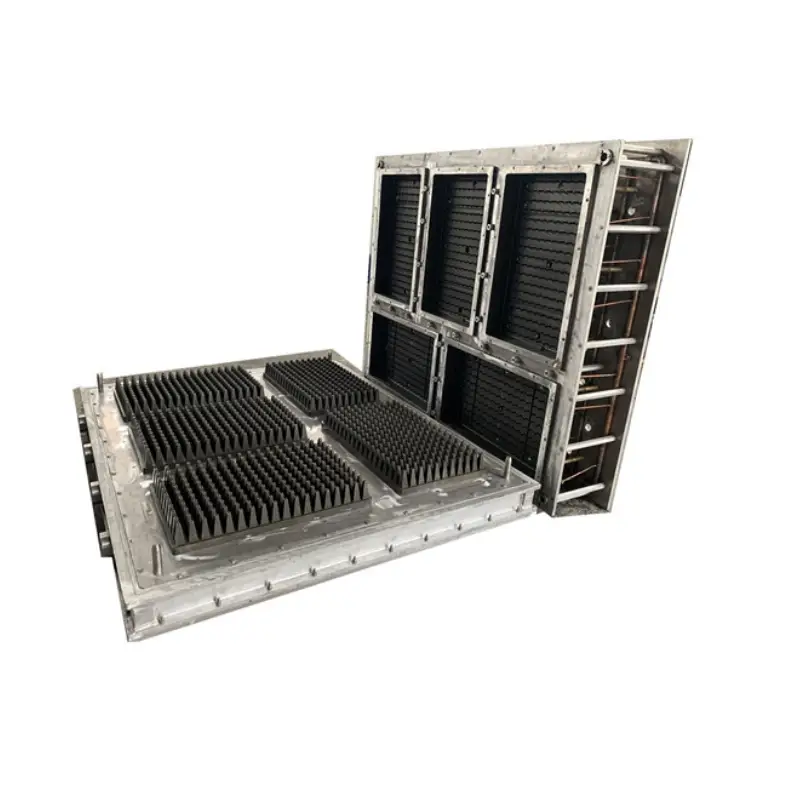

EPS Seed Tray Mold
An EPS seed tray mold is a specialized tool used to create the plastic trays with individual compartments that are commonly used for starting seeds indoors. Made from expanded polystyrene (EPS), these trays provide a lightweight, durable, and insulating environment for seedling growth.
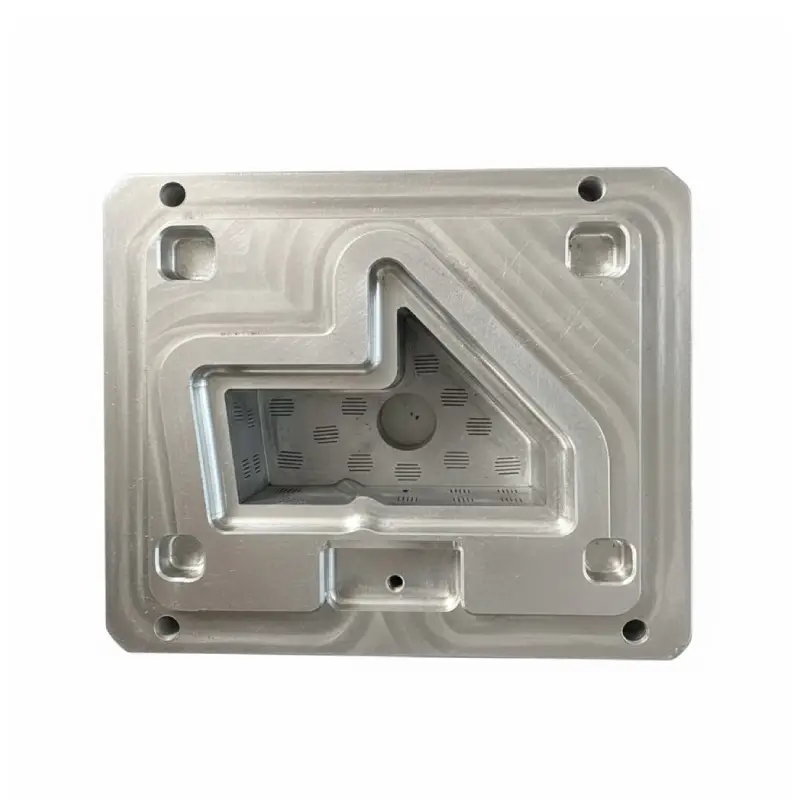

EPS Injection mold
We offer EPS Injection Molds that deliver high-precision, customized foam components rapidly. This advanced process ensures excellent dimensional accuracy and robust impact protection for sensitive products in packaging or construction. Benefit from our expertise in high-volume, cost-effective production runs, providing the lightweight yet durable EPS solutions your clients demand efficiently.
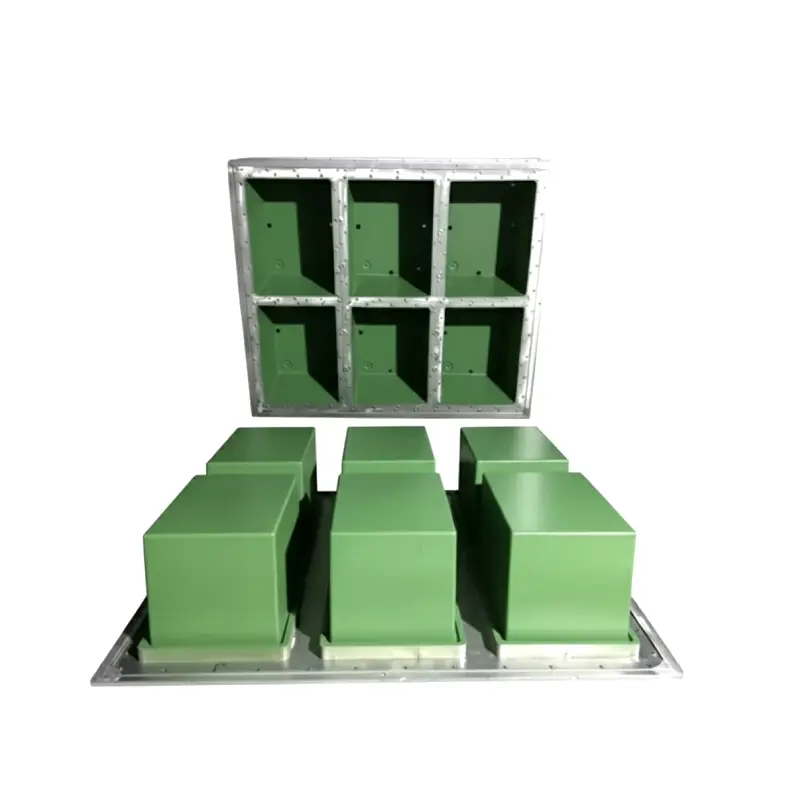

EPS shape box Mold
We offer customizable EPS shape box molds made from durable materials like aluminum. These molds precisely shape Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) beads into required box forms for packaging (like fish boxes, fruit/veg packaging) or insulation. They ensure lightweight, and shock-resistant final products through an efficient steam molding process.
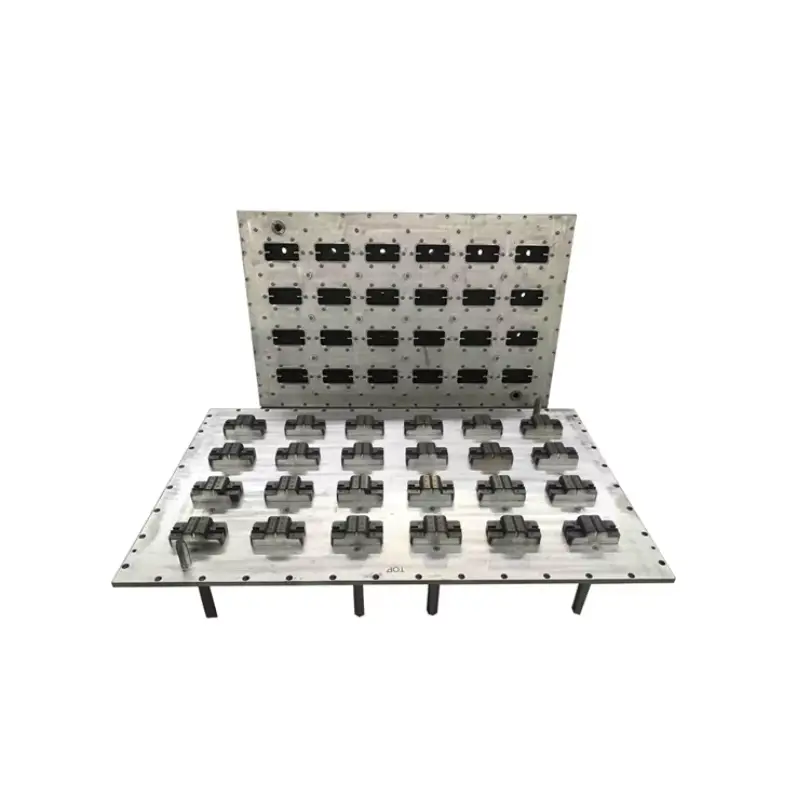

EPS fruit box Mold
We design and manufacture Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) fruit box molds. Our precision-engineered molds ensure consistent, lightweight, and durable protective packaging for all your produce. Fast tooling and competitive pricing guaranteed. Optimize your fruit transportation and presentation today!
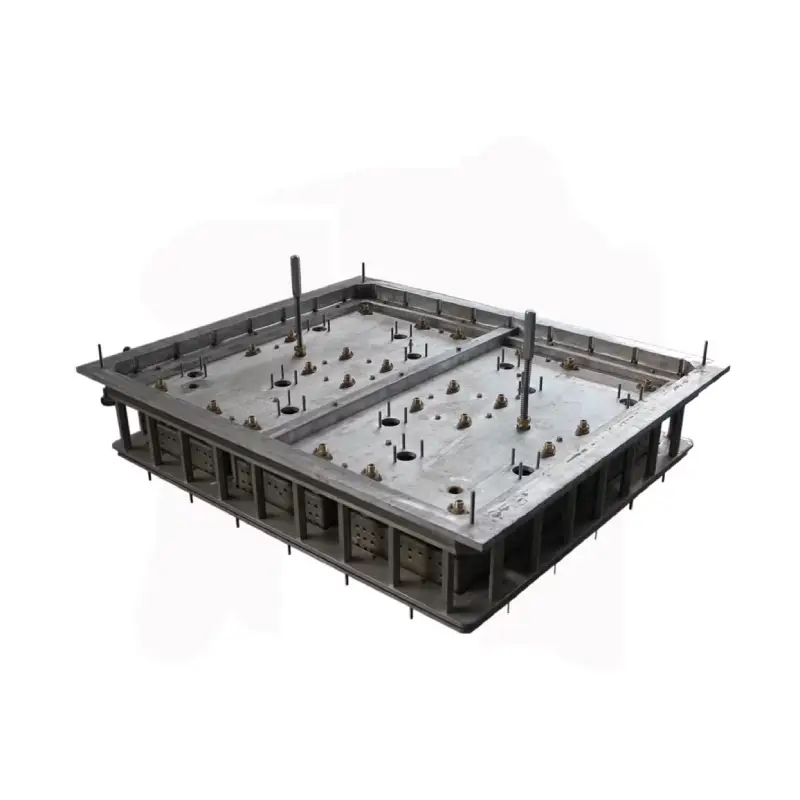

EPS packaging Mold
We offer custom EPS packaging molds engineered for precision and protection. Our services include design, tooling fabrication, and high-volume production of lightweight, impact-resistant expanded polystyrene forms. We ensure tight tolerance for delicate electronics, medical devices, or industrial parts, maximizing product safety and minimizing shipping costs.
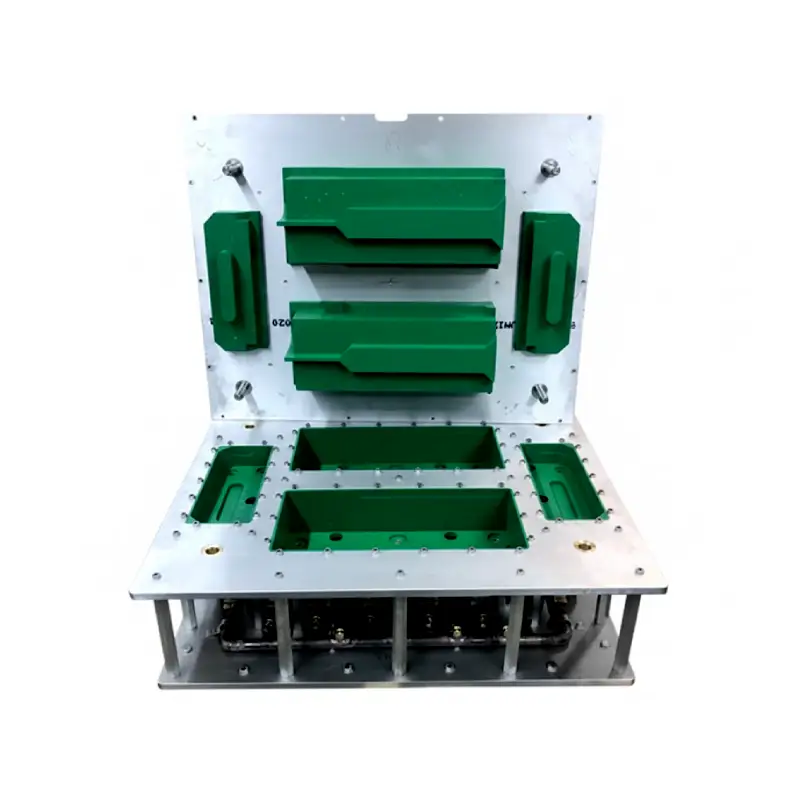

EPS EPP shape mold
We offer custom-engineered EPS and EPP shape molds, providing durable and precise tooling for producing expanded foam products. Our molds are manufactured from robust aluminum alloys to ensure fast heat transfer and exceptional longevity under repeated use. We provide these molds to support the efficient and consistent production of packaging, automotive parts, and construction components.
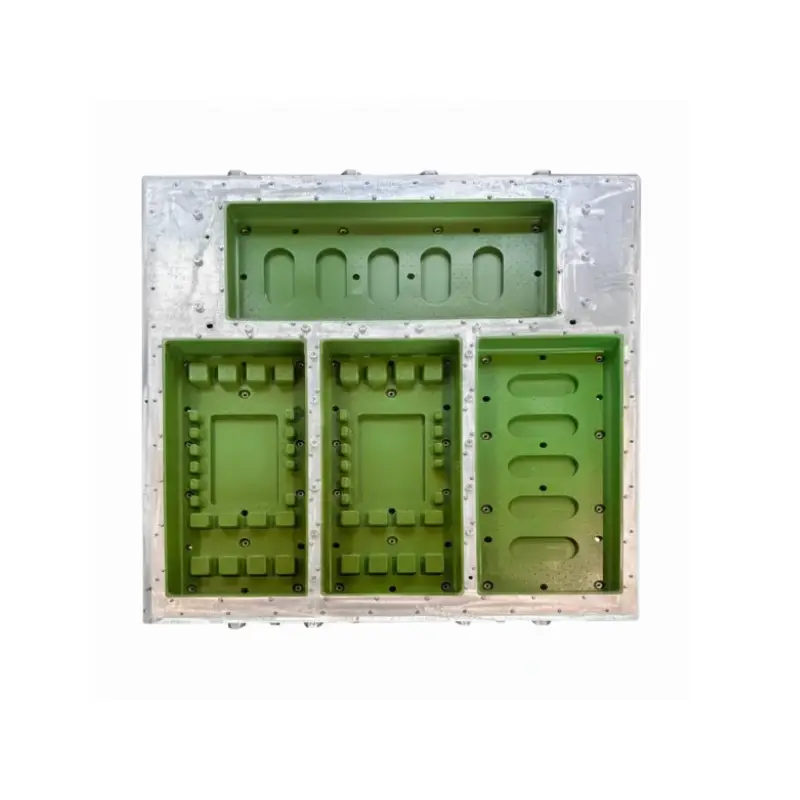

custom EPS product shape molds
We offer custom-designed EPS product shape molds, meticulously engineered to match your precise specifications for packaging, insulation, or technical components. Our tooling is built from durable aluminum, ensuring optimal steam distribution and rapid cooling for efficient, repeatable production cycles. We provide these molds to guarantee the perfect shape and finish for your expanded polystyrene items every time.
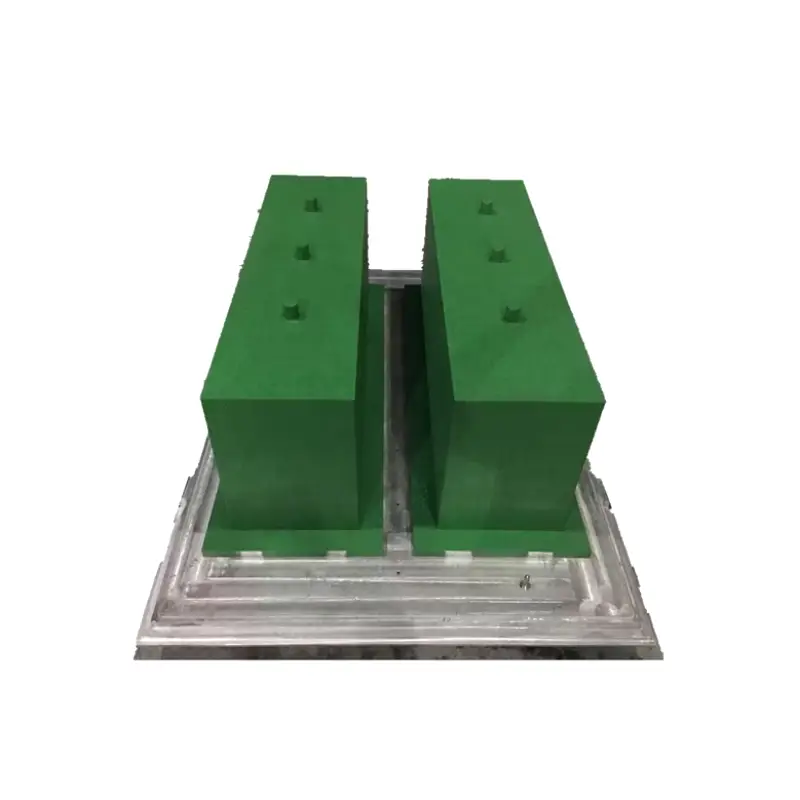
EPS mould for lost foam casting mold
We offer precision-engineered EPS molds for the lost foam casting process, creating accurate and highly detailed foam patterns. Our molds are designed for exceptional durability and reliable mass production, ensuring the foam patterns burn away cleanly without leaving residue. We provide this tooling to enable foundries to cast complex metal components with superior surface finish and minimal machining requirements.
FAQs about EPS Mold
What is EPS Mold?
An EPS mold is a specialized tool used to shape expanded polystyrene (EPS) beads into various products. It’s essentially a container that gives the molten EPS its final form.
how does EPS mold work?
An EPS mold is a specialized tool used to shape expanded polystyrene (EPS) beads into various products. It’s essentially a container that gives the molten EPS its final form.
How to mould EPS?
Molding EPS is a complex process requiring specialized equipment and expertise.
Here’s a simplified overview:
1. Mold Preparation
- Design: Create a detailed mold design based on the desired product.
- Mold Construction: Build the mold using materials like aluminum or steel, ensuring precision and durability.
- Mold Assembly: Prepare the mold for the molding process, including closing mechanisms and cooling systems.
2. EPS Bead Preparation
- Pre-expansion: Expand polystyrene beads to a specific size.
- Drying: Remove moisture from the beads.
3. Mold Filling
- Bead Injection: Fill the mold cavity with pre-expanded EPS beads.
4. Molding Process
- Heating: Apply heat to the mold, causing the EPS beads to expand and fuse together.
- Pressurization: Apply pressure to the mold to compress the EPS and achieve desired density.
- Cooling: Cool the mold to solidify the EPS foam.
5. Demolding
- Opening: Carefully open the mold.
- Removal: Extract the molded product.
- Trimming: Remove any excess material.
Additional Considerations:
- Molding Equipment: Industrial-grade machines are required for efficient and consistent molding.
- Temperature and Pressure Control: Precise control is essential for optimal results.
- Mold Material: The choice of mold material affects product quality and mold lifespan.
- EPS Bead Quality: Consistent bead size and density are crucial for uniform results.
It’s important to note that this is a simplified explanation. The actual process involves intricate machinery, precise temperature and pressure control, and specialized knowledge.
Is EPS mold resistant?
EPS (Expanded Polystyrene) molds themselves are not inherently resistant; they are a tool typically made of aluminum used to shape and form EPS foam products.
However, the resulting EPS foam products are generally considered moisture-resistant but not entirely waterproof or mold-proof.
We manufacture molds with precision cooling channels to produce EPS foam that has a closed-cell structure, which minimizes water absorption and therefore significantly inhibits the growth of mold and mildew on the material’s surface, making it suitable for construction and insulation where moisture is a concern.
What is EPS molding process?
This EPS molding process is essential for producing insulation, packaging, and custom components with precise dimensions. We focus on optimizing each step, from bead expansion to final cooling, to ensure low cycle times and consistent product integrity in every batch we manufacture.
-
Pre-Expansion of Raw Material: We start by heating raw EPS resin beads using steam, which causes the material to soften and the trapped foaming agent to expand. This step is precisely controlled to achieve the target density for the final product. The resulting expanded beads are then aged in silos to allow for stabilization and preparation for the final molding phase.
-
Molding and Shaping: We inject the stabilized pre-expanded beads into our custom-engineered aluminum molds. Steam is then introduced again to fuse the beads together, forcing them to take the exact shape of the mold cavity under pressure. This stage dictates the final dimensions and structural performance of the EPS product.
-
Cooling and Ejection: We quickly cool the mold using water circulated through the integrated channels within the aluminum tooling. Cooling solidifies the fused EPS structure, locking in the final shape and size. Once cooled, the finished EPS product is carefully ejected from the mold, ready for post-processing and packaging.
-
Trimming and Post-Processing: We perform any necessary final steps, such as trimming excess flash or adding features like holes and grooves using specialized cutting tools. This ensures every piece meets the tight tolerances required by the client. The resulting EPS products are then checked for dimensional accuracy and surface finish before shipment.

