Expanded Polystyrene (EPS), also known as Styrofoam, is a ubiquitous material found in everything from protective packaging peanuts to building insulation boards. But how does this lightweight and versatile material come to life? The answer lies in the EPS pre-expansion process, a crucial first step that transforms tiny beads into the building blocks of countless EPS products.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the EPS pre-expansion process, exploring the science behind it, the different types of machinery involved, and the factors to consider when choosing the right equipment for your needs.
The Magic Behind EPS Pre-Expansion
Imagine tiny, dense beads – that’s the starting point for EPS. These beads contain a hidden secret – a blowing agent, usually pentane gas. The EPS pre-expansion process utilizes heat and pressure to activate this agent, causing it to expand and puff up the beads. This transformation dramatically increases the volume of the beads while reducing their density, making them perfect for molding into various EPS shapes.
EPS Pre-Expansion Process
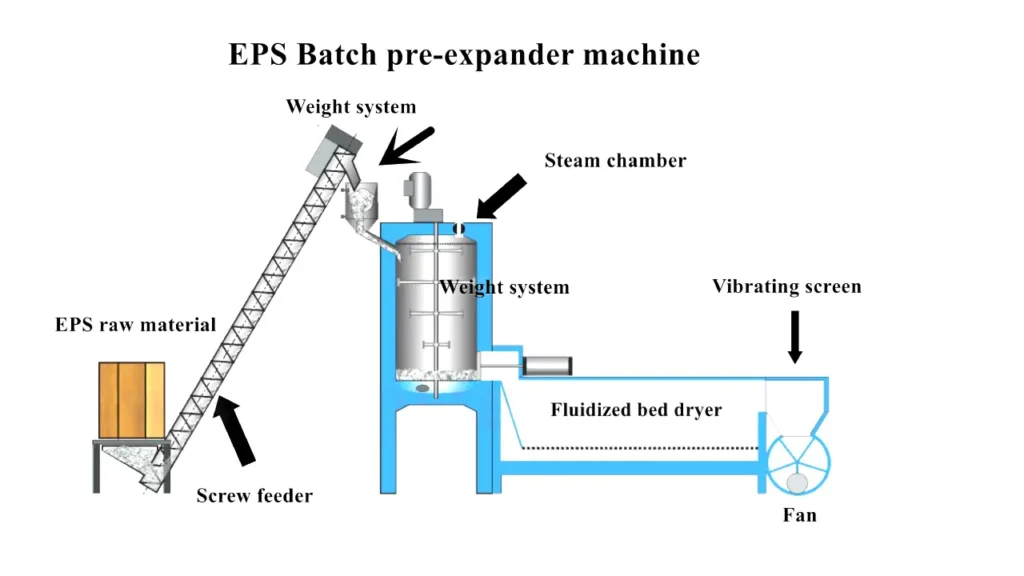
A Step-by-Step Journey Through the EPS Pre-Expansion Process
The EPS pre-expansion process transforms tiny, dense beads into the building blocks for various EPS products. Let’s embark on a step-by-step journey to understand this crucial stage:
Step 1: Bead Loading (Batch or Continuous)
- Batch Pre-Expanders: A pre-weighed batch of EPS beads is manually poured into the pressure vessel of the pre-expander.
- Continuous Pre-Expanders: A hopper and metering screw continuously feed a controlled amount of EPS beads into the pre-expander chamber.
Step 2: Pre-Steaming (Optional)
- This step, primarily used in batch pre-expansion, involves exposing the beads to low-pressure steam for a short duration.
- Its purpose is to remove any surface moisture present on the beads. This helps ensure uniform heating and prevents bead cracking during the main expansion process.
Step 3: Heating
- Steam or hot air is introduced into the pre-expander chamber.
- The temperature is precisely controlled to activate the blowing agent (pentane gas) within the EPS beads.
- Sensors within the chamber monitor the temperature continuously, and the control system adjusts the heating process accordingly.
Step 4: Pressurization
- Once the desired temperature is reached, the pressure inside the chamber is gradually increased.
- This serves two purposes:
- It further softens the polystyrene matrix of the beads, allowing for easier expansion.
- It helps to disperse the pentane gas more uniformly within the beads.
- Pressure gauges monitor the internal pressure to ensure it remains within the optimal range.
Step 5: Depressurization
- This is the critical moment where the magic happens.
- In a rapid and controlled process, the pressure inside the chamber is drastically reduced.
- This sudden drop in pressure triggers the pentane gas to expand rapidly.
- As the gas expands, it pushes against the softened polystyrene shell of the bead, causing it to inflate and increase in volume.
- The speed of depressurization plays a vital role. A rapid depressurization ensures efficient bead expansion and minimizes the risk of incomplete expansion or bead rupture.
Step 6: Cooling
- After depressurization, the pre-expanded beads are rapidly cooled down.
- This serves two purposes:
- It stabilizes the expanded structure of the beads and prevents further expansion.
- It prevents the beads from sticking together.
- Cooling is typically achieved using either air or water cooling systems. Air cooling is more common due to its simplicity and lower energy consumption.
Step 7: Discharge
- Batch Pre-Expanders: Once cooled, the pre-expanded beads are manually unloaded from the pressure vessel.
- Continuous Pre-Expanders: A pneumatic conveying system or screw conveyor automatically transfers the pre-expanded beads to a storage silo.
- The silo holds the pre-expanded beads until they are needed for the next stage – molding into various EPS products.
Additional Considerations:
- Residence Time: The amount of time the beads spend in the pre-expander at a specific temperature and pressure influences their final expansion ratio and density.
- Monitoring and Control: Modern pre-expanders have sophisticated control systems that monitor pressure, temperature, and other parameters to ensure consistent bead quality.
- Bead Aging (Optional): In some applications, the pre-expanded beads may undergo an aging process before molding. This allows for the remaining pentane gas to further diffuse and be replaced by air, improving the dimensional stability of the beads for molding.
By understanding these detailed steps, you gain valuable insight into the intricate process of EPS pre-expansion. This knowledge empowers you to appreciate the importance of choosing the right pre-expander with features that can deliver the specific bead characteristics required for your EPS production needs.
Choosing the Right EPS Pre-Expander Machine: Batch vs. Continuous
Now that you understand the science behind the EPS pre-expansion process, let’s explore the two main types of machines used to achieve this:
Batch EPS Pre-Expander Machine
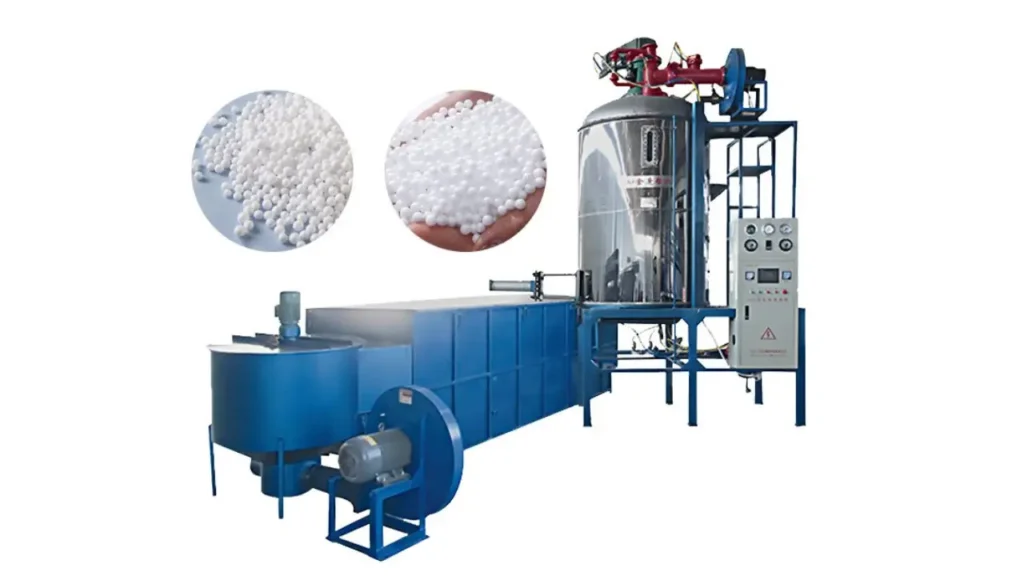

This is the most common type of pre-expander. It works by processing a fixed batch of EPS beads at a time. Here’s what a batch pre-expander typically offers:
- Lower Investment Cost: Batch pre-expanders are generally more affordable than continuous models.
- Simpler Operation: They tend to be easier to operate and require less maintenance.
- Higher Bead Size Consistency: Batch processing can produce pre-expanded beads with a more consistent size distribution.
However, there are also some limitations to consider:
- Lower Production Capacity: They are suitable for lower to medium production volumes.
- Higher Labor Costs: Batch processing requires manual loading and unloading, leading to increased labor needs.
- Lower Efficiency: The stop-and-start nature of batch processing can be less efficient than continuous operation.
Recommendation: EPS Batch Pre-Expander Machine by epsole
If you’re starting an EPS production line or have a moderate production volume, a batch pre-expander might be the ideal choice. Look for a reputable eps expander machine manufacturer like us that offers high-quality batch pre-expanders with features like:
- Automated Feeding Systems: These systems can eliminate the need for manual loading, improving efficiency.
- Precise Temperature and Pressure Control: Consistent control ensures uniform bead expansion and high-quality results.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Easy-to-use interfaces make operation and monitoring simple.
- Continuous EPS Pre-Expander Machine
For high-volume production lines, a continuous EPS pre-expander is the way to go. Here are some key benefits:
- High Production Capacity: They can continuously process large volumes of EPS beads, ideal for large-scale production.
- Reduced Labor Costs: Continuous operation minimizes manual intervention, leading to lower labor requirements.
- Improved Process Efficiency: The continuous flow ensures optimized bead processing and eliminates downtime between batches.
However, continuous pre-expanders also have some drawbacks:
More Complex Operation: Startup and shutdown procedures require more planning and may involve additional training for
Higher Investment Cost: They tend to be more expensive than batch models.
Larger Footprint: These machines require more space due to their continuous processing design.
EPS Continuous Pre-Expander Machine
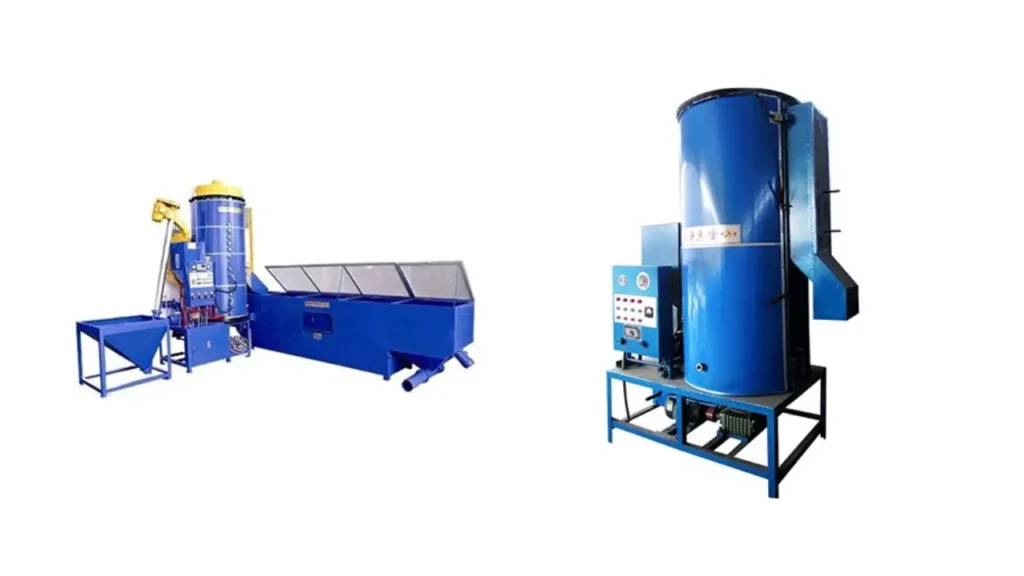

If you have a high-volume EPS production line and prioritize efficiency and output, a continuous pre-expander is a wise investment. Consider a company like [Manufacturer Name] known for their reliable and feature-rich continuous EPS pre-expanders. Look for features like:
- Multi-Stage Preheating: This allows for more precise control over bead heating and expansion.
- Efficient Cooling Systems: Effective cooling ensures stable pre-expanded beads and prevents overheating.
- Automated Discharge Systems: These systems automatically transfer pre-expanded beads to storage silos, minimizing manual handling.
- Advanced Control Systems: PLC-based control systems offer precise control, monitoring, and data logging capabilities for optimized operation.
Additional Considerations Beyond Machine
Choosing the right EPS pre-expander goes beyond just batch vs. continuous. Here are some additional factors to consider:
- Production Volume: Align your machine’s capacity with your anticipated production needs.
- Bead Size and Density Requirements: Different machines may be better suited for specific bead size and density requirements of your final EPS products.
- Budget: Consider the initial investment cost as well as ongoing maintenance expenses.
- Brand Reputation: Opt for a reputable manufacturer with a proven track record and reliable after-sales support.
Conclusion
The EPS pre-expansion process plays a vital role in transforming raw EPS beads into the versatile building blocks used in countless applications. Understanding the science behind this process and the different types of pre-expanders available empowers you to make informed decisions for your EPS production line.
Whether you require a cost-effective batch model for moderate production or a high-capacity continuous pre-expander for large-scale operations, there’s an ideal machine to meet your needs. By carefully considering your specific requirements and exploring options from reputable manufacturers like [Manufacturer Name], you can ensure a smooth and efficient EPS production process.
Contact US Today to consult our premium EPS expansion machine!
Ready to elevate your EPS production? Contact us today to discuss your EPS pre-expansion needs and explore our selection of high-quality batch and continuous EPS pre-expanders. Our team of experts is here to help you choose the perfect machine to optimize your production process and achieve your EPS production goals.



