Today, we’re delving into a topic that’s both interesting and environmentally significant – how to compact Styrofoam. Styrofoam, that ubiquitous lightweight material, has become a common sight in our daily lives.
But have you ever wondered what can be done to reduce its volume and manage it more efficiently? Well, you’re in the right place as we explore various methods to achieve this.
What is Styrofoam?

Styrofoam is a lightweight, low-density plastic material that is widely recognized for its insulating and cushioning properties.It is composed of numerous tiny air-filled cells, which give it its characteristic lightness and ability to resist heat transfer. This makes it highly useful in applications such as packaging to protect fragile items during shipping, and in construction for insulation purposes to help maintain stable indoor temperatures and reduce energy consumption.
It is often molded into various shapes and forms, such as foam cups, food containers, and packaging blocks. However, Styrofoam poses significant environmental challenges. It is not biodegradable and can persist in the environment for a long time, contributing to plastic waste pollution. Recycling Styrofoam can be difficult and costly, and improper disposal can have negative impacts on ecosystems and wildlife.
Different Styrofoam Compression Tools and Equipment
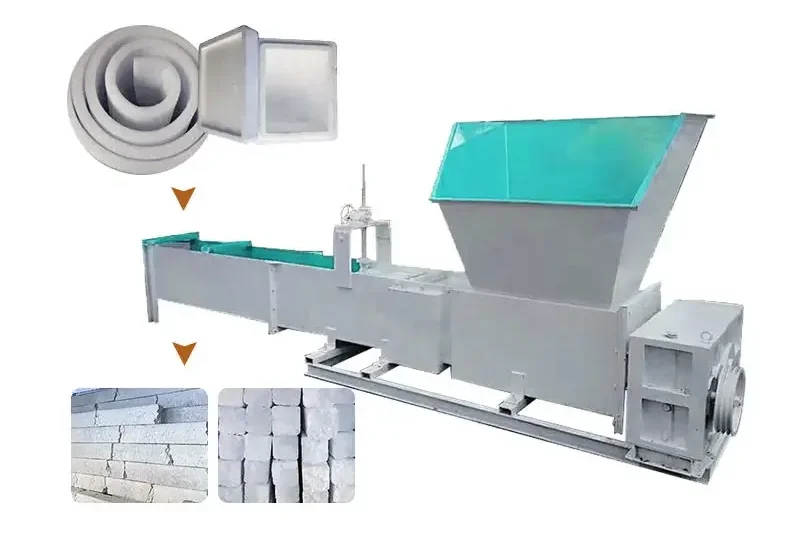

The following introduces several common compression tools and equipment and their advantages and disadvantages:
Piston Compressor
Advantages: Wide applicable pressure range, regardless of flow rate, can reach the required pressure; high thermal efficiency, low unit power consumption; strong adaptability, can adapt to a wider pressure range and refrigeration capacity requirements; the device system is relatively simple and easy to repair; low material requirements, mostly ordinary steel materials, simple processing, and low cost; relatively mature technology, and rich experience in production and use.
Disadvantages: low speed, large and heavy machine; many wearing parts, large repair volume; discontinuous exhaust, causing air flow pulsation; large vibration during operation.
Centrifugal Compressor
Advantages: large exhaust volume, uniform exhaust, no air flow pulse; high speed; good sealing effect, less leakage; flat performance curve, wide operating range; few wearing parts, less maintenance, long working cycle; easy to realize automation and large-scale.
Disadvantages: poor adaptability of operation, the nature of the gas has a great influence on the operating performance; the air flow velocity is high, and the parts in the flow channel have a large friction loss; there is a surge phenomenon, which is more harmful to the machine.
Screw Compressor
Advantages: fewer parts, fewer wearing parts, high reliability; convenient operation and maintenance; no unbalanced inertia force, stable and safe operation, small vibration; with the characteristics of forced gas transmission, the exhaust volume is almost not affected by the exhaust pressure, and the adaptability to working conditions is strong; there is a gap on the rotor tooth surface, which is not sensitive to wet stroke and can withstand liquid impact; the exhaust temperature is low and can operate under higher pressure ratio conditions; the flow rate is steplessly adjusted to save operating costs.
Pressing Equipment
Advantages: high product dimensional accuracy and good repeatability; high production efficiency, easy to achieve specialized and automated production; can be formed in one time for complex structural products; high surface brightness, no need for secondary modification; can be mass-produced at low cost.
Disadvantages: complex mold manufacturing, high investment cost; limited by the machine model, most of the mass production is small and medium-sized products.
How to Compact Styrofoam?

Mechanical Compression Method
Mechanical compression is a common method of compressing polystyrene foam (Styrofoam). This often requires the use of specially designed polystyrene foam compressors.The EPS foam compactor employs a helical compression mechanism to compress EPS foam into blocks. The operator places the foam block into the hopper, where the shredder breaks the foam into pieces, and then the screw mechanism extrudes the small pieces of EPS foam into compressed blocks.
This compressor works by applying strong pressure to squeeze Styrofoam into a smaller volume. The advantage is that the compression efficiency is high and significant volume reduction can be achieved in a relatively short period of time.
However, there are some limitations to using this approach. First, there can be a high cost to purchase and maintain this specialized equipment. Secondly, a certain amount of energy is consumed during operation.
Thermal Compression Method
Achieving compression by applying heat to Styrofoam is another possible method. You can use an oven or a heat gun as a heat source.
When polystyrene foam is heated, it softens, making it easier to compress. But in this process, precise temperature control is required. If the temperature is too high, it may cause the polystyrene foam to melt excessively or even burn, damaging the material. On the contrary, if the temperature is too low, good compression effect cannot be achieved.
Chemical Compression Method
Certain chemicals can be used in the compression treatment of Styrofoam. When polystyrene foam comes into contact with certain chemical agents, its molecular structure may change, allowing it to compress.
But extreme caution must be taken when using chemical methods. Because the chemicals used may be hazardous, safe operating procedures need to be strictly followed. In addition, chemically treated waste also needs to be properly disposed of to avoid environmental pollution.
When choosing a method of compressing Styrofoam, factors such as cost, efficiency, safety and environmental impact should be considered based on actual conditions.
How to Precisely Control the Temperature of Hot-Compressed Styrofoam?
Use a Temperature Controller
Install an accurate temperature controller, such as a digital temperature controller, on the heating device. This allows the target temperature to be set, and the output of the heating element can be monitored and adjusted in real time through sensors to maintain a stable temperature.
Choose the Right Heating Device
Choose a device that can heat evenly according to the amount and size of the polystyrene foam that needs to be compressed. For example, use professional equipment such as an oven or heat press with a constant temperature control function, which usually has better temperature uniformity and stability.
Preheat the Equipment
Before hot compression, preheat the heating equipment to near the set temperature to reduce the impact of temperature fluctuations on the polystyrene foam.
Monitor Temperature Distribution
If possible, use a multi-point temperature measurement tool (such as a thermocouple or infrared thermometer) to monitor the temperature of different parts of the polystyrene foam to ensure that the overall temperature is uniform. If the temperature is found to be uneven, the position of the heating device can be adjusted or other measures can be taken to improve the temperature distribution.
Control the Heating Time
In addition to temperature, heating time also affects the degree of heating of polystyrene foam. Based on experience and experiments, determine the appropriate heating time to avoid overly long or short heating that causes the temperature to be too high or too low.
Conduct Small-scale Tests
Before formal large-scale compression, conduct small-scale tests to find the best temperature and heating time combination for specific polystyrene foam materials and shapes. Through the test, the changes in polystyrene foam can be observed so that the parameters can be adjusted to achieve the purpose of precise temperature control.
Stable Ambient Temperature
Try to perform hot compression operations in places with relatively stable ambient temperatures to avoid large fluctuations in ambient temperature that affect the temperature control effect of the heating equipment.
Regularly Calibrate Temperature Measuring Equipment:
Ensure the accuracy of temperature measuring equipment and calibrate it regularly to prevent inaccurate temperature control due to measurement errors.
Experience Accumulation
As the number of operations increases, experience is gradually accumulated, and the temperature during hot compression can be better controlled according to the characteristics and actual conditions of polystyrene foam.
It should be noted that polystyrene foams of different types and thicknesses may have different sensitivities to temperature, so in actual operations, adjustments and optimizations need to be made according to specific circumstances. At the same time, the state of the polystyrene foam should be closely observed during the heating process to ensure that it will not melt, deform or burn due to excessive temperature. Safety is of paramount importance. Follow the relevant safety operating procedures to avoid accidents.
Best Compact Styrofoam Tools: Eps Compactor
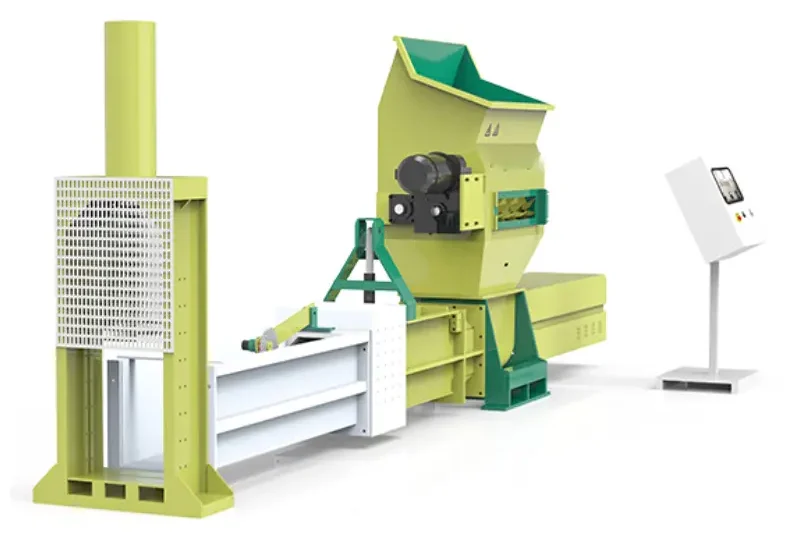

Crush clutter and boost your bottom line! Eps Compactor maximizes space, minimizes waste removal costs, and streamlines workflow.
Reduced Waste Volume: Their compactor can significantly reduce the volume of your EPS waste, typically by a ratio of 40:1. This frees up valuable storage space and cuts down on the number of waste pickups you need.
Cost Savings: By reducing your waste volume, you’ll likely save money on hauling and disposal fees. In some cases, compacted EPS can even be sold to recyclers, generating additional revenue.
Environmental Benefits: Diverting EPS waste from landfills is good for the environment. Compaction makes recycling more efficient and cost-effective, encouraging responsible waste management.
Variety of Options: They may offer a range of EPS compactor models to suit different waste volumes and business needs.
Safety Precautions
Here are some safety precautions that need to be emphasized during the compression of polystyrene foam (Styrofoam):
Static Electricity Prevention
Polystyrene foam is prone to static electricity during the compression process. Static electricity may cause sparks and pose a fire hazard. To avoid static electricity, ensure that the compression equipment and work area are well grounded. Operators should wear anti-static clothing and footwear to reduce the possibility of static electricity accumulation. In dry environments, humidifiers can be used to increase air humidity and reduce the risk of static electricity.
Dust Protection
Dust is generated when polystyrene foam is compressed. Inhalation of this dust may cause damage to the respiratory system. Operators must wear suitable dust masks to ensure effective filtration of dust particles. The work area should be well ventilated to exhaust dust and reduce dust concentration in the air. Regularly inspect and maintain ventilation equipment to ensure its normal operation.
High Temperature Protection
If hot compression methods are used, prevent high temperature burns. Use heat-resistant gloves when contacting heated parts or heated polystyrene foam. Set up obvious high temperature warning signs to remind operators to take precautions.
Mechanical Safety
When operating compression equipment, be careful to prevent limbs from being caught or pinched. Be familiar with the equipment’s operating procedures and the location of the emergency stop button. Before the equipment is operated, ensure that the protective devices are installed and functioning properly.
Fire Prevention Measures
Polystyrene foam is flammable. Appropriate fire extinguishing equipment should be equipped in the work area, and ensure that the operator knows how to use it correctly. It is strictly forbidden to perform compression operations near open flames or high temperature sources.
Electrical Safety
The electrical part of the compression equipment should be checked regularly to ensure that the wires are not damaged and the plugs and sockets are firmly connected. Avoid water or humid environments from affecting electrical equipment to prevent electric shock accidents.
Personal Protective Equipment
In addition to the above, operators should also wear goggles to protect their eyes from possible flying particles.
Strictly following these safety precautions can effectively ensure the safety of personnel and the safety of the working environment during the polystyrene foam compression process.
Conclusion

This article discusses how to compress foam plastics and recommended compression machines. It covers mechanical compression using specialized equipment, hot compression with precise temperature control, and chemical compression with caution due to the presence of hazardous materials. If you need it, please click on our machine link.
