Polystyrene microspheres are tiny, spherical particles made from polystyrene, a common type of plastic. These minuscule beads, often invisible to the naked eye, possess unique properties that make them incredibly versatile across a wide range of scientific and industrial applications.
From their uniform size and shape to their high surface area and excellent optical properties, polystyrene microspheres exhibit a remarkable combination of characteristics that allow them to function as essential components in various fields, including biomedicine, diagnostics, materials science, and industrial processes.
What Are Polystyrene Microspheres
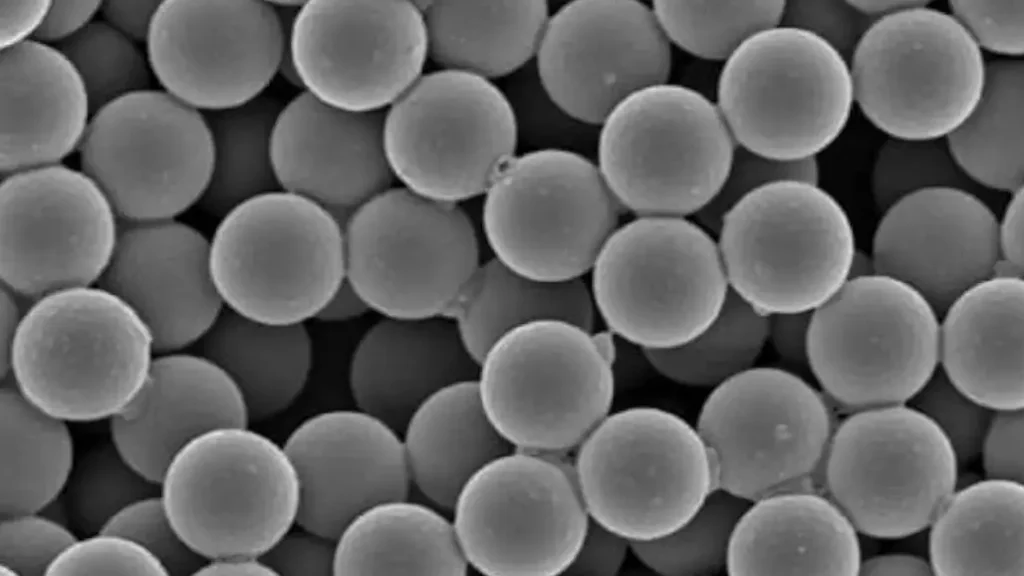
Polystyrene microspheres are tiny, spherical particles made of polystyrene, a common type of plastic. These microspheres are incredibly small, typically ranging from a few micrometers to several hundred micrometers in diameter.
Due to their uniform size and shape, high surface area, and chemical inertness, polystyrene microspheres possess a wide range of valuable properties. These characteristics make them highly versatile and useful in various scientific and industrial applications.
What Do Polystyrene Microspheres Do
Polystyrene microspheres find widespread use in various fields due to their unique properties. In research, they serve as calibration standards for microscopy and flow cytometry, ensuring accurate measurements and data analysis. Their uniform size and known refractive index make them ideal for calibrating the magnification and resolution of microscopes.
In medical diagnostics, these microspheres play a crucial role in various assays. They can be coated with specific antibodies or other molecules, enabling the detection and quantification of target substances in biological samples. For example, in lateral flow assays, such as pregnancy tests, colored polystyrene microspheres act as indicators, revealing the presence or absence of specific hormones.
Furthermore, polystyrene microspheres are utilized in industrial applications. They can be incorporated into paints and coatings to enhance their reflective properties, improving visibility and durability. In chromatography, they act as stationary phases, separating complex mixtures of molecules based on their size, charge, or other physical properties.
What Polymers Are Used in Microspheres
You’re absolutely right! Here are some of the common polymers used in the production of microspheres:
- Polystyrene (PS): This is one of the most widely used polymers for microspheres. It’s readily available, relatively inexpensive, and can be easily modified to achieve desired properties.
- Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) (PMMA): Known for its high optical clarity and good mechanical strength, PMMA microspheres are often used in applications requiring high refractive index or excellent resistance to abrasion.
- Polyethylene (PE): These microspheres are typically used in applications where low density and good chemical resistance are crucial.
- Polypropylene (PP): PP microspheres are known for their excellent resistance to heat and chemicals, making them suitable for demanding applications.
- Cellulose Acetate: This biocompatible polymer is often used in biomedical applications, such as drug delivery systems.
Other Polymers:
- Polylactic Acid (PLA)
- Polyglycolic Acid (PGA)
- Polycaprolactone (PCL)
These are just a few examples, and the choice of polymer depends heavily on the specific application and desired properties of the microspheres.
What is the Difference Between Microspheres and Nanoparticles
Microspheres and nanoparticles are both tiny particles with unique properties, but they differ significantly in size.
- Nanoparticles: These are extremely small particles, typically defined as having at least one dimension less than 100 nanometers (nm). This is incredibly small, as 1 nanometer is one-billionth of a meter. Due to their minuscule size, nanoparticles exhibit unique physical, chemical, and biological properties compared to their bulk counterparts.
- Microspheres: These particles are larger than nanoparticles, typically ranging from 1 micrometer (µm) to 1000 µm (1 millimeter) in diameter. While still small, they are significantly larger than nanoparticles.
| Feature | Microspheres | Nanoparticles |
|---|---|---|
| Size Range | 1 µm – 1000 µm | 1 nm – 100 nm |
| Relative Size | Larger | Smaller |
| Surface Area to Volume Ratio | High | Extremely High |
| Properties | Unique properties due to size, but less pronounced than nanoparticles | Exhibit unique quantum and surface effects |
| Applications | Chromatography, drug delivery, cosmetics | Drug delivery, electronics, catalysis, medicine |
Note: These are general definitions and the specific properties and applications of microspheres and nanoparticles can vary widely depending on their composition and specific characteristics.
Polystyrene Microspheres vs Expandable Polystyrene
Polystyrene Microspheres
- Size: Extremely small, typically from a few micrometers to several hundred micrometers in diameter.
- Form: Spherical particles.
- Properties:
- High surface area
- Uniform size and shape
- Chemical inertness
- Applications:
- Research (microscopy calibration, flow cytometry)
- Medical diagnostics (assays, lateral flow tests)
- Industrial applications (paints, coatings, chromatography)
Expandable Polystyrene (EPS)
- Form: Solid beads containing a blowing agent.
- Process: Beads are expanded under heat and pressure, forming a rigid foam.
- Properties:
- Lightweight
- Good insulation
- High impact resistance
- Applications:
- Packaging
- Insulation (building, packaging)
- Protective packaging
- Decorative items
Key Differences
- Size: Microspheres are significantly smaller than the individual cells within expanded polystyrene foam.
- Form: Microspheres are individual, discrete particles, while EPS is a cellular foam structure.
- Applications: Microspheres are primarily used in scientific and industrial applications, while EPS has broader applications in packaging and construction.
In essence:
- Polystyrene microspheres are tiny, individual particles with specialized uses.
- Expandable polystyrene is a lightweight foam material with excellent insulation and protective properties.
Conclusion
In conclusion, polystyrene microspheres are versatile materials with a wide range of applications across various industries. Their unique properties, such as uniform size, high surface area, and chemical inertness, make them valuable tools in research, medicine, and industrial processes. Understanding the fundamental principles of polystyrene microsphere production and their diverse functionalities provides valuable insights into their potential for future advancements.
Ready to explore the possibilities of EPS foam for your specific needs? EPSole is your trusted source for high-quality expanded polystyrene products. We offer a wide range of EPS foam solutions, from packaging materials to insulation and more. Contact us today to discuss your wholesale EPS foam requirements and discover how we can help you achieve your business goals.
