Have you ever stopped to think about how your building gets its heat? Or how electricity is generated? The answer to both of these questions might involve a fascinating device called a steam boiler.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the world of steam boilers, explaining what they are, how they work, and the important role they play in our everyday lives. So, whether you’re a homeowner, a facility manager, or simply curious about how things work, keep reading to learn about steam boilers!
What is Steam Boiler
A steam boiler is a closed vessel that heats water to produce steam. The steam can then be used for a variety of purposes, including heating buildings, generating electricity, and powering industrial processes.
Steam Boiler Types
In the industry of steam boilers, two main designs reign supreme: firetube and watertube boilers. Each has its own strengths and applications, making them suitable for different needs. Let’s fire up our knowledge and explore these fascinating machines:
1. Firetube Boilers:
Imagine a metal shell with water inside. Now, picture hot combustion gases whooshing through tubes that snake through this water bath. That’s the essence of a firetube boiler. Here’s a closer look:
- Construction: The water chamber is the main body, and the firetubes (usually horizontal or vertical) run through it. The hot gases from burning fuel travel through these tubes, transferring heat to the surrounding water.
- Pros: These boilers are simpler in design, making them generally less expensive to purchase and maintain. They’re also compact and work well for smaller applications.
- Cons: Firetube boilers are limited in steam pressure they can produce due to the size constraints of the main shell. Additionally, they have a larger water volume, which means slower start-up times.
- Applications: Firetube boilers are ideal for low to medium-pressure steam needs, such as heating buildings, laundries, and smaller industrial processes.
2. Watertube Boilers:
Now, flip the concept. Instead of hot gases traveling through tubes submerged in water, water travels through tubes heated by the surrounding combustion chamber. Here’s the breakdown for watertube boilers:
- Construction: These boilers consist of multiple tubes arranged in a loop or spiral form. Water circulates through these tubes, absorbing heat from the combustion gases outside. The heated water then turns into steam and is collected in a separate steam drum.
- Pros: Watertube boilers can handle much higher steam pressures due to the design separating water and pressurized steam. They also start up faster because of the smaller water volume in the tubes.
- Cons: The more complex design makes them generally costlier than firetube boilers. They also require more maintenance due to the numerous tubes and connections.
- Applications: Watertube boilers are the workhorses of high-pressure steam applications. They’re crucial in power generation, large-scale industrial processes, and district heating systems.
What Does a Steam Boiler Do
A steam boiler’s main function is to generate steam by heating water in a closed vessel. This steam is then the workhorse that gets used for various applications:
- Heating Buildings: In many residential and commercial buildings, steam boilers are the heart of the heating system. The high-temperature steam travels through pipes, releasing heat through radiators or convectors that warm up the space.
- Generating Electricity: Steam plays a vital role in electricity generation. In power plants, fossil fuels or nuclear energy heat water in a boiler to produce high-pressure steam. This steam spins turbines which are connected to generators, converting the mechanical energy into electricity.
- Powering Industrial Processes: Across numerous industries, steam is a critical element for various processes. It can be used for sterilization in food processing, fabricating products in chemical plants, or driving machinery in refineries. The specific use depends on the desired outcome, such as providing heat, creating pressure, or initiating chemical reactions.
- Other Applications: Beyond these main categories, steam boilers have a range of other applications. They can be used for sterilizing medical equipment, drying materials like lumber or concrete, and even de-icing roads or airport runways.
Steam Boiler Working Principle
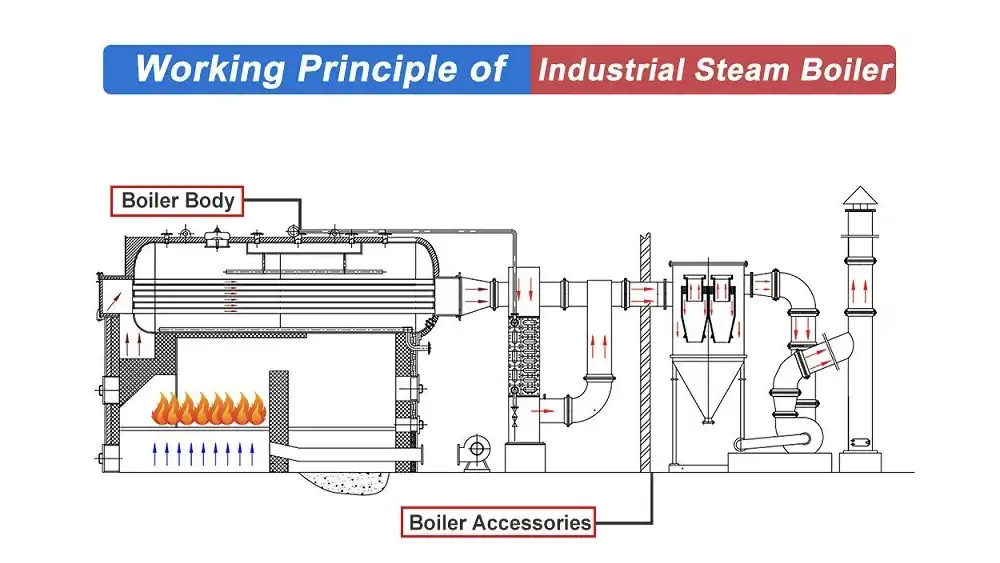
Steam boilers may seem complex, but their core principle is straightforward: transferring water into steam through heat transfer. Here’s a breakdown of the working principle of steam boiler:
1. Fuel Combustion: The journey starts with a fire. The boiler uses various fuels like natural gas, oil, coal, or biomass, which are burned in a designated combustion chamber. This burning process generates heat energy.
2. Heat Transfer: This heat energy doesn’t stay put in the combustion chamber. It needs to reach the water to create steam. Depending on the boiler type (firetube or watertube), the heat transfer method differs:
Firetube Boiler: Here, the hot combustion gases travel through tubes submerged within the main water chamber. The heat from the gases radiates and conducts through the walls of the tubes, heating the surrounding water.
Watertube Boiler: In contrast, water takes center stage. The water circulates through numerous tubes positioned within the hot combustion chamber. The furnace heat directly warms the tubes, transferring the heat to the water flowing inside.
3. Water Heating and Steam Generation: As the heat from the combustion chamber reaches the water, it increases the water temperature. Once the water reaches its boiling point (at the specific pressure inside the boiler), it starts to vaporize, transforming into steam.
4. Steam Separation and Control: The generated steam is usually a mixture of water droplets and pure steam. Most boilers have a steam separator that removes any leftover water droplets, ensuring dry steam for optimal performance. Sensors and control systems monitor the pressure and steam quality, regulating the fuel flow and combustion process to maintain desired steam output.
5. Delivering the Steam Powerhouse: Finally, the produced steam is ready for action! It exits the boiler through a valve and travels through pipes to its designated application. Whether it’s heating a building, powering a turbine, or driving an industrial process, the high-pressure steam delivers its potent heat energy to get the job done.
Additional Points:
- Feedwater and Blowdown: To maintain proper water quality and prevent mineral buildup within the boiler, fresh water (feedwater) is continuously introduced. Additionally, a controlled amount of water is periodically drained (blowdown) to remove any accumulated impurities.
- Safety Measures: Steam boilers operate under high pressure and heat. Safety features like pressure relief valves and automatic shut-off mechanisms are crucial to prevent accidents. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the boiler’s safe and efficient operation.
By understanding this fundamental working principle, you gain valuable insight into how these fascinating machines create the steam that plays a vital role in our everyday lives.
Steam Boiler Working Pressure
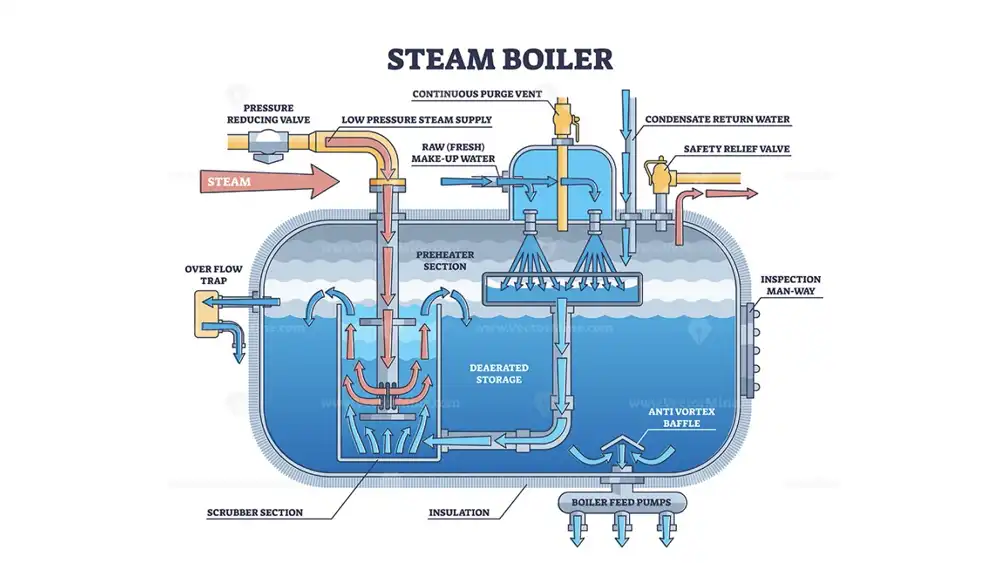
The working pressure of a steam boiler refers to the pressure at which the steam is typically generated and used within the boiler system. It’s important to distinguish between two key pressure ratings:
- Maximum Allowable Working Pressure (MAWP): This is the absolute maximum pressure a boiler is certified to safely handle. It’s a critical safety rating set by the manufacturer and enforced by regulations. Exceeding the MAWP can lead to dangerous situations like boiler explosions.
- Operating Pressure: This is the actual pressure at which the boiler runs during normal operation. It typically stays well below the MAWP, providing a safety buffer.
Here’s a breakdown of typical working pressures for steam boilers:
- Residential Steam Boilers: These generally operate at very low pressures, ranging from 1 psi to 2 psi (pounds per square inch).
- Commercial and Industrial Boilers: These can have a wider range of working pressures depending on the application. Low-pressure boilers for smaller commercial buildings might function around 5-15 psi, while high-pressure industrial boilers can operate at hundreds of psi.
Understanding the Pressure Ratings:
- Safety First: Always prioritize safety. Never attempt to tamper with or exceed the MAWP of your boiler. It’s a crucial safety rating set for a reason.
- Matching Needs and Design: The appropriate working pressure depends on the specific application. Residential heating systems require much lower pressure compared to industrial processes that leverage high-pressure steam for tasks like powering turbines.
- Boiler Specifications: The manufacturer‘s specifications for your specific boiler model will clearly indicate the MAWP and recommended operating pressure range.
Additional Considerations:
- Pressure Gauge Monitoring: Steam boiler systems typically have a pressure gauge that allows you to monitor the operating pressure in real-time. This is essential for ensuring safe operation and identifying any potential issues.
- Regular Maintenance: Proper maintenance of your steam boiler, including pressure relief valve checks, is crucial for ensuring the boiler operates safely and efficiently within its designated pressure range.
Steam Boiler Application

Steam boilers are incredibly versatile machines that play a vital role in many aspects of our lives. Their core function is generating steam through heating water in a closed vessel. This high-pressure steam is then utilized for various applications across different industries. Here’s a glimpse into some of the widespread applications of steam boilers:
1. Heating Buildings:
Steam boilers are a traditional and efficient way to heat residential and commercial buildings. They work by heating water in the boiler, which turns into steam. The hot steam travels through pipes to radiators or convectors located throughout the building, releasing heat to warm up the space.
2. Electricity Generation:
In power plants, steam boilers are the workhorses behind electricity generation. Fossil fuels or nuclear energy heat water in a boiler to produce high-pressure steam. This steam spins turbines connected to generators, converting the mechanical energy into electricity that powers our homes and businesses.
3. Industrial Processes:
Across numerous industries, steam is an essential element for various processes. Here are some specific examples:
- Food Processing: Steam is used for sterilization in food processing to eliminate harmful bacteria and extend shelf life.
- Chemical Manufacturing: Steam provides heat for various chemical reactions and processes in chemical plants.
- Oil Refining: Steam plays a role in distillation processes within oil refineries.
- Textile Industry: Steam is used for dyeing fabrics and other textile processes.
4. Other Applications:
Beyond these main categories, steam boilers have a range of other applications, including:
- Sterilization of Medical Equipment: Steam effectively sterilizes medical instruments and equipment in hospitals and healthcare facilities.
- Material Drying: Steam is used for drying materials like lumber, concrete, or agricultural products.
- De-icing Applications: In some cases, steam can even be used for de-icing roads or airport runways.
By understanding the diverse applications of steam boilers, we gain a greater appreciation for their significant contribution to our modern world.
Conclusion
In conclusion, steam boilers are remarkable gadgets that play a significant role in our world. By transforming water into potent steam, they provide heat for our buildings, power generation for electricity, and drive various industrial processes. We explored the two main types – firetube and watertube – and unraveled the working principle behind their fiery magic.
But the journey doesn’t end here! The world of steam boilers is vast. Depending on your interest, you could delve deeper into:
- Specific applications of steam boilers in different industries.
- The evolution of boiler technology and advancements in efficiency and sustainability.
- Safety regulations and best practices for boiler operation and maintenance.
If you’re a homeowner with a steam boiler system, familiarizing yourself with its basic operation and maintenance needs can be empowering. For those curious about the unseen forces that keep our world running, understanding steam boilers opens a door to appreciating the intricate network of technologies that shape our lives.
Ready to Harness the Power of Steam
Don’t wait any longer! Get a quote for a steam boiler today. Knowing your specific requirements, a qualified contractor can assess your needs and provide a tailored quote for a steam boiler system that perfectly fits your application.

