Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) is a versatile material with applications ranging from crafting to construction. Knowing how to cut it efficiently is essential for various projects.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the techniques, tools, and safety measures involved in cutting expanded polystyrene.
EPS, commonly known as Styrofoam, exhibits lightweight and insulating properties. Understanding its characteristics is crucial for precise cutting, ensuring the desired outcome without compromising its integrity.
Necessary tools for cutting expanded polystyrene
Before diving into cutting techniques, gather the essential tools, including
- hot wire cutters
- knives
- saws
Prioritize safety by wearing protective gear such as gloves and goggles. Following safety guidelines is paramount to prevent accidents.
Methods of Cutting Expanded polystyrene
Hot Wire Cutting
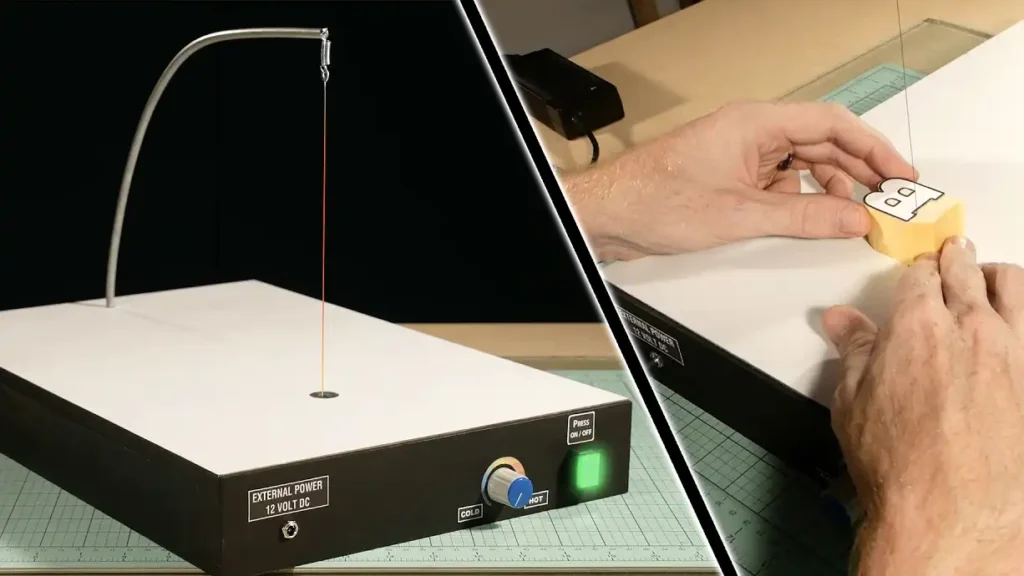

Hot wire cutting is a specialized technique used for cutting Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) with precision and finesse. In this method, a heated wire is employed to slice through the EPS material, creating clean and smooth cuts. The process is particularly effective for intricate designs and shapes, making it a popular choice in various crafting and construction projects.
Here’s a more detailed explanation of the Hot Wire Cutting process:
Hot Wire Cutting Process:
- Equipment Setup:
- A hot wire cutting setup typically consists of a frame that holds a tensioned wire, often made of nickel-chromium alloy.
- The wire is connected to a power source that heats it to a specific temperature.
- Temperature Control:
- Controlling the temperature of the wire is crucial. The ideal temperature varies based on the thickness and type of EPS being cut.
- Higher temperatures are suitable for thicker EPS, while lower temperatures are preferred for thinner sheets.
- Material Placement:
- The EPS material to be cut is placed on a stable surface beneath the hot wire.
- Guiding the Wire:
- The user manually guides the hot wire through the EPS material, following the desired cutting path.
- The heat from the wire melts through the EPS, creating a smooth and precise cut.
- Benefits of Hot Wire Cutting:
- Clean Edges: Hot wire cutting produces edges that are free from jaggedness or roughness, resulting in a polished finish.
- Intricate Designs: It is ideal for cutting intricate shapes and designs with high accuracy.
- Efficiency: The process is relatively quick and efficient, making it suitable for both small-scale and large-scale projects.
- Applications:
- Hot wire cutting finds applications in various industries, including:
- Architectural Modeling: Creating detailed architectural models and prototypes.
- Artistic Projects: Crafting intricate sculptures and artistic pieces.
- Construction: Precision cutting for insulation and construction projects.
- Hot wire cutting finds applications in various industries, including:
- Considerations:
- While hot wire cutting is highly effective, users must adhere to safety guidelines to prevent accidents.
- Protective gear, such as gloves and eye protection, is often recommended to ensure user safety.
Understanding the nuances of hot wire cutting allows enthusiasts and professionals alike to harness its capabilities for achieving precise and high-quality results in their EPS cutting endeavors.
Knife and Saw Techniques
Knife and saw techniques are traditional yet effective methods for cutting Expanded Polystyrene (EPS). These approaches provide versatility and are well-suited for various projects, ranging from simple crafts to construction tasks. Let’s delve into the details of knife and saw techniques for cutting EPS:
Knife Techniques:
- Choosing the Right Knife:
- Selecting an appropriate knife is crucial. A sharp utility knife or a craft knife with a retractable blade is often preferred.
- The blade should be long enough to cut through the entire thickness of the EPS material.
- Marking and Scoring:
- Before making the final cut, mark the cutting line on the EPS surface using a straightedge or a template.
- Consider scoring the material lightly along the marked line. This helps guide the knife and ensures a straight cut.
- Slicing Motion:
- Use a smooth and controlled slicing motion with the knife. Avoid applying excessive pressure to prevent the EPS from breaking or cracking.
- For curved cuts, make small, successive cuts to maintain precision.
- Rotary Cutter for Curves:
- In situations requiring curved cuts, a rotary cutter with a circular blade can be beneficial. It allows for more fluid and precise curved cuts.
Saw Techniques:
- Selecting the Right Saw:
- Hand saws, coping saws, or even jigsaws can be used for cutting EPS with saw techniques.
- Choose a fine-toothed blade to minimize rough edges.
- Securing the EPS Material:
- Ensure the EPS material is securely fixed in place before making cuts. This prevents movement and ensures accuracy.
- Straight Cuts with Hand Saws:
- Hand saws are suitable for straight cuts. Use a straightedge or guide to maintain a straight cutting line.
- Apply even pressure while sawing to achieve clean and precise cuts.
- Coping Saw for Intricate Shapes:
- Coping saws are excellent for intricate shapes and curves. Their narrow blades allow for maneuvering through tight corners.
Benefits of Knife and Saw Techniques:
- Accessibility: These methods are accessible to DIY enthusiasts and professionals alike, requiring basic tools that are readily available.
- Versatility: Knife and saw techniques can handle a wide range of cutting requirements, from simple shapes to more complex designs.
- Cost-Effective: Compared to some specialized cutting methods, knife and saw techniques are often more budget-friendly.
Considerations:
- Safety Precautions: Always prioritize safety by using appropriate safety gear, including gloves and eye protection.
- Blade Maintenance: Keep blades sharp to ensure clean cuts and prevent unnecessary strain on the EPS material.
By mastering knife and saw techniques, individuals can confidently tackle EPS cutting projects, enjoying the flexibility and practicality these methods offer across various applications.
CNC Cutting
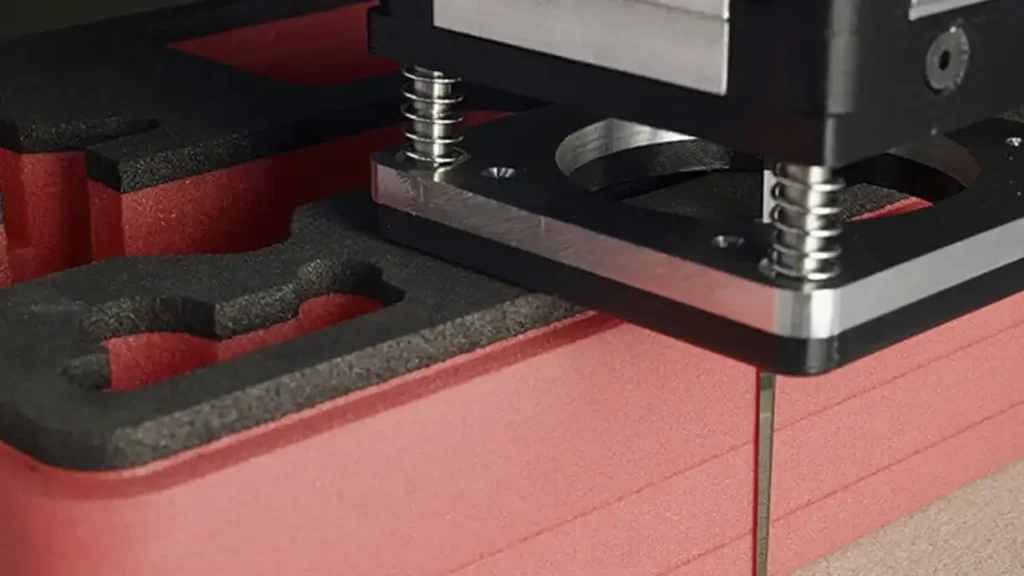

CNC (Computer Numerical Control) cutting is a sophisticated and highly precise method used for cutting Expanded Polystyrene (EPS). This automated process involves the use of a computer-controlled machine that executes precise movements to cut EPS into intricate shapes and designs. Here’s a closer look at CNC cutting and its applications:
CNC Cutting Process:
- Design Input:
- The process begins with creating a digital design or blueprint of the desired shape or pattern using computer-aided design (CAD) software.
- Programming:
- The digital design is then converted into a set of instructions, or G-code, that the CNC machine can interpret. This programming step dictates the machine’s movements and cutting paths.
- Material Setup:
- The EPS material is securely fixed onto the CNC cutting bed. Proper fixation ensures stability during the cutting process.
- Machine Calibration:
- Before cutting begins, the CNC machine undergoes calibration to ensure accuracy. This involves setting the origin point and confirming the dimensions of the EPS material.
- Automated Cutting:
- Once calibrated, the CNC machine executes the programmed cutting paths with precision. The cutting tool, typically a router or hot wire, moves along the specified coordinates to carve out the desired shape.
- Complex Geometries:
- CNC cutting is particularly advantageous for intricate designs and complex geometries that may be challenging to achieve manually or with other cutting methods.
Benefits of CNC Cutting:
- Precision and Accuracy:
- CNC cutting ensures a high level of precision and accuracy, meeting exact specifications outlined in the digital design.
- Repeatability:
- The automated nature of CNC cutting allows for consistent and repeatable results, making it ideal for large-scale production.
- Versatility:
- CNC machines can accommodate a wide range of shapes and designs, making them versatile for various applications across industries.
- Efficiency:
- The automated process significantly reduces production time compared to manual cutting methods, improving overall efficiency.
- Minimal Material Waste:
- The precise nature of CNC cutting minimizes material waste, contributing to cost-effectiveness.
Applications of CNC Cutting:
- Architectural Models:
- Creating detailed architectural models with intricate features and precise details.
- Prototyping:
- Rapid prototyping for product development, ensuring accurate representation of designs.
- Art and Sculpture:
- Crafting artistic pieces and sculptures with intricate and detailed designs.
- Industrial Production:
- Mass production of components and parts with consistent quality and precision.
Considerations:
- Programming Expertise: Utilizing CNC cutting requires expertise in programming and operating the CNC machine. Professionals with experience in CAD software are often involved in this process.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance of the CNC machine is essential to ensure optimal performance and accuracy.
CNC cutting stands at the forefront of precision cutting technology, offering a level of detail and efficiency that is particularly beneficial for projects demanding intricate designs and high accuracy.
Tips for Precision and Clean Cuts
Achieving clean cuts requires attention to detail and the right approach.
- Maintain a consistent temperature for the best results.
- Select the appropriate blade based on the thickness of the EPS.
- Apply even pressure during cutting to prevent jagged edges.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
To ensure a successful cutting process, steer clear of these common mistakes:
- Avoid overheating the EPS, which can lead to melting.
- Use the correct tools to prevent damage to the material.
- Adhere strictly to safety guidelines to prevent accidents.
Applications of Cut Expanded Polystyrene
The versatility of cut EPS extends to various applications, including:
- Crafting and DIY projects for artistic creations.
- Construction and insulation in architecture and building projects.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Consider sustainable practices and explore recycling options for EPS to minimize environmental impact. Responsible disposal and recycling contribute to a greener future.
FAQs about Cutting Expanded Polystyrene
- Are there any eco-friendly cutting methods?
- Can EPS be recycled after cutting?
- What safety gear is essential for cutting EPS?
- How to achieve smooth edges while cutting?
- Are there alternatives to traditional cutting methods?
- How do temperature variations affect cutting?
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering the art of cutting Expanded Polystyrene opens doors to a myriad of creative and practical possibilities. By understanding the material, utilizing proper tools, and following safety measures, you can embark on projects with confidence, knowing you have the skills needed for success.
