EPS Manufacturing: The Secret to High-Profit EPS Products
Learn how EPS manufacturing can revolutionize your product development process and unlock hidden margins. Contact us today for a free consultation and discover how EPS can maximize your return on investment!
EPS Manufacturing Process
EPS recycling machine is playing a crucial role in reducing waste and promoting sustainability. We can offer the premium EPS recycling machine to meet all of your requirements, here we can provide you all to support EPS recycling machine.

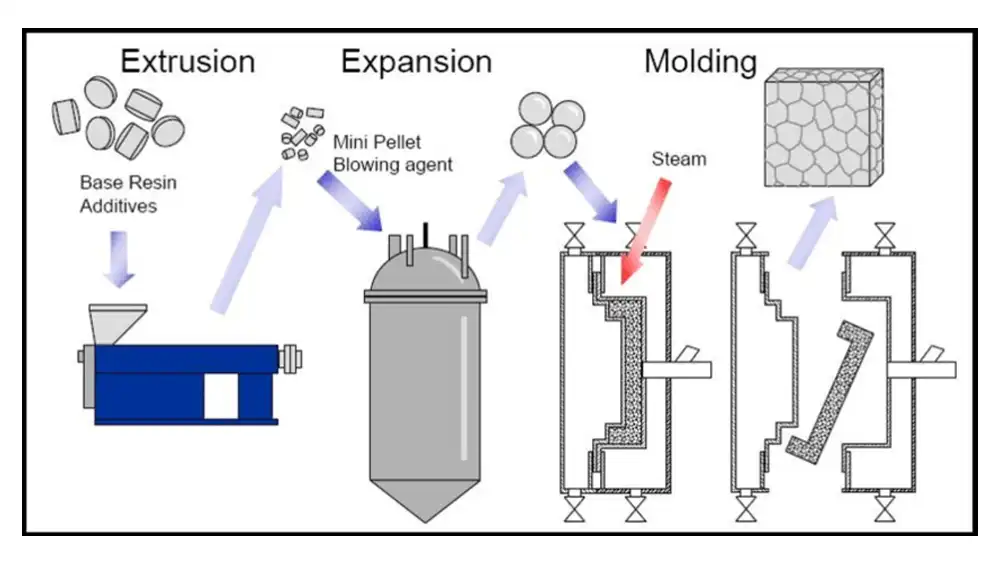
The EPS manufacturing process starts with polystyrene beads, derived from petroleum and natural gas byproducts. These tiny beads are the building blocks of EPS.
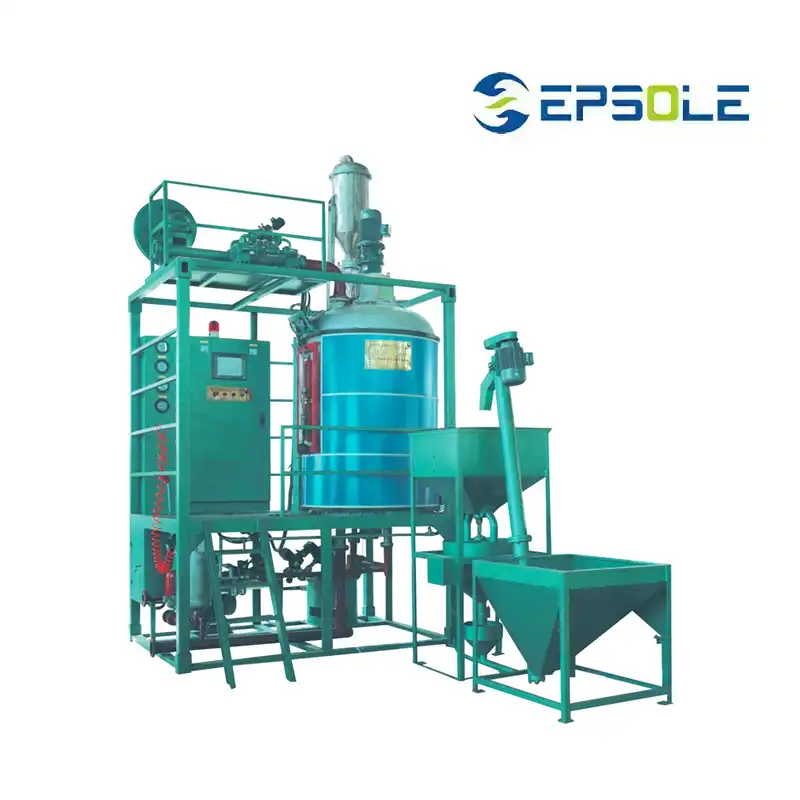

- These eps beads enter a pre-expander machine, where they meet their transformation.
- Inside, the beads are exposed to steam (sometimes with air) which causes them to soften and pre-expand up to 40 times their original size.
- This pre-expansion is crucial because it creates the air pockets that give EPS its signature lightweight and insulating properties.
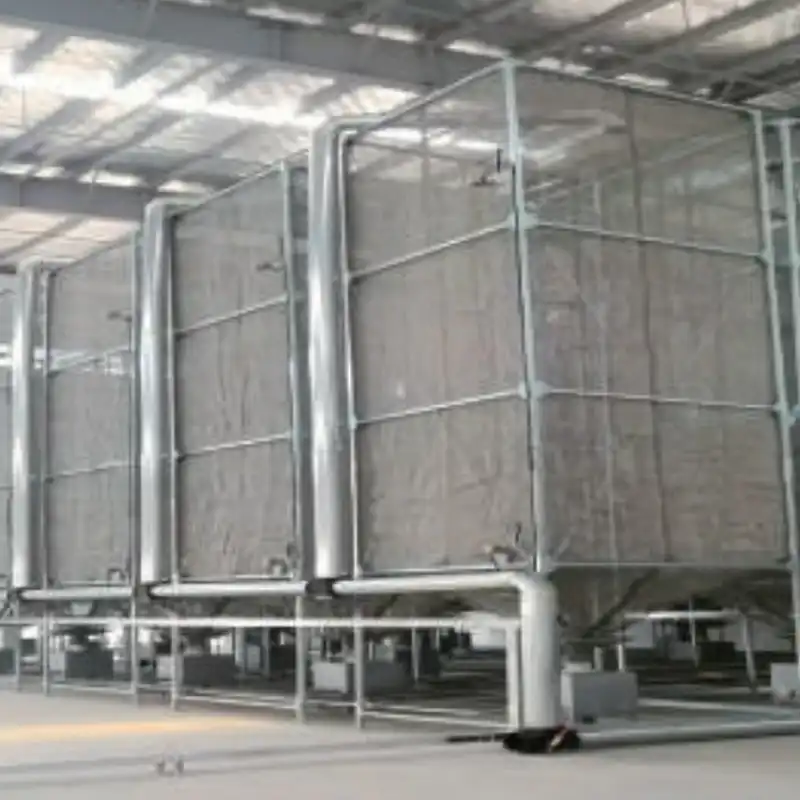

- After pre-expansion, the beads, now significantly larger and lighter, are transferred to a storage silo.
- This allows them to age for a few hours. This aging period helps the beads cool down and stabilize, ensuring they are ready for the next step.
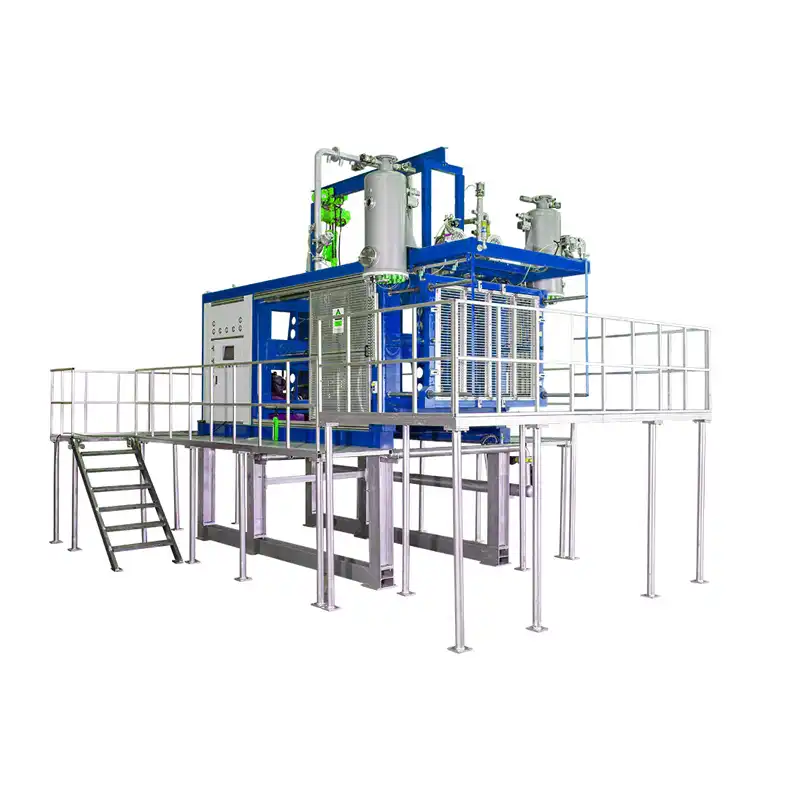

- Depending on the desired final product, some manufacturers might use an EPS shape molding machine.
- This machine injects steam directly into the pre-expanded beads, causing them to further expand and take on a specific pre-shaped form.
- This pre-shape can then be fed into the block molding machine for final shaping.
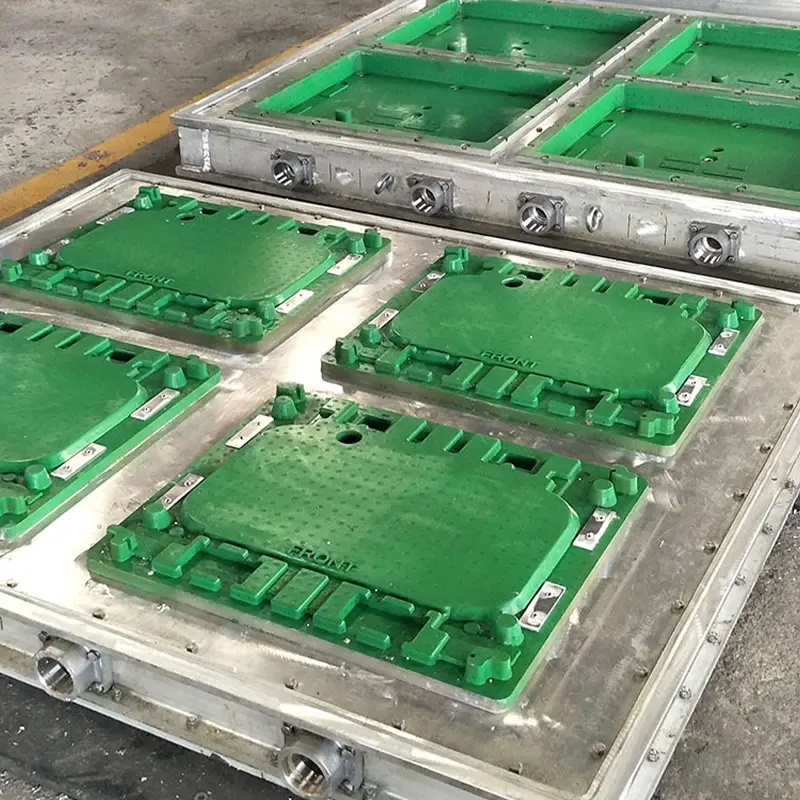

The heart of the molding process is the EPS mold. This mold is a hollow cavity designed to create the final shape of the EPS product.
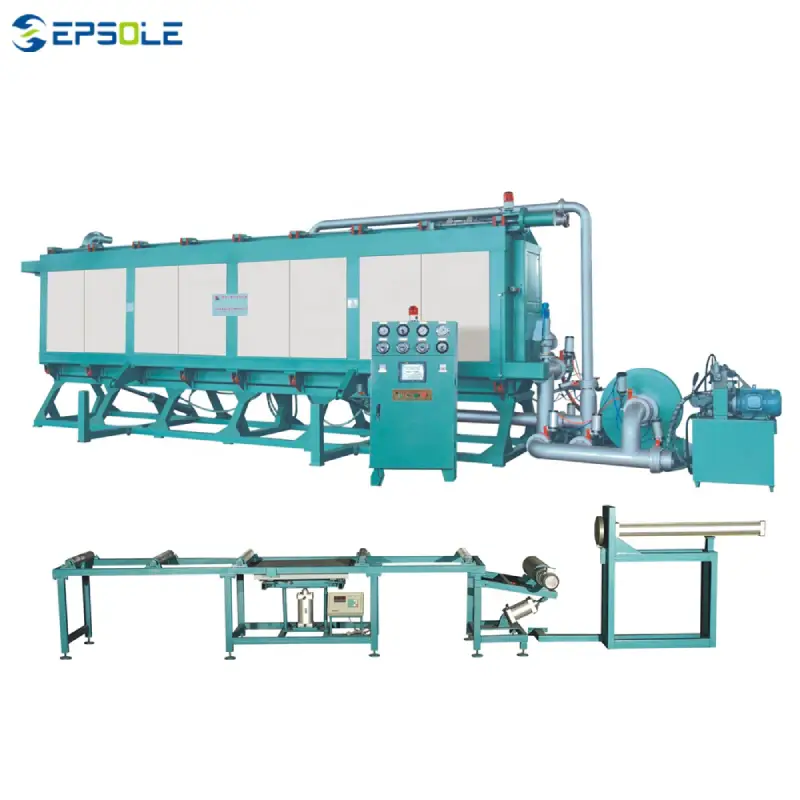

- The aged pre-expanded beads (or pre-shaped beads if the shape molding machine was used) are then fed into the EPS block molding machine.
- Inside the machine, steam is again used to further expand the beads and fuse them together. The mold cavity dictates the final shape of the EPS block.

- Once the molding cycle is complete, the EPS block is cooled with air or water to solidify its shape.
- This cooled EPS block can then be cut into desired shapes and sizes using hot wires, saws, or CNC machines.
- The final product can be everything from protective packaging materials and building insulation to helmet liners and surfboard blanks.
EPS Foam Manufacturing Process
The EPS foam manufacturing process can be broken down into several key steps:
1. Pre-expansion:
- The journey begins with tiny polystyrene beads, the building blocks of EPS.
- These beads are loaded into a pre-expander machine.
- Inside the pre-expander, the beads are exposed to steam (sometimes with added air).
- This steam treatment softens the beads and triggers a pre-expansion process, causing them to inflate up to 40 times their original size.
- This pre-expansion is crucial because it creates the air pockets within the beads that give EPS its signature lightweight and insulating properties.
2. Storage and Aging:
- After pre-expansion, the significantly larger and lighter beads are transferred to a storage silo.
- Here, the beads undergo an aging period of a few hours. This allows them to cool down and stabilize, ensuring they are ready for the next stage.
3. Shape Molding (Optional):
- Depending on the desired final product shape, some manufacturers might utilize a shape molding machine.
- This machine injects steam directly into the pre-expanded beads, causing them to further expand and take on a specific pre-shaped form.
- This pre-shaped form can then be fed into the block molding machine for final shaping, potentially increasing efficiency.
4. Molding:
The core of the process is the molding stage. Here, the EPS takes its final shape.
Two main types of molding machines are used: vertical and horizontal.
Vertical Block Molding:
- The mold cavity is positioned vertically.
- Aged, pre-expanded beads (or pre-shaped beads if used) are typically fed from the top of the machine.
- The beads fall under gravity into the mold.
- Steam is introduced from the bottom, causing the beads to further expand and fuse together, filling the mold cavity.
- This method is more efficient for denser EPS blocks due to the weight of the beads aiding in packing the mold.
Horizontal Block Molding:
- The mold cavity is positioned horizontally.
- Pre-expanded beads are fed into one side of the closed mold.
- Steam is introduced, causing the beads to expand and fill the mold.
- A movable plate or ram compresses the beads to ensure proper density throughout the block.
- This method is better suited for lower-density EPS blocks as the packing relies on steam pressure and the compression mechanism.
5. Cooling:
- Once the molding cycle is complete, the newly formed EPS block is cooled with air or water. This solidifies the shape and prevents the EPS from deforming.
6. Cutting:
- The cooled EPS block is then cut into desired shapes and sizes using various methods:
- Hot wires: These electrically heated wires can precisely cut and shape the EPS due to their ability to melt the material on contact.
- Saws: Specialized saws can be used for thicker or straighter cuts.
- CNC machines: For complex shapes and high-volume production, Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines offer precise and automated cutting.
7. Finishing (Optional):
- Depending on the application, the EPS product might undergo additional finishing steps, such as:
- Coating: Applying a protective or decorative layer.
- Lamination: Bonding multiple EPS pieces together.
Following these steps, the EPS product is ready for use in various applications, from protective packaging and building insulation to craft supplies and sports equipment.
Vertical vs Horizontal Block Molding Machines in EPS Manufacturing
Both vertical and horizontal block molding machines are used in EPS manufacturing to create the final shaped blocks from pre-expanded beads. However, they differ in their design, operation, and suitability for different EPS applications:
EPS Vertical Molding Machine
-1.webp)
Design:
The mold cavity is positioned vertically.
The pre-expanded beads are typically fed from the top of the machine.
Operation:
The beads fall under gravity into the mold cavity.
Steam is introduced from the bottom, causing the beads to expand and fill the mold.
After the molding cycle, the bottom of the mold opens, and the finished EPS block is released downwards.
Suitability:
More efficient for denser EPS blocks due to the weight of the beads aiding in packing the mold cavity.
Offers greater molding pressure due to the vertical arrangement, allowing for denser products.
May be better suited for taller block shapes as the vertical orientation provides more molding space.
EPS Horizontal Molding Machine
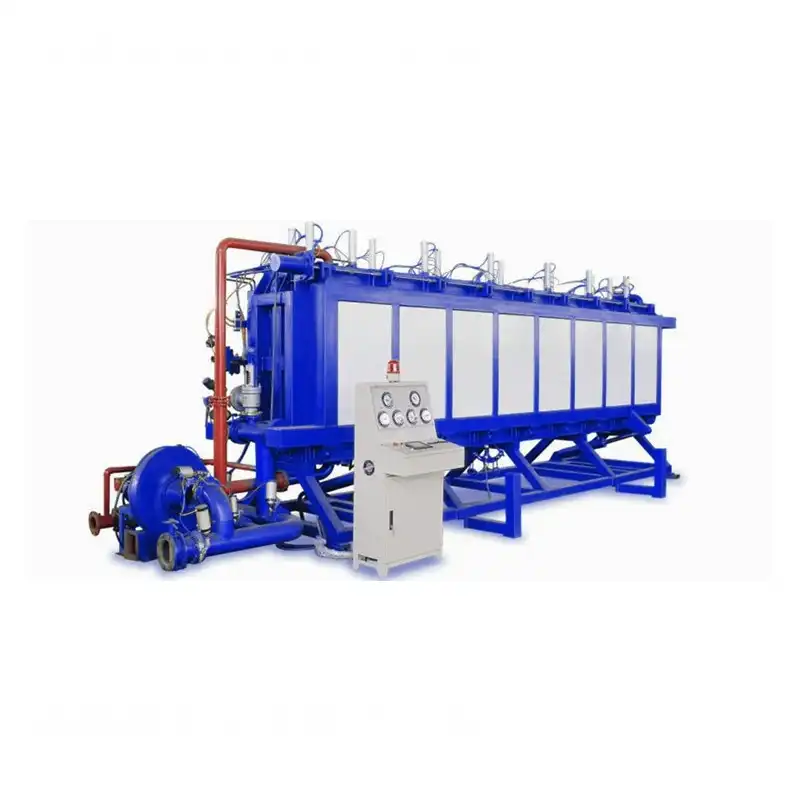

Design:
The mold cavity is positioned horizontally.
The pre-expanded beads are fed into one side of the closed mold.
Operation:
Steam is introduced, causing the beads to expand and fill the mold cavity.
A movable plate or ram compresses the beads to ensure proper density.
After the molding cycle, the mold opens horizontally, and the finished EPS block is removed.
Suitability:
More efficient for lower-density EPS blocks as the packing relies on steam pressure and the movable plate.
Offers good control over uniform density throughout the block due to the compression mechanism.
May be better suited for wider block shapes as the horizontal design allows for more mold width.
| Feature | Vertical Block Molding Machine | Horizontal Block Molding Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Mold Cavity Position | Vertical | Horizontal |
| Bead Feeding | From Top | From Side |
| Filling Mechanism | Gravity + Steam | Steam + Compression Plate |
| Suitability for Density | Denser EPS | Lower Density EPS |
| Molding Pressure | Higher | Controlled by Compression Plate |
| Block Shape Preference | Taller Blocks | Wider Blocks |
Choosing the Right EPS Molding Machine:
The choice between a vertical and horizontal block molding machine depends on the desired EPS product characteristics:
- Density: For denser blocks, a vertical machine is preferred.
- Shape: Taller blocks favor a vertical machine, while wider blocks may be better suited for horizontal molding.
- Production Speed: Both machines offer similar cycle times.
Ultimately, consulting with an EPS machinery manufacturer will help you determine the best machine for your specific production needs and product requirements.
FAQs about EPS Manufacturing
What is EPS and what are its benefits?
EPS stands for Expanded Polystyrene. It’s a lightweight, closed-cell plastic known for its:
- High insulation: Trapping air for excellent thermal insulation.
- Shock absorption: Protecting products from impact damage.
- Versatility: Moldable into various shapes and sizes.
- Cost-effectiveness: Affordable material with efficient production.
- Sustainability: 100% recyclable.
What is the raw material used in EPS manufacturing?
The EPS raw material is polystyrene beads, derived from petroleum and natural gas byproducts.
How does the EPS manufacturing process work?
The process involves several steps:
- Pre-expansion: Beads are steamed to expand and create air pockets.
- Molding: Pre-expanded beads are placed in a mold and steamed again to fuse and take the desired shape. (Vertical or horizontal machines may be used)
- Cooling: The molded EPS block is cooled to solidify its form.
- Cutting: The block is cut into desired shapes and sizes.
What are some common EPS products?
- Protective packaging materials (e.g., appliance boxes, food containers)
- Building insulation boards
- Helmets liners
- Surfboard blanks
- Craft and art supplies
Is EPS environmentally friendly?
EPS is 100% recyclable and contains no harmful CFCs or HCFCs. However, disposal practices are crucial for minimizing environmental impact.
