EPP (Expanded Polypropylene) is a versatile closed-cell bead foam known for its unique combination of properties. This lightweight yet robust material boasts excellent energy absorption, chemical resistance, and thermal insulation.
From automotive components ensuring safety to packaging protecting delicate goods and even sporting equipment enhancing performance, EPP’s adaptability makes it a valuable material across diverse industries. Let’s explore its benefits and wide-ranging applications.
What is EPP Material

Definition and Composition
Expanded Polypropylene (EPP) is a type of foam made from polypropylene, a thermoplastic polymer known for its toughness and flexibility. EPP foam is created by expanding polypropylene beads with steam, resulting in a lightweight, closed-cell structure that provides excellent shock absorption and insulation.
History and Development
EPP was developed in the 1980s and has since gained popularity due to its superior properties compared to other foams. Initially used in the automotive industry for impact protection, its applications have expanded into packaging, consumer goods, and more.
EPP Material Foam Properties
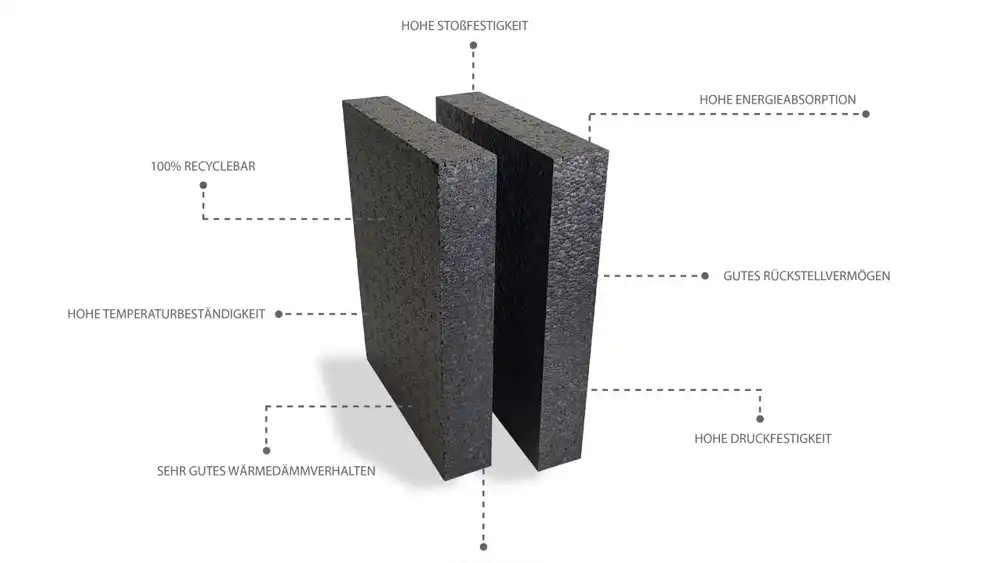
Expanded Polypropylene (EPP) foam is renowned for its unique combination of properties that make it suitable for a wide range of applications. Here’s an in-depth look at its physical and chemical properties:
Physical Properties
Density:
EPP foam has a variable density range, typically from 20 to 200 grams per liter. This flexibility allows it to be tailored for specific applications, balancing weight and strength requirements.
Flexibility:
EPP foam is highly resilient, capable of absorbing impacts and returning to its original shape without permanent deformation. This makes it ideal for applications requiring repeated use and durability.
Temperature Resistance:
EPP maintains its structural integrity across a wide temperature range, from -40°C to 130°C. This property is crucial for applications in environments with fluctuating temperatures or extreme conditions.
Water Resistance:
The closed-cell structure of EPP foam makes it highly resistant to water absorption. This characteristic is particularly beneficial for applications exposed to moisture, as it prevents degradation and maintains performance.
Lightweight:
One of the standout features of EPP is its lightweight nature. Despite being light, it does not compromise on strength, which is essential for reducing overall weight in automotive and packaging applications without sacrificing durability.
EPP Material Chemical Properties
Chemical Inertness:
EPP is chemically inert, meaning it does not react with most chemicals, including acids, bases, and solvents. This resistance makes it suitable for use in chemically aggressive environments.
Resistance to Oils and Greases:
EPP foam is resistant to oils and greases, which is advantageous in automotive and industrial applications where contact with these substances is common.
Non-Toxic and Biocompatible:
EPP is non-toxic and biocompatible, making it safe for use in medical applications, food packaging, and consumer products. It does not release harmful substances, ensuring safety in sensitive environments.
EPP Material Applications

EPP’s remarkable versatility allows it to excel in numerous applications across diverse industries, leveraging its unique blend of properties. Let’s delve into some key sectors where EPP makes a significant impact.
Automotive Industry
EPP plays a crucial role in enhancing safety and efficiency within the automotive sector. Its application in bumper cores provides significant impact absorption during collisions. Interior safety components, such as headrests and door panels, utilize EPP’s energy-absorbing capabilities to protect occupants. Furthermore, its lightweight nature contributes to overall vehicle weight reduction, leading to improved fuel efficiency and1 lower emissions. EPP’s durability also ensures the longevity of these automotive parts, making it a reliable material choice.
Packaging Industry
The packaging industry benefits significantly from EPP’s exceptional protective qualities. Its closed-cell structure offers superior cushioning and shock absorption, making it ideal for safeguarding fragile and sensitive goods during transit. Delicate electronics, medical devices, and other high-value items are often packaged using custom-molded EPP to minimize the risk of damage. Moreover, EPP is a recyclable material, aligning with the growing demand for sustainable packaging solutions and reducing environmental impact.
Consumer Goods
In the realm of consumer goods, EPP’s lightweight yet durable nature makes it a popular choice for a wide array of products. Sports equipment, such as helmets and protective padding, utilizes EPP’s impact resistance to enhance safety and performance. Toys made from EPP are often lightweight, safe for children, and durable enough to withstand rough play. Even furniture components can benefit from EPP’s structural integrity and comfort. Its versatility allows manufacturers to create innovative and long-lasting consumer products.
Medical Industry
The medical industry leverages EPP’s biocompatibility and ease of sterilization for various critical applications. Orthotic supports and prosthetics often incorporate EPP for its lightweight comfort and cushioning properties. Protective packaging for sensitive medical instruments ensures their sterility and prevents damage during transportation and storage. Additionally, EPP can be found as a component in certain medical devices, where its inert nature and durability are essential for patient safety and device functionality.
EPP Material Benefits

EPP material offers a compelling array of benefits that contribute to its widespread adoption across various industries. Its unique characteristics provide significant advantages in terms of performance, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness.
Durability
A key advantage of EPP is its exceptional durability. Unlike some other foam materials, EPP can endure repeated stresses and impacts without undergoing significant deformation or losing its inherent properties. This resilience makes it an ideal material for applications where long-term performance and resistance to wear and tear are critical, such as in automotive safety components and reusable packaging solutions.
Lightweight
EPP’s low density translates directly into its lightweight nature. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in industries like automotive and packaging, where minimizing weight is crucial. In vehicles, lighter components contribute to improved fuel efficiency and handling. In packaging, reduced weight can lead to lower shipping costs and easier handling. This combination of strength and lightness makes EPP a highly efficient material.
Environmental Impact
EPP offers notable environmental advantages. It is a recyclable material, allowing for the reuse of production scraps and end-of-life products, thus reducing landfill waste. Furthermore, the inherent durability of EPP often translates to a longer product lifespan. This extended usability minimizes the need for frequent replacements, further reducing resource consumption and waste generation, making EPP a more sustainable material choice compared to less durable alternatives.
EPP vs EPS (Expanded Polystyrene)
While both EPP (Expanded Polypropylene) and EPS (Expanded Polystyrene) are closed-cell foam materials with applications in packaging, insulation, and safety gear, they possess distinct characteristics.
EPP stands out for its superior durability and ability to withstand repeated impacts, readily springing back to its original shape, unlike the more brittle EPS which can be permanently dented. This elasticity makes EPP suitable for reusable applications and demanding environments.
Furthermore, EPP generally offers better chemical resistance and can withstand higher temperatures, even being microwaveable in some food container applications, a property EPS lacks. While EPS is often more cost-effective for high-volume, single-use applications due to lower initial costs, EPP’s long-term durability and reusability can offset its higher upfront price in many scenarios.
Key differences between EPP and EPS include:
- Applications: Both are used in packaging and insulation, but EPP’s resilience makes it ideal for automotive parts and reusable containers, while EPS is common in protective packaging and insulation where high volume and lower cost are primary concerns.
- Durability: EPP is more elastic and impact-resistant, returning to its original shape. EPS is more brittle and prone to permanent damage.
- Temperature Resistance: EPP generally has a higher temperature resistance compared to EPS.
- Chemical Resistance: EPP typically exhibits better resistance to various chemicals.
- Cost: EPS is often more cost-effective for large volumes, while EPP’s durability can be more economical long-term for reusable applications.
EPE vs EPP
While both EPP (Expanded Polypropylene) and EPE (Expanded Polyethylene) are closed-cell foam materials, they differ significantly in their properties and ideal applications. EPP excels in energy absorption and retains its shape after impact, offering superior durability and making it suitable for reusable packaging and structural automotive parts.
In contrast, EPE is softer, more flexible, and known for its excellent cushioning properties and smooth, non-abrasive surface, which is gentle on delicate items. EPE is often favored for surface protection and lightweight packaging where repeated impacts are less of a concern. While both are lightweight and offer some level of insulation, EPP generally boasts better chemical and higher temperature resistance compared to EPE.
The choice between the two often comes down to the specific requirements of the application, with EPP prioritized for impact resistance and longevity, and EPE for cushioning and surface protection.
Key differences include:
- Applications: EPP is commonly used in automotive (bumpers, headrests), reusable packaging, and sports equipment where impact resistance is key. EPE is prevalent in protective packaging for electronics, surface protection, and thermal insulation where cushioning and flexibility are prioritized.
- Durability: EPP is significantly more rigid and offers superior impact resistance and shape recovery compared to the softer and more flexible EPE.
- Cushioning: EPE provides excellent cushioning and surface protection due to its softer nature.
- Chemical Resistance: EPP generally has better resistance to oils and chemicals.
- Temperature Resistance: EPP typically withstands higher temperatures than EPE.
- Surface Properties: EPE has a smoother, non-abrasive surface, making it ideal for protecting delicate finishes.
Conclusion
In summary, EPP stands out as a highly versatile material, offering a unique combination of durability, lightweight properties, and environmental benefits. Its ability to absorb impact, resist chemicals, and provide insulation makes it invaluable across diverse sectors, from enhancing automotive safety to protecting sensitive goods and improving consumer products.
The comparison with other foam materials like EPS and EPE further highlights EPP’s specific strengths, particularly its resilience and suitability for demanding and reusable applications. While each material has its niche, EPP’s long-term performance and sustainability often make it a compelling choice for various engineering and packaging needs.
Ready to leverage the exceptional properties of EPP for your business? Contact us today to explore our wholesale options and discover how our high-quality EPP material can enhance your products and applications.
How is EPP different From Other Foams?
EPP distinguishes itself from other foam materials primarily through its exceptional resilience and energy absorption capabilities. Unlike more brittle foams like EPS (Expanded Polystyrene), EPP can withstand repeated impacts and compression without permanent deformation, consistently returning to its original shape.
This “memory” characteristic makes it ideal for applications requiring durability and repeated use, such as automotive bumpers and reusable packaging. Compared to softer foams like EPE (Expanded Polyethylene), EPP offers greater rigidity and structural integrity, providing better support and impact protection.
Is EPP Environmentally friendly?
Yes, EPP is generally considered an environmentally friendly material, especially when its entire lifecycle is taken into account. A significant factor is its 100% recyclability; EPP can be reprocessed into new products, effectively closing the loop in a circular economy.
Its durability also plays a crucial role in reducing environmental impact, as products made from EPP have a longer lifespan, minimizing the need for frequent replacements and thus reducing raw material consumption and waste generation.
EPP’s lightweight nature contributes to fuel efficiency in transportation (e.g., in automotive parts or packaging), leading to lower emissions. Its production often requires less energy compared to some other materials, and it’s free from harmful blowing agents, further enhancing its eco-credentials.
Is EPP Foam Toxic?
EPP foam is generally considered non-toxic in its finished state. It is made from polypropylene, a material widely used in food packaging and other applications where it comes into contact with humans.
EPP is free from CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons) and other harmful blowing agents used in the production of some other foams. Safety Data Sheets for EPP material typically indicate that it is non-hazardous under normal conditions of use and handling, with low potential for skin or eye irritation. While the raw materials and processing might involve some chemicals, the final EPP product is stable and does not readily release toxic substances.
