Geofoam road construction is rapidly gaining traction as a cutting-edge approach to building and rehabilitating roadways. This innovative technique utilizes the remarkable lightweight properties of expanded polystyrene (EPS) geofoam to address long-standing challenges in roadbed engineering. By significantly reducing the load on underlying soils, geofoam offers solutions for projects built on weak or compressible ground, minimizing settlement and enhancing stability.
This blog delves into the transformative potential of geofoam in road construction. We will explore its numerous benefits, from accelerating construction timelines and lowering costs to improving the long-term durability and performance of roadbeds. Join us as we examine how this lightweight solution is revolutionizing the way we engineer and build our transportation infrastructure for a more sustainable and resilient future.
Why Geofoam Road Construction
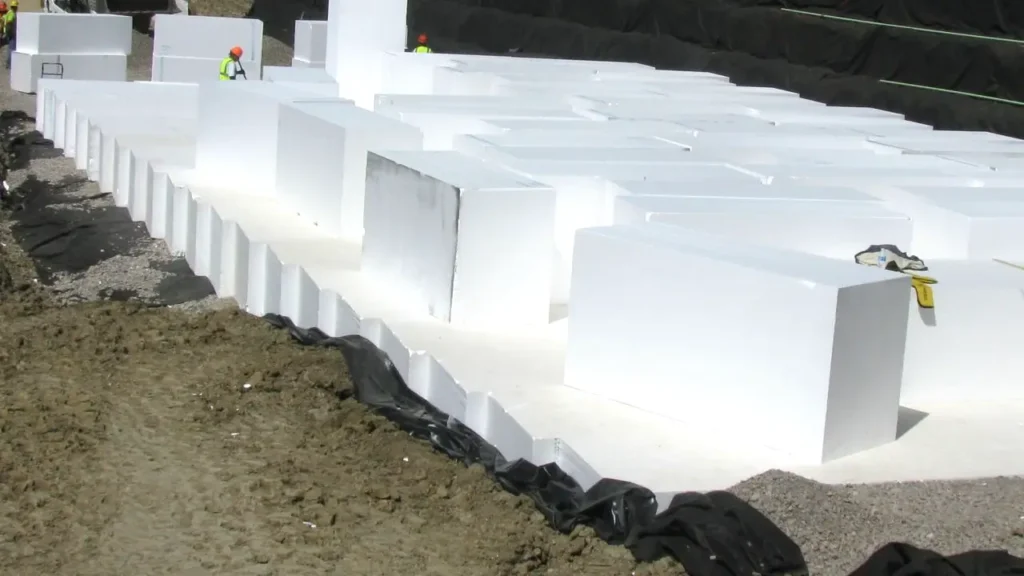

Geofoam has emerged as a compelling alternative to traditional fill materials in road construction, offering a range of advantages that address common challenges in geotechnical engineering. Its adoption is driven by its unique properties that contribute to more efficient, sustainable, and long-lasting infrastructure.
Reducing Settlement
One primary reason for using geofoam in road construction is its ability to significantly reduce settlement, particularly when building over weak or compressible soils. Traditional heavy fill materials exert substantial pressure on the underlying ground, leading to consolidation and long-term settlement issues. Geofoam’s extremely low density minimizes this vertical load, preserving the integrity of the road structure and ensuring a smoother, more durable driving surface over time.
Accelerating Construction Schedules
The lightweight nature and ease of handling of geofoam blocks contribute to faster construction timelines. Unlike traditional fill, which requires heavy machinery for placement and compaction, geofoam can often be installed manually or with lighter equipment. This rapid installation process allows for quicker project completion, minimizing traffic disruptions and reducing overall construction costs associated with time.
Minimizing Environmental Impact
Geofoam can be manufactured with recycled content, reducing the demand for virgin materials and diverting waste from landfills. Its lightweight nature also translates to lower transportation energy consumption compared to hauling heavy fill materials. Furthermore, by reducing the need for extensive ground improvement techniques on poor soils, geofoam can minimize disturbance to the surrounding environment.
Enhancing Stability on Unstable Ground
For road construction projects on unstable or challenging terrain, such as soft clays or landslide-prone areas, geofoam provides a stable and lightweight solution. Its low density reduces the driving forces that can contribute to slope instability, while its structural integrity can enhance the overall stability of the roadbed, ensuring a safer and more reliable infrastructure in difficult conditions.
Cost-Effectiveness Over the Long Term
While the initial material cost of geofoam might be higher than some traditional fill, its long-term benefits often translate to overall cost savings. Reduced settlement minimizes the need for frequent and expensive maintenance. Faster construction schedules can lower labor and equipment costs. Additionally, the reduced load on underlying structures can potentially lead to less extensive and costly foundation designs for bridges and overpasses associated with the roadway.
Geofoam Benefits for Roads
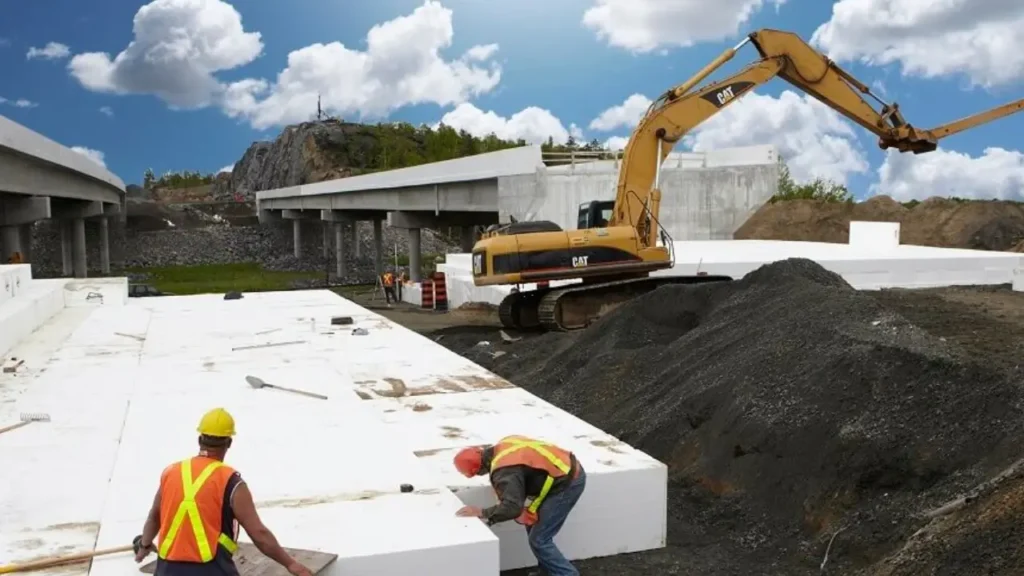

Geofoam has revolutionized road construction by offering a lightweight and stable alternative to traditional fill, addressing numerous challenges inherent in geotechnical engineering. Its adoption stems from its unique properties that lead to more efficient, sustainable, and durable infrastructure.
Alleviating Load and Preventing Settlement
A fundamental reason for utilizing geofoam in road construction is its remarkable ability to reduce the load on underlying soils, thereby preventing significant settlement. Traditional heavy fill materials impose substantial vertical pressure, leading to soil consolidation and long-term unevenness in the road surface. Geofoam’s exceptionally low density minimizes this stress, ensuring a stable and level roadway that requires less maintenance over its lifespan.
Expediting Construction Processes
The lightweight nature of geofoam blocks translates to ease of handling and faster installation times. Unlike conventional fill, which necessitates heavy machinery for placement and compaction, geofoam can often be maneuvered and positioned with lighter equipment or even manually. This accelerated construction schedule minimizes traffic disruptions and reduces the overall project duration, leading to potential cost savings in labor and equipment.
Promoting Environmental Sustainability
Geofoam can be manufactured incorporating recycled polystyrene, contributing to waste reduction and resource conservation. Its light weight also means lower energy consumption during transportation compared to the significant energy required to move large volumes of traditional fill. Furthermore, by mitigating the need for extensive ground improvement on weak soils, geofoam can lessen the environmental impact associated with site preparation.
Enhancing Stability in Challenging Environments
For road projects situated on unstable terrain, such as soft clays or areas prone to landslides, geofoam offers a crucial advantage in enhancing stability. Its low density reduces the driving forces that can trigger slope failure, while its inherent structural integrity contributes to a more stable roadbed. This makes it a valuable material for constructing reliable infrastructure in difficult geographical conditions.
Offering Long-Term Economic Benefits
While the initial cost of geofoam might be a consideration, its long-term benefits often lead to overall economic advantages. The significant reduction in settlement minimizes the need for frequent and costly repairs. The faster construction timelines can lower labor and equipment expenses. Additionally, the reduced load on associated structures like bridges and overpasses can potentially lead to more economical foundation designs.
How to Build a Road with Geofoam
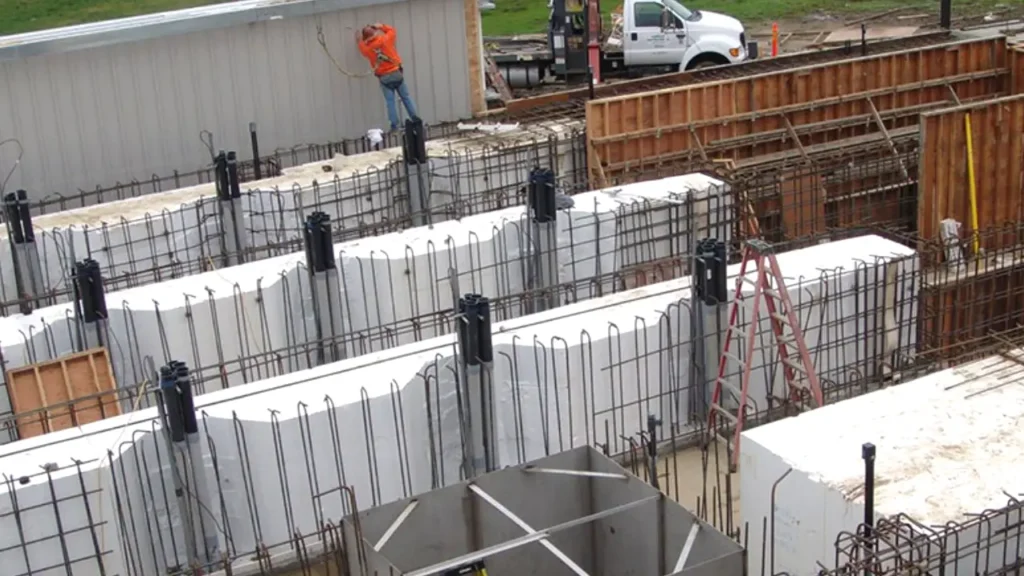

Constructing a road using geofoam involves a systematic approach that leverages the material’s lightweight and stable properties. This process ensures a durable and long-lasting roadbed, particularly advantageous in areas with poor soil conditions. Proper planning and execution of each step are crucial for a successful geofoam road construction project.
Step 1: Site Preparation and Grading
You’ll begin with thorough site preparation, including clearing vegetation, removing unsuitable topsoil, and ensuring proper drainage. The subgrade is then graded to the required profile and compacted to provide a stable base for the geofoam blocks. Accurate grading is essential for ensuring a level and consistent foundation for the subsequent layers of the road structure.
Step 2: Geofoam Block Placement
Once the subgrade is prepared, you’ll carefully place the lightweight geofoam blocks according to the project design specifications. These blocks are typically installed in layers, and their interlocking or butt-jointed arrangement creates a stable and continuous fill. Due to their light weight, you can often handle and position the blocks manually or with light equipment, speeding up the construction process.
Step 3: Shaping and Adjustments
You can easily cut and shape the geofoam blocks on-site using simple tools like hot-wire cutters or saws to accommodate curves, slopes, and other specific design requirements of the road. This adaptability allows for precise adjustments and ensures the geofoam layer conforms accurately to the intended road geometry. Proper shaping minimizes gaps and provides a uniform base for the pavement structure.
Step 4: Load Distribution Layer
Next, you’ll place a load distribution layer, typically made of granular material such as aggregate or concrete, over the geofoam blocks. This layer serves to distribute the traffic loads evenly across the lightweight fill, preventing excessive stress on the geofoam and ensuring the stability of the pavement structure. The thickness and composition of this layer are determined by the anticipated traffic volume and axle loads.
Step 5: Pavement Construction
The final step involves constructing the road pavement on top of the load distribution layer. This typically includes layers of sub-base, base course, and the final wearing surface (asphalt or concrete). The stable and lightweight geofoam foundation, combined with the load distribution layer, provides a durable and long-lasting road structure capable of withstanding traffic loads and environmental stresses.
Expanded Polystyrene Geofoam in Pavement Construction
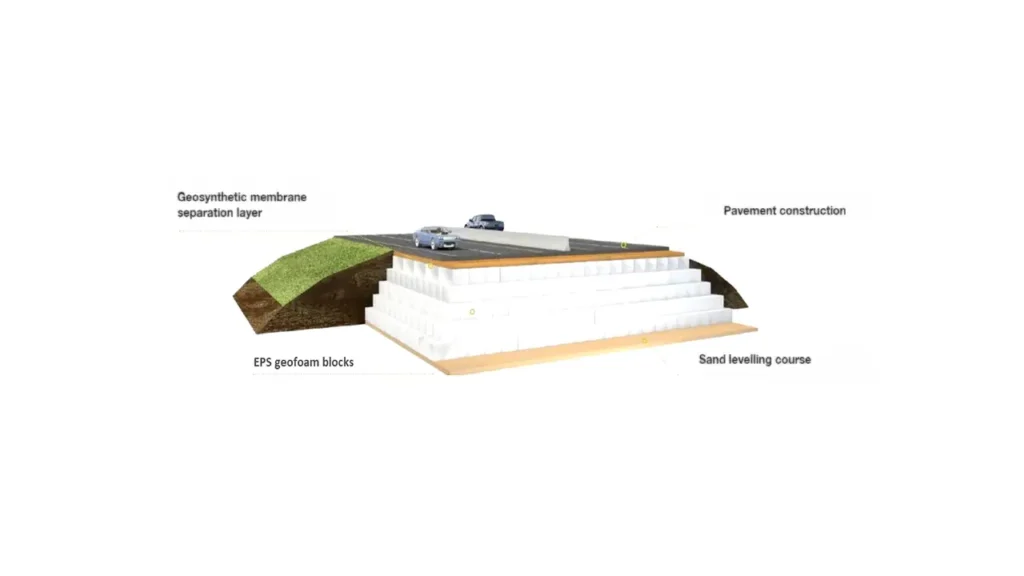
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) geofoam has emerged as a valuable material in pavement construction due to its unique lightweight and compressible properties. Its application addresses several challenges associated with traditional road building methods, particularly in areas with poor soil conditions or the need for rapid construction. By utilizing geofoam, engineers can design and build more stable and efficient pavement structures.
Here are key applications of EPS geofoam in pavement construction:
Compressible Layers for Seismic Isolation: In earthquake-prone areas, geofoam can be incorporated into pavement structures as a compressible layer. During seismic events, the geofoam can compress and absorb some of the ground movement, reducing the stress transmitted to the pavement surface and potentially mitigating damage. This application enhances the resilience of the road infrastructure in seismically active regions, ensuring better performance and quicker recovery after an earthquake.
Lightweight Embankment Fill: Geofoam’s significantly lower density compared to soil reduces the vertical load on the subgrade. This is crucial when constructing roads over soft, compressible soils like peat or clay, where traditional fill would cause excessive settlement and potential instability. The reduced weight also minimizes lateral pressures on adjacent structures, such as retaining walls or buried utilities, ensuring their integrity.
Void Filling and Leveling: Geofoam blocks can be used to efficiently fill voids or create a level sub-base for pavement construction. This is particularly useful in areas with uneven terrain or where underground structures need to be covered without adding significant weight. The ease of shaping and cutting geofoam allows for precise adjustments to achieve the desired grade and profile for the roadbed, simplifying the construction process and ensuring a uniform foundation for the pavement layers.
Thermal Insulation: In regions with severe winter climates, EPS geofoam’s inherent insulation properties can help prevent differential icing on pavement surfaces. By insulating the subgrade, geofoam reduces the transfer of heat from the ground to the pavement, delaying the formation of ice compared to adjacent, non-insulated road sections. This can enhance road safety and reduce the need for excessive de-icing measures, contributing to lower maintenance costs and improved winter driving conditions.
Conclusion
Geofoam road construction presents a paradigm shift in infrastructure development, offering a lightweight yet robust alternative to traditional methods. Its ability to significantly reduce settlement, expedite construction timelines, and minimize environmental impact positions it as a cornerstone of modern roadbed engineering. The versatility of geofoam allows for innovative solutions in diverse and challenging terrains.
By leveraging the unique properties of geofoam, engineers and contractors can achieve enhanced stability, reduced maintenance, and long-term cost savings in their road construction projects. The ease of installation and durability of geofoam contribute to more efficient and sustainable infrastructure development, paving the way for safer and more reliable roadways.
Ready to revolutionize your road construction projects with the power of lightweight geofoam? Contact Epsole today for high-quality geofoam blocks and expert guidance. Discover how our premium geofoam solutions can elevate your engineering endeavors.
